| Oracle® Database Application Developer's Guide - Object-Relational Features 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10799-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database Application Developer's Guide - Object-Relational Features 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10799-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter explains the implementation and performance characteristics of the Oracle object-relational model. Use this information to map a logical data model into an Oracle physical implementation, and when developing applications that use object-oriented features. You should be familiar with the basic concepts behind Oracle objects before you read this chapter.
This chapter covers the following topics:
This section discusses general storage considerations for various object types.
You can store objects in columns of relational tables as column objects, or in object tables as row objects. Objects that have meaning outside of the relational database object in which they are contained, or objects that are shared among more than one relational database object, should be made referenceable as row objects. That is, such objects should be stored in an object table instead of in a column of a relational table.
For example, an object of object type customer has meaning outside of any particular purchase order, and should be referenceable; therefore, customer objects should be stored as row objects in an object table. An object of object type address, however, has little meaning outside of a particular purchase order and can be one attribute within a purchase order; therefore, address objects should be stored as column objects in columns of relational tables or object tables. So, address might be a column object in the customer row object.
The storage of a column object is the same as the storage of an equivalent set of scalar columns that collectively make up the object. The only difference is that there is the additional overhead of maintaining the atomic null values of the object and its embedded object attributes. These values are called null indicators because, for every column object, a null indicator specifies whether the column object is null and whether each of its embedded object attributes is null. However, null indicators do not specify whether the scalar attributes of a column object are null. Oracle uses a different method to determine whether scalar attributes are null.
Consider a table that holds the identification number, name, address, and phone numbers of people within an organization. You can create three different object types to hold the name, address, and phone number. First, to create the name_objtyp object type, enter the following SQL statement:
CREATE TYPE name_objtyp AS OBJECT ( first VARCHAR2(15), middle VARCHAR2(15), last VARCHAR2(15)); /
Next, to create the address_objtyp object type, enter the following SQL statement:
CREATE TYPE address_objtyp AS OBJECT ( street VARCHAR2(200), city VARCHAR2(200), state CHAR(2), zipcode VARCHAR2(20)); /
Finally, to create the phone_objtyp object type, enter the following SQL statement:
CREATE TYPE phone_objtyp AS OBJECT ( location VARCHAR2(15), num VARCHAR2(14)); /
Because each person may have more than one phone number, create a nested table type phone_ntabtyp based on the phone_objtyp object type:
CREATE TYPE phone_ntabtyp AS TABLE OF phone_objtyp; /
Once all of these object types are in place, you can create a table to hold the information about the people in the organization with the following SQL statement:
CREATE TABLE people_reltab ( id NUMBER(4) CONSTRAINT pk_people_reltab PRIMARY KEY, name_obj name_objtyp, address_obj address_objtyp, phones_ntab phone_ntabtyp) NESTED TABLE phones_ntab STORE AS phone_store_ntab;
Figure 8-1 Representation of the people_reltab Relational Table
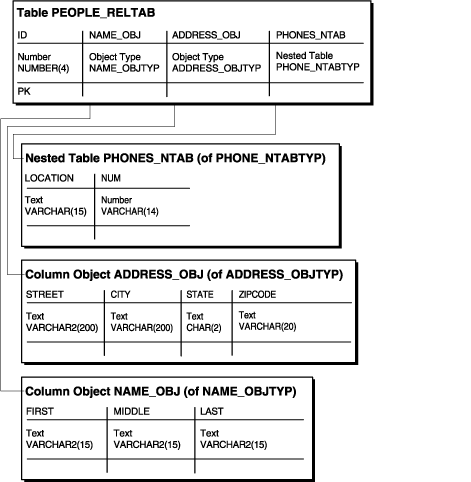
The people_reltab table has three column objects: name_obj, address_obj, and phones_ntab. The phones_ntab column object is also a nested table.
|
Note: Thepeople_reltab table and its columns and related types are used in examples throughout this chapter. |
The storage for each object stored in the people_reltab table is the same as that of the attributes of the object. For example, the storage required for a name_obj object is the same as the storage for the first, middle, and last attributes combined, except for the null indicator overhead.
If the COMPATIBLE parameter is set to 8.1.0 or higher, the null indicators for an object and its embedded object attributes occupy one bit each. Thus, an object with n embedded object attributes (including objects at all levels of nesting) has a storage overhead of CEIL(n/8) bytes. In the people_reltab table, for example, the overhead of the null information for each row is one byte because it translates to CEIL(3/8) or CEIL(.37), which rounds up to one byte. In this case, there are three objects in each row: name_obj, address_obj, and phones_ntab.
If, however, the COMPATIBLE parameter is set to a value lower than 8.1.0, such as 8.0.0, the storage is determined by the following calculation:
CEIL(n/8) + 6
Here, n is the total number of all attributes (scalar and object) within the object. Therefore, in the people_reltab table, for example, the overhead of the null information for each row is seven bytes because it translates to the following calculation:
CEIL(4/8) + 6 = 7
CEIL(4/8) is CEIL(.5), which rounds up to one byte. In this case, there are three objects in each row and one scalar.
Therefore, the storage overhead and performance of manipulating a column object is similar to that of the equivalent set of scalar columns. The storage for collection attributes are described in the "Viewing Object Data in Relational Form with Unnesting Queries" section.
Row objects are stored in object tables. An object table is a special kind of table that holds objects and provides a relational view of the attributes of those objects. An object table is logically and physically similar to a relational table whose column types correspond to the top level attributes of the object type stored in the object table. The key difference is that an object table can optionally contain an additional object identifier (OID) column and index.
By default, every row object in an object table has an associated logical object identifier (OID) that uniquely identifies it in an object table. Oracle assigns each row object a unique system-generated OID, 16 bytes in length that is automatically indexed for efficient OID-based lookups. The OID column is the equivalent of having an extra 16-byte primary key column. In a distributed and replicated environment, the system-generated unique identifier lets Oracle identify objects unambiguously.
Oracle provides no documentation of or access to the internal structure of object identifiers. This structure can change at any time. The OID column of an object table is a hidden column. Once it is set up, you can ignore it and focus instead on fetching and navigating objects through object references.
An OID allows the corresponding row object to be referred to from other objects or from relational tables. A built-in datatype called a REF represents such references. A REF encapsulates a reference to a row object of a specified object type.
REFs use object identifiers (OIDs) to point to objects. You can use either system-generated OIDs or primary-key based OIDs. The differences between these types of OIDs are outlined in "Row Object Storage in Object Tables". If you use system-generated OIDs for an object table, Oracle maintains an index on the column that stores these OIDs. The index requires storage space, and each row object has a system-generated OID, which requires an extra 16 bytes of storage for each row.
If a primary key column is available, you can avoid the storage and performance overhead of maintaining the 16-byte OID column and its index. Instead of using the system-generated OIDs, you can use a CREATE TABLE statement to specify that the system use the primary key column(s) as the OIDs of the objects in the table. Therefore, you can use existing columns as the OIDs of the objects or use application generated OIDs that are smaller than the 16-byte globally unique OIDs generated by Oracle.
You can avoid these added storage requirements by using the primary key for the object identifiers, instead of system-generated OIDs. You can enforce referential integrity on columns that store references to these row objects in a way similar to foreign keys in relational tables.
Primary-key based identifiers also make it faster and easier to load data into an object table. By contrast, system-generated object identifiers need to be remapped using some user-specified keys, especially when references to them are also stored.
However, if each primary key value requires more than 16 bytes of storage and you have a large number of REFs, using the primary key might require more space than system-generated OIDs because each REF is the size of the primary key. In addition, each primary-key based OID is locally (but not necessarily globally) unique. If you require a globally unique identifier, you must ensure that the primary key is globally unique or use system-generated OIDs.
You can compare objects by invoking the map or order methods defined on the object type. A map method converts objects into scalar values while preserving the ordering of the objects. Mapping objects into scalar values, if it can be done, is preferred because it allows the system to efficiently order objects once they are mapped.
The way objects are mapped has significant performance implications when sorting is required on the objects for ORDER BY or GROUP BY processing because an object may need to be compared to other objects many times, and it is much more efficient if the objects can be mapped to scalar values first. If the comparison semantics are extremely complex, or if the objects cannot be mapped into scalar values for comparison, you can define an order method that, given two objects, returns the ordering determined by the object implementor. Order methods are not as efficient as map methods, so performance may suffer if you use order methods. In any one object type, you can implement either map or order methods, but not both.
Once again, consider an object type address consisting of four character attributes: street, city, state, and zipcode. Here, the most efficient comparison method is a map method because each object can be converted easily into scalar values. For example, you might define a map method that orders all of the objects by state.
On the other hand, suppose you want to compare binary objects, such as images. In this case, the comparison semantics may be too complex to use a map method; if so, you can use an order method to perform comparisons. For example, you could create an order method that compares images according to brightness or the number of pixels in each image.
If an object type does not have either a map or order method, only equality comparisons are allowed on objects of that type. In this case, Oracle performs the comparison by doing a field-by-field comparison of the corresponding object attributes, in the order they are defined. If the comparison fails at any point, a FALSE value is returned. If the comparison matches at every point, a TRUE value is returned. However, if an object has a collection of LOB attributes, then Oracle does not compare the object on a field-by-field basis. Such objects must have a map or order method to perform comparisons.
This section discusses considerations when working with REFs.
A REF contains the following three logical components:
OID of the object referenced. A system-generated OID is 16 bytes long. The size of a primary-key based OID depends on the size of the primary key column(s).
OID of the table or view containing the object referenced, which is 16 bytes long.
Rowid hint, which is 10 bytes long.
Referential integrity constraints on REF columns ensure that there is a row object for the REF. Referential integrity constraints on REFs create the same relationship as specifying a primary key/foreign key relationship on relational data. In general, you should use referential integrity constraints wherever possible because they are the only way to ensure that the row object for the REF exists. However, you cannot specify referential integrity constraints on REFs that are in nested tables.
A scoped REF is constrained to contain only references to a specified object table. You can specify a scoped REF when you declare a column type, collection element, or object type attribute to be a REF.
In general, you should use scoped REFs instead of unscoped REFs because scoped REFs are stored more efficiently. Whereas an unscoped REF takes at least 36 bytes to store (more if it uses rowids), a scoped REF is stored as just the OID of its target object and can take less than 16 bytes, depending on whether the referenced OID is system-generated or primary-key based. A system-generated OID requires 16 bytes; a PK-based OID requires enough space to store the primary key value, which may be less than 16 bytes. However, a REF to a PK-based OID, which must be dynamically constructed on being selected, may take more space in memory than a REF to a system-generated OID.
Besides requiring less storage space, scoped REFs often enable the optimizer to optimize queries that dereference a scoped REF into more efficient joins. This optimization is not possible for unscoped REFs because the optimizer cannot determine the containing table(s) for unscoped REFs at query-optimization time.
Unlike referential integrity constraints, scoped REFs do not ensure that the referenced row object exists; they only ensure that the referenced object table exists. Therefore, if you specify a scoped REF to a row object and then delete the row object, the scoped REF becomes a dangling REF because the referenced object no longer exists.
|
Note: Referential integrity constraints are scoped implicitly. |
Unscoped REFs are useful if the application design requires that the objects referenced be scattered in multiple tables. Because rowid hints are ignored for scoped REFs, you should use unscoped REFs if the performance gain of the rowid hint, as explained in the "Speeding up Object Access Using the WITH ROWID Option", outweighs the benefits of the storage saving and query optimization of using scoped REFs.
You can build indexes on scoped REF columns using the CREATE INDEX command. Then, you can use the index to efficiently evaluate queries that dereference the scoped REFs. Such queries are turned into joins implicitly. For certain types of queries, Oracle can use an index on the scoped REF column to evaluate the join efficiently.
For example, suppose the object type address_objtyp is used to create an object table named address_objtab:
CREATE TABLE address_objtab OF address_objtyp ;
Then, a people_reltab2 table can be created that has the same definition as the people_reltab table discussed in "Column Object Storage", except that a REF is used for the address:
CREATE TABLE people_reltab2 ( id NUMBER(4) CONSTRAINT pk_people_reltab2 PRIMARY KEY, name_obj name_objtyp, address_ref REF address_objtyp SCOPE IS address_objtab, phones_ntab phone_ntabtyp) NESTED TABLE phones_ntab STORE AS phone_store_ntab2 ;
Now, an index can be created on the address_ref column:
CREATE INDEX address_ref_idx ON people_reltab2 (address_ref) ;
The following query dereferences the address_ref:
SELECT id FROM people_reltab2 p WHERE p.address_ref.state = 'CA' ;
When this query is executed, the address_ref_idx index is used to efficiently evaluate it. Here, address_ref is a scoped REF column that stores references to addresses stored in the address_objtab object table. Oracle implicitly transforms the preceding query into a query with a join:
SELECT p.id FROM people_reltab2 p, address_objtab a WHERE p.address_ref = ref(a) AND a.state = 'CA' ;
The Oracle query optimizer might create a plan to perform a nested-loops join with address_objtab as the outer table and look up matching addresses using the index on the address_ref scoped REF column.
If the WITH ROWID option is specified for a REF column, Oracle maintains the rowid of the object referenced in the REF. Then, Oracle can find the object referenced directly using the rowid contained in the REF, without the need to fetch the rowid from the OID index. Therefore, you use the WITH ROWID option to specify a rowid hint. Maintaining the rowid requires more storage space because the rowid adds 10 bytes to the storage requirements of the REF.
Bypassing the OID index search improves the performance of REF traversal (navigational access) in applications. The actual performance gain may vary from application to application depending on the following factors:
How large the OID indexes are.
Whether the OID indexes are cached in the buffer cache.
How many REF traversals an application does.
The WITH ROWID option is only a hint because, when you use this option, Oracle checks the OID of the row object with the OID in the REF. If the two OIDs do not match, Oracle uses the OID index instead. The rowid hint is not supported for scoped REFs, for REFs with referential integrity constraints, or for primary key-based REFs.
This section discusses considerations when working with collections.
An unnesting query on a collection allows the data to be viewed in a flat (relational) form. You can execute unnesting queries on single-level and multilevel collections of either nested tables or varrays. This section contains examples of unnesting queries.
Nested tables can be unnested for queries using the TABLE syntax, as in the following example:
SELECT p.name_obj, n.num FROM people_reltab p, TABLE(p.phones_ntab) n ;
Here, phones_ntab specifies the attributes of the phones_ntab nested table. To retrieve even parent rows that have no child rows (no phone numbers, in this case), use the outer join syntax, with the +. For example:
SELECT p.name_obj, n.num FROM people_reltab p, TABLE(p.phones_ntab) (+) n ;
If the SELECT list of a query does not refer to any columns from the parent table other than the nested table column, the query is optimized to execute only against the nested table's storage table.
The unnesting query syntax is the same for varrays as for nested tables. For instance, suppose the phones_ntab nested table is instead a varray named phones_var. The following example shows how to use the TABLE syntax to query the varray:
SELECT p.name_obj, v.num FROM people_reltab p, TABLE(p.phones_var) v ;
You can create procedures and functions that you can then execute to perform unnesting queries. For example, you can create a function called home_phones() that returns only the phone numbers where location is home. To create the home_phones() function, you enter code like the following:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION home_phones(allphones IN phone_ntabtyp)
RETURN phone_ntabtyp IS
homephones phone_ntabtyp := phone_ntabtyp();
indx1 number;
indx2 number := 0;
BEGIN
FOR indx1 IN 1..allphones.count LOOP
IF
allphones(indx1).location = 'home'
THEN
homephones.extend; -- extend the local collection
indx2 := indx2 + 1;
homephones(indx2) := allphones(indx1);
END IF;
END LOOP;
RETURN homephones;
END;
/
Now, to query for a list of people and their home phone numbers, enter the following:
SELECT p.name_obj, n.num
FROM people_reltab p, TABLE(
CAST(home_phones(p.phones_ntab) AS phone_ntabtyp)) n ;
To query for a list of people and their home phone numbers, including those people who do not have a home phone number listed, enter the following:
SELECT p.name_obj, n.num
FROM people_reltab p,
TABLE(home_phones(p.phones_ntab) AS phone_ntabtyp)(+) n ;
The size of a stored varray depends only on the current count of the number of elements in the varray and not on the maximum number of elements that it can hold. Because the storage of varrays incurs some overhead, such as null information, the size of the varray stored may be slightly greater than the size of the elements multiplied by the count.
Varrays are stored in columns either as raw values or LOBs. Oracle decides how to store the varray when the varray is defined, based on the maximum possible size of the varray computed using the LIMIT of the declared varray. If the size exceeds approximately 4000 bytes, then the varray is stored in LOBs. Otherwise, the varray is stored in the column itself as a raw value. In addition, Oracle supports inline LOBs which means that elements that fit in the first 4000 bytes of a large varray, with some bytes reserved for the LOB locator, are stored in the column of the row.
When changing the size of a VARRAY type, a new type version is generated for the dependent types. It is important to be aware of this when a VARRAY column is not explicitly stored as a LOB and its maximum size is originally smaller than 4000 bytes. If the size is larger than or equal to 4000 bytes after the increase, the VARRAY column has to be stored as a LOB. This requires an extra operation to upgrade the metadata of the VARRAY column in order to set up the necessary LOB metadata information including the LOB segment and LOB index.
The CASCADE option in the ALTER TYPE statement propagates the VARRAY size change to its dependent types and tables. A new version is generated for each valid dependent type and dependent tables metadata are updated accordingly based on the different case scenarios described previously. If the VARRAY column is in a cluster table, an ALTER TYPE statement with the CASCADE option fails because a cluster table does not support a LOB.
The CASCADE option in the ALTER TYPE statement also provides the [NOT] INCLUDING TABLE DATA option. The NOT INCLUDING TABLE DATA option only updates the metadata of the table, but does not convert the data image. In order to convert the VARRAY image to the latest version format, you can either specify INCLUDING TABLE DATA explicitly in ALTER TYPE CASCADE statement or issue ALTER TABLE UPGRADE statement.
If the entire collection is manipulated as a single unit in the application, varrays perform much better than nested tables. The varray is stored packed and requires no joins to retrieve the data, unlike nested tables.
The unnesting syntax can be used to access varray columns similar to the way it is used to access nested tables.
Piece-wise updates of a varray value are not supported. Thus, when a varray is updated, the entire old collection is replaced by the new collection.
The following sections contain design considerations for using nested tables.
Oracle stores the rows of a nested table in a separate storage table. A system generated NESTED_TABLE_ID, which is 16 bytes in length, correlates the parent row with the rows in its corresponding storage table.
Figure 8-2 shows how the storage table works. The storage table contains each value for each nested table in a nested table column. Each value occupies one row in the storage table. The storage table uses the NESTED_TABLE_ID to track the nested table for each value. So, in Figure 8-2, all of the values that belong to nested table A are identified, all of the values that belong to nested table B are identified, and so on.
If a nested table has a primary key, you can organize the nested table as an index-organized table (IOT). If the NESTED_TABLE_ID column is a prefix of the primary key for a given parent row, Oracle physically clusters its child rows together. So, when a parent row is accessed, all its child rows can be efficiently retrieved. When only parent rows are accessed, efficiency is maintained because the child rows are not inter-mixed with the parent rows.
Figure 8-3 shows how the storage table works when the nested table is in an IOT. The storage table groups by NESTED_TABLE_ID the values for each nested table in a nested table column. In Figure 8-3, for each nested table in the NT_DATA column of the parent table, the data is grouped in the storage table: all of the values in nested table A are grouped together, all of the values in nested table B are grouped together, and so on.
In addition, the COMPRESS clause enables prefix compression on the IOT rows. It factors out the key of the parent in every child row. That is, the parent key is not repeated in every child row, thus providing significant storage savings.
In other words, if you specify nested table compression using the COMPRESS clause, the amount of space required for the storage table is reduced because the NESTED_TABLE_ID is not repeated for each value in a group. Instead, the NESTED_TABLE_ID is stored only once for each group, as illustrated in Figure 8-4.
Figure 8-4 Nested Table in IOT Storage with Compression
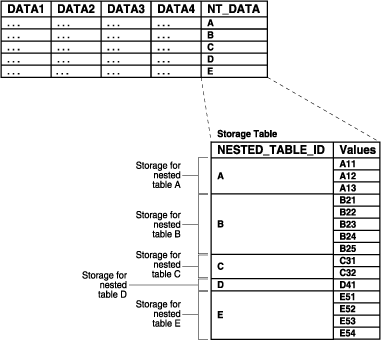
In general, Oracle recommends that nested tables be stored in an IOT with the NESTED_TABLE_ID column as a prefix of the primary key. Further, prefix compression should be enabled on the IOT. However, if you usually do not retrieve the nested table as a unit and you do not want to cluster the child rows, do not store the nested table in an IOT and do not specify compression.
For nested tables stored in heap tables (as opposed to IOTs), you should create an index on the NESTED_TABLE_ID column of the storage table. The index on the corresponding ID column of the parent table is created by Oracle automatically when the table is created. Creating an index on the NESTED_TABLE_ID column enables Oracle to access the child rows of the nested table more efficiently, because Oracle must perform a join between the parent table and the nested table using the NESTED_TABLE_ID column.
For large child sets, the parent row and a locator to the child set can be returned so that the child rows can be accessed on demand; the child sets also can be filtered. Using nested table locators enables you to avoid unnecessarily transporting child rows for every parent.
You can perform either one of the following actions to access the child rows using the nested table locator:
Call the OCI collection functions. This action occurs implicitly when you access the elements of the collection in the client-side code, such as OCIColl* functions. The entire collection is retrieved implicitly on the first access.
|
See Also: Oracle Call Interface Programmer's Guide for more information about OCI collection functions. |
Use SQL to retrieve the rows corresponding to the nested table.
In a multilevel collection, you can use a locator with a specified collection at any level of nesting. Following are described two ways in which to specify that a collection is to be retrieved as a locator.
When the collection type is being used as a column type and the NESTED TABLE storage clause is used, you can use the RETURN AS LOCATOR clause to specify that a particular collection is to be retrieved as a locator.
For instance, suppose that inner_table is a collection type consisting of three levels of nested tables. In the following example, the RETURN AS LOCATOR clause specifies that the third level of nested tables is always to be retrieved as a locator.
CREATE TYPE inner_table AS TABLE OF NUMBER;/
CREATE TYPE middle_table AS TABLE OF inner_table;/
CREATE TYPE outer_table AS TABLE OF middle_table;/
CREATE TABLE tab1 (
col1 NUMBER,
col2 outer_table)
NESTED TABLE col2 STORE AS col2_ntab
(NESTED TABLE COLUMN_VALUE STORE AS cval1_ntab
(NESTED TABLE COLUMN_VALUE STORE AS cval2_ntab RETURN AS LOCATOR) );
A query can retrieve a collection as a locator by means of the hint NESTED_TABLE_GET_REFS. Here is an example of retrieving the column col2 from the table tab1 as a locator:
SELECT /*+ NESTED_TABLE_GET_REFS +*/ col2 FROM tab1 WHERE col1 = 2;
Unlike with the RETURN AS LOCATOR clause, however, you cannot specify a particular inner collection to return as a locator when using the hint.
Set membership queries are useful when you want to search for a specific item in a nested table. For example, the following query tests the membership in a child-set; specifically, whether the location home is in the nested table phones_ntab, which is in the parent table people_reltab:
SELECT * FROM people_reltab p WHERE 'home' IN (SELECT location FROM TABLE(p.phones_ntab)) ;
Oracle can execute a query that tests the membership in a child-set more efficiently by transforming it internally into a semijoin. However, this optimization only happens if the ALWAYS_SEMI_JOIN initialization parameter is set. If you want to perform semijoins, the valid values for this parameter are MERGE and HASH; these parameter values indicate which join method to use.
|
Note: In the preceding example,home and location are child set elements. If the child set elements are object types, they must have a map or order method to perform a set membership query. |
Chapter 2 describes how to nest collection types to create a true multilevel collection, such as a nested table of nested tables, a nested table of varrays, a varray of nested tables, a varray of nested tables, or a varray or nested table of an object type that has an attribute of a collection type.
You can also nest collections indirectly using REFs. For example, you can create a nested table of an object type that has an attribute that references an object that has a nested table or varray attribute. If you do not actually need to access all elements of a multilevel collection, then nesting a collection with REFs may provide better performance because only the REFs need to be loaded, not the elements themselves.
True multilevel collections (specifically multilevel nested tables) perform better for queries that access individual elements of the collection. Using nested table locators can improve the performance of programmatic access if you do not need to access all elements.
For an example of a collection that uses REFs to nest another collection, suppose you want to create a new object type called person_objtyp using the object types described in "Column Object Storage", which are name_objtyp, address_objtyp, and phone_ntabtyp. Remember that the phone_ntabtyp object type is a nested table because each person may have more than one phone number.
To create the person_objtyp object type, issue the following SQL statement:
CREATE TYPE person_objtyp AS OBJECT ( id NUMBER(4), name_obj name_objtyp, address_obj address_objtyp, phones_ntab phone_ntabtyp);
To create an object table called people_objtab of person_objtyp object type, issue the following SQL statement:
CREATE TABLE people_objtab OF person_objtyp (id PRIMARY KEY) NESTED TABLE phones_ntab STORE AS phones_store_ntab ;
The people_objtab table has the same attributes as the people_reltab table discussed in "Column Object Storage". The difference is that the people_objtab is an object table with row objects, while the people_reltab table is a relational table with three column objects.
Figure 8-5 Object-Relational Representation of the people_objtab Object Table
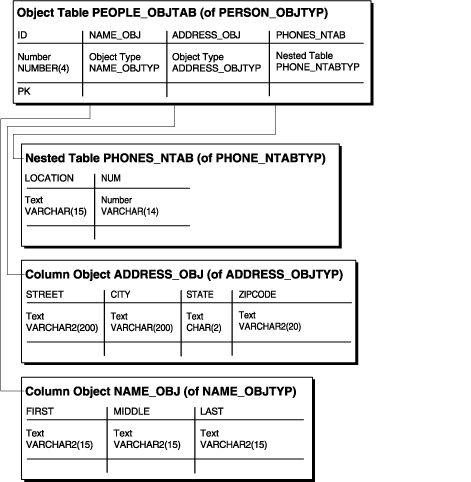
Now you can reference the row objects in the people_objtab object table from other tables. For example, suppose you want to create a projects_objtab table that contains:
A project identification number for each project.
The title of each project.
The project lead for each project.
A description of each project.
Nested table collection of the team of people assigned to each project.
You can use REFs to the people_objtab for the project leads, and you can use a nested table collection of REFs for the team. To begin, create a nested table object type called personref_ntabtyp based on the person_objtyp object type:
CREATE TYPE personref_ntabtyp AS TABLE OF REF person_objtyp; /
Now you are ready to create the object table projects_objtab. First, create the object type projects_objtyp by issuing the following SQL statement:
CREATE TYPE projects_objtyp AS OBJECT ( id NUMBER(4), title VARCHAR2(15), projlead_ref REF person_objtyp, description CLOB, team_ntab personref_ntabtyp); /
Next, create the object table projects_objtab based on the projects_objtyp:
CREATE TABLE projects_objtab OF projects_objtyp (id PRIMARY KEY) NESTED TABLE team_ntab STORE AS team_store_ntab ;
Figure 8-6 Object-Relational Representation of the projects_objtab Object Table
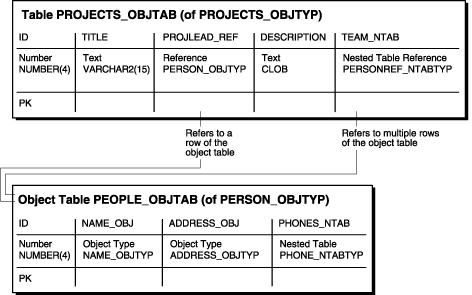
Once the people_objtab object table and the projects_objtab object table are in place, you indirectly have a nested collection. That is, the projects_objtab table contains a nested table collection of REFs that point to the people in the people_objtab table, and the people in the people_objtab table have a nested table collection of phone numbers.
You can insert values into the people_objtab table in the following way:
INSERT INTO people_objtab VALUES (
0001,
name_objtyp('JOHN', 'JACOB', 'SCHMIDT'),
address_objtyp('1252 Maple Road', 'Fairfax', 'VA', '22033'),
phone_ntabtyp(
phone_objtyp('home', '650.339.9922'),
phone_objtyp('work', '510.563.8792'))) ;
INSERT INTO people_objtab VALUES (
0002,
name_objtyp('MARY', 'ELLEN', 'MILLER'),
address_objtyp('33 Spruce Street', 'McKees Rocks', 'PA', '15136'),
phone_ntabtyp(
phone_objtyp('home', '415.642.6722'),
phone_objtyp('work', '650.891.7766'))) ;
INSERT INTO people_objtab VALUES (
0003,
name_objtyp('SARAH', 'MARIE', 'SINGER'),
address_objtyp('525 Pine Avenue', 'San Mateo', 'CA', '94403'),
phone_ntabtyp(
phone_objtyp('home', '510.804.4378'),
phone_objtyp('work', '650.345.9232'),
phone_objtyp('cell', '650.854.9233'))) ;
Then, you can insert into the projects_objtab relational table by selecting from the people_objtab object table using a REF operator, as in the following examples:
INSERT INTO projects_objtab VALUES (
1101,
'Demo Product',
(SELECT REF(p) FROM people_objtab p WHERE id = 0001),
'Demo the product, show all the great features.',
personref_ntabtyp(
(SELECT REF(p) FROM people_objtab p WHERE id = 0001),
(SELECT REF(p) FROM people_objtab p WHERE id = 0002),
(SELECT REF(p) FROM people_objtab p WHERE id = 0003))) ;
INSERT INTO projects_objtab VALUES (
1102,
'Create PRODDB',
(SELECT REF(p) FROM people_objtab p WHERE id = 0002),
'Create a database of our products.',
personref_ntabtyp(
(SELECT REF(p) FROM people_objtab p WHERE id = 0002),
(SELECT REF(p) FROM people_objtab p WHERE id = 0003))) ;
|
Note: This example uses nested tables to storeREFs, but you also can store REFs in varrays. That is, you can have a varray of REFs. |
This section discusses considerations when working with methods.
Method functions can be implemented in any of the languages supported by Oracle, such as PL/SQL, Java, or C. Consider the following factors when you choose the language for a particular application:
Ease of use
SQL calls
Speed of execution
Same/different address space
In general, if the application performs intense computations, C is preferable, but if the application performs a relatively large number of database calls, PL/SQL or Java is preferable.
A method implemented in C executes in a separate process from the server using external procedures. In contrast, a method implemented in Java or PL/SQL executes in the same process as the server.
The example described in this section involves an object type whose methods are implemented in different languages. In the example, the object type ImageType has an ID attribute, which is a NUMBER that uniquely identifies it, and an IMG attribute, which is a BLOB that stores the raw image. The object type ImageType has the following methods:
The method get_name fetches the name of the image by looking it up in the database. This method is implemented in PL/SQL.
The method rotate rotates the image. This method is implemented in C.
The method clear returns a new image of the specified color. This method is implemented in Java.
For implementing a method in C, a LIBRARY object must be defined to point to the library that contains the external C routines. For implementing a method implemented in Java, this example assumes that the Java class with the method has been compiled and uploaded into Oracle.
Here is the object type specification and its methods:
CREATE LIBRARY myCfuncs TRUSTED AS STATIC
/
CREATE TYPE ImageType AS OBJECT (
id NUMBER,
img BLOB,
MEMBER FUNCTION get_name return VARCHAR2,
MEMBER FUNCTION rotate return BLOB,
STATIC FUNCTION clear(color NUMBER) return BLOB);/
CREATE TYPE BODY ImageType AS
MEMBER FUNCTION get_name RETURN VARCHAR2
IS
imgname VARCHAR2(100);
sqlstmt VARCHAR2(200);
BEGIN
sqlstmt := 'SELECT name INTO imgname FROM imgtab WHERE imgid = id';
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE sqlstmt;
RETURN imgname;
END;
MEMBER FUNCTION rotate RETURN BLOB
AS LANGUAGE C
NAME "Crotate"
LIBRARY myCfuncs;
STATIC FUNCTION clear(color NUMBER) RETURN BLOB
AS LANGUAGE JAVA
NAME 'myJavaClass.clear(oracle.sql.NUMBER) return oracle.sql.BLOB';
END;
/
|
Restriction: Type methods can be mapped only to static Java methods. |
|
See Also:
|
Static methods differ from member methods in that the SELF value is not passed in as the first parameter. Methods in which the value of SELF is not relevant should be implemented as static methods. Static methods can be used for user-defined constructors.
The following example is a constructor-like method that constructs an instance of the type based on the explicit input parameters and inserts the instance into the specified table:
CREATE TYPE atype AS OBJECT(
a1 NUMBER,
STATIC PROCEDURE newa (
p1 NUMBER,
tabname VARCHAR2,
schname VARCHAR2));
/
CREATE TYPE BODY atype AS
STATIC PROCEDURE newa (p1 NUMBER, tabname VARCHAR2, schname VARCHAR2)
IS
sqlstmt VARCHAR2(100);
BEGIN
sqlstmt := 'INSERT INTO '||schname||'.'||tabname|| ' VALUES (atype(:1))';
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE sqlstmt USING p1;
END;
END;
/
CREATE TABLE atab OF atype;
BEGIN
atype.newa(1, 'atab', 'OBJTEST1');
END;
/
In member procedures, if SELF is not declared, its parameter mode defaults to IN OUT. However, the default behavior does not include the NOCOPY compiler hint.
Because the value of the IN OUT actual parameter is copied into the corresponding formal parameter, the copying slows down execution when the parameters hold large data structures such as instances of large object types.
For performance reasons, you may want to include SELF IN OUT NOCOPY when passing a large object type as a parameter. For example:
MEMBER PROCEDURE my_proc (SELF IN OUT NOCOPY my_LOB)
|
See Also:
|
A function-based index is an index based on the return values of an expression or function. The function may be a method function of an object type.
A function-based index built on a method function precomputes the return value of the function for each object instance in the column or table being indexed and stores those values in the index. There they can be referenced without having to evaluate the function again.
Function-based indexes are useful for improving the performance of queries that have a function in the WHERE clause. For example, the following code contains a query of an object table emps:
CREATE TYPE emp_t AS OBJECT( name VARCHAR2(36), salary NUMBER, MEMBER FUNCTION bonus RETURN NUMBER DETERMINISTIC); / CREATE TYPE BODY emp_t IS MEMBER FUNCTION bonus RETURN NUMBER DETERMINISTIC IS BEGIN RETURN self.salary * .1; END; END; / CREATE TABLE emps OF emp_t ; SELECT e.name FROM emps e WHERE e.bonus() > 2000;
To evaluate this query, Oracle must evaluate bonus() for each row object in the table. If there is a function-based index on the return values of bonus(), then this work has already been done, and Oracle can simply look up the results in the index. This enables Oracle to return a result from the query more quickly.
Return values of a function can be usefully indexed only if those values are constant, that is, only if the function always returns the same value for each object instance. For this reason, to use a user-written function in a function-based index, the function must have been declared with the DETERMINISTIC keyword, as in the preceding example. This keyword promises that the function always returns the same value for each object instance's set of input argument values.
The following example creates a function-based index on the method bonus() in the table emps:
CREATE INDEX emps_bonus_idx ON emps x (x.bonus()) ;
|
See Also: Oracle Database Concepts and Oracle Database SQL Reference for detailed information about function-based indexes |
To create generic object types that can be used in any schema, you must define the type to use invoker rights, through the AUTHID CURRENT_USER option of CREATE OR REPLACE TYPE. In general, use invoker rights when both of the following conditions are true:
There are type methods that access and manipulate data.
Users who did not define these type methods must use them.
For example, you can grant user OBJTEST2 execute privileges on type atype created by OBJTEST1 in "Static Methods", and then create table atab based on the type:
GRANT EXECUTE ON atype TO OBJTEST2; CONNECT OBJTEST2/OBJTEST2; CREATE TABLE atab OF OBJTEST1.atype ;
Now, suppose user OBJTEST2 tries to use atype in the following statement:
BEGIN OBJTEST1.atype.newa(1, 'atab', 'OBJTEST2'); -- raises an error END; /
This statement raises an error because the definer of the type (OBJTEST1) does not have the privileges required to perform the insert in the newa procedure. You can avoid this error by defining atype using invoker rights. Here, you first drop the atab table in both schemas and re-create atype using invoker rights:
DROP TABLE atab;
CONNECT OBJTEST1/OBJTEST1;
DROP TABLE atab; DROP TYPE atype; commit;
CREATE TYPE atype AUTHID CURRENT_USER AS OBJECT(
a1 NUMBER,
STATIC PROCEDURE newa(p1 NUMBER, tabname VARCHAR2, schname VARCHAR2));
/
CREATE TYPE BODY atype AS
STATIC PROCEDURE newa(p1 NUMBER, tabname VARCHAR2, schname VARCHAR2)
IS
sqlstmt VARCHAR2(100);
BEGIN
sqlstmt := 'INSERT INTO '||schname||'.'||tabname|| '
VALUES (OBJTEST1.atype(:1))';
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE sqlstmt USING p1;
END;
END;
/
Now, if user OBJTEST2 tries to use atype again, the statement executes successfully:
GRANT EXECUTE ON atype TO OBJTEST2; CONNECT OBJTEST2/OBJTEST2; CREATE TABLE atab OF OBJTEST1.atype; BEGIN OBJTEST1.atype.newa(1, 'atab', 'OBJTEST2'); END; /
The statement is successful this time because the procedure is executed under the privileges of the invoker (OBJTEST2), not the definer (OBJTEST1).
In a type hierarchy, a subtype has the same rights model as its immediate supertype. That is, it implicitly inherits the rights model of the supertype and cannot explicitly specify one. Furthermore, if the supertype was declared with definer rights, the subtype must reside in the same schema as the supertype. These rules allow invoker-rights type hierarchies to span schemas. However, type hierarchies that use a definer-rights model must reside within a single schema. For example:
CREATE TYPE deftype1 AS OBJECT (...); --Definer-rights type CREATE TYPE subtype1 UNDER deftype1 (...); --subtype in same schema as supertype CREATE TYPE schema2.subtype2 UNDER deftype1 (...); --ERROR CREATE TYPE invtype1 AUTHID CURRENT_USER AS OBJECT (...); --Invoker-rights type CREATE TYPE schema2.subtype2 UNDER invtype1 (...); --LEGAL
Object tables and object views can be replicated as materialized views. You can also replicate relational tables that contain columns of an object, collection, or REF type. Such materialized views are called object-relational materialized views.
All user-defined types required by an object-relational materialized view must exist at the materialized view site as well as at the master site. They must have the same object type IDs and versions at both sites.
To be updatable, a materialized view based on a table that contains an object column must select the column as an object in the query that defines the view: if the query selects only certain attributes of the column's object type, then the materialized view is read-only.
The view-definition query can also select columns of collection or REF type. REFs can be either primary-key based or have a system-generated key, and they can be either scoped or unscoped. Scoped REF columns can be rescoped to a different table at the site of the materialized view—for example, to a local materialized view of the master table instead of the original, remote table.
A materialized view based on an object table is called an object materialized view. Such a materialized view is itself an object table. An object materialized view is created by adding the OF type keyword to the CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW statement. For example:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW customer OF cust_objtyp
AS SELECT * FROM Scott.Customer_objtab@dbs1;
As with an ordinary object table, each row of an object materialized view is an object instance, so the view-definition query that creates the materialized view must select entire objects from the master table: the query cannot select only a subset of the object type's attributes. For example, the following materialized view is not allowed:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW customer OF cust_objtyp AS SELECT CustNo FROM Scott.Customer_objtab@dbs1;
You can create an object-relational materialized view from an object table by omitting the OF type keyword, but such a view is read-only: you cannot create an updatable object-relational materialized view from an object table.
For example, the following CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW statement creates a read-only object-relational materialized view of an object table. Even though the view-definition query selects all columns and attributes of the object type, it does not select them as attributes of an object, so the view created is object-relational and read-only:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW customer
AS SELECT * FROM Scott.Customer_objtab@dbs1;
For both object-relational and object materialized views that are based on an object table, if the type of the master object table is not FINAL, the FROM clause in the materialized view definition query must include the ONLY keyword. For example:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW customer OF cust_objtyp
AS SELECT CustNo FROM ONLY Scott.Customer_objtab@dbs1;
Otherwise, the FROM clause must omit the ONLY keyword.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Advanced Replication for more information on replicating object tables and columns |
Oracle does not support constraints and defaults in type specifications. However, you can specify the constraints and defaults when creating the tables:
CREATE TYPE customer_type AS OBJECT( cust_id INTEGER); / CREATE TYPE department_type AS OBJECT( deptno INTEGER); / CREATE TABLE customer_tab OF customer_type ( cust_id default 1 NOT NULL); CREATE TABLE department_tab OF department_type ( deptno PRIMARY KEY); CREATE TABLE customer_tab1 ( cust customer_type DEFAULT customer_type(1) CHECK (cust.cust_id IS NOT NULL), some_other_column VARCHAR2(32));
The following sections contain design considerations relating to type evolution.
Once a type has evolved on the server side, all client applications using this type need to make the necessary changes to structures associated with the type. You can do this with OTT/JPUB. You also may need to make programmatic changes associated with the structural change. After making these changes, you must recompile your application and relink.
Types may be altered between releases of a third-party application. To inform client applications that they need to recompile to become compatible with the latest release of the third-party application, you can have the clients call a release-oriented compatibility initialization function. This function could take as input a string that tells it which release the client application is working with. If the release string mismatches with the latest version, an error is generated. The client application must then change the release string as part of the changes required to become compatible with the latest release.
For example:
FUNCTION compatibility_init(rel IN VARCHAR2, errmsg OUT VARCHAR2) RETURN NUMBER;
where:
rel is a release string that is chosen by the product, such as, 'Release 10.1'
errmsg is any error message that may need to be returned
The function returns 0 on success and a nonzero value on error
When a type is altered, its default, system-defined constructors need to be changed in order (for example) to include newly added attributes in the parameter list. If you are using default constructors, you need to modify their invocations in your program in order for the calls to compile.
You can avoid having to modify constructor calls if you define your own constructor functions instead of using the system-defined default ones.
When you alter a type T1 from FINAL to NOT FINAL, any attribute of type T1 in the client program changes from being an inlined structure to a pointer to T1. This means that you need to change the program to use dereferencing when this attribute is accessed.
Conversely, when you alter a type from NOT FINAL to FINAL, the attributes of that type change from being pointers to inlined structures.
For example, say that you have the types T1(a int) and T2(b T1), where T1's property is FINAL. The C/JAVA structure corresponding to T2 is T2(T1 b). But if you change T1's property to NOT FINAL, then T2's structure becomes T2(T1 *b).
Oracle lets you perform parallel queries with objects and objects synthesized in views, when you follow these rules:
To make queries involving joins and sorts parallel (using the ORDER BY, GROUP BY, and SET operations), a MAP function is required. In the absence of a MAP function, the query automatically becomes serial.
Parallel queries on nested tables are not supported. Even if there are parallel hints or parallel attributes for the table, the query is serial.
Parallel DML and parallel DDL are not supported with objects. DML and DDL are always performed in serial.
Parallel DML is not supported on views with INSTEAD-OF trigger. However, the individual statements within the trigger may be parallelized.
The following sections provide assorted tips on various aspects of working with Oracle object types.
As an application goes through its life cycle, the question often arises whether to change an existing user-defined type or to create a specialized subtype to meet new requirements. The answer depends on the nature of the new requirements and their context in the overall application semantics. Here are two examples:
Suppose that we have a user-defined type address with attributes Street, State, and ZIP:
CREATE TYPE address AS OBJECT ( Street VARCHAR2(80), State VARCHAR2(20), ZIP VARCHAR2(10)); /
We later find that we need to extend the address type by adding a Country attribute to support addresses internationally. Is it better to create a subtype of address or to evolve the address type itself?
With a general base type that has been widely used throughout an application, it is better to implement the change using type evolution.
Suppose that an existing type hierarchy of Graphic types (for example, curve, circle, square, text) needs to accommodate an additional variation, namely, Bezier curve. To support a new specialization of this sort that does not reflect a shortcoming of the base type, we should use inheritance and create a new subtype BezierCurve under the Curve type.
To sum up, the semantics of the required change dictates whether we should use type evolution or inheritance. For a change that is more general and affects the base type, use type evolution. For a more specialized change, implement the change using inheritance.
ANYDATA is an Oracle-supplied type that can hold instances of any Oracle datatype, whether built-in or user-defined. ANYDATA is a self-describing type and supports a reflection-like API that you can use to determine the shape of an instance.
While both inheritance, through the substitutability feature, and ANYDATA provide the polymorphic ability to store any of a set of possible instances in a placeholder, the two models give the capability two very different forms.
In the inheritance model, the polymorphic set of possible instances must form part of a single type hierarchy. A variable can potentially hold instances only of its defined type or of its subtypes. You can access attributes of the supertype and call methods defined in the supertype (and potentially overridden by the subtype). You can also test the specific type of an instance using the IS OF and the TREAT operators.
ANYDATA variables, however, can store heterogeneous instances. You cannot access attributes or call methods of the actual instance stored in an ANYDATA variable (unless you extract out the instance). You use the ANYDATA methods to discover and extract the type of the instance. ANYDATA is a very useful mechanism for parameter passing when the function/procedure does not care about the specific type of the parameter(s).
Inheritance provides better modeling, strong typing, specialization, and so on. Use ANYDATA when you simply want to be able to hold one of any number of possible instances that do not necessarily have anything in common.
Chapter 5 describes how to build up a view hierarchy from a set of object views each of which contains objects of a single type. Such a view hierarchy enables queries on a view within the hierarchy to see a polymorphic set of objects contained by the queried view or its subviews.
As an alternative way to support such polymorphic queries, you can define an object view based on a query that returns a polymorphic set of objects. This approach is especially useful when you want to define a view over a set of tables or views that already exists.
For example, an object view of Person_t can be defined over a query that returns Person_t instances, including Employee_t instances. The following statement creates a view based on queries that select persons from a persons table and employees from an employees table.
CREATE VIEW Persons_view OF Person_t AS SELECT Person_t(...) FROM persons UNION ALL SELECT TREAT(Employee_t(...) AS Person_t) FROM employees;
An INSTEAD OF trigger defined for this view can use the VALUE function to access the current object and to take appropriate action based on the object's most specific type.
Polymorphic views and object view hierarchies have these important differences:
Addressability: In a view hierarchy, each subview can be referenced independently in queries and DML statements. Thus, every set of objects of a particular type has a logical name. However, a polymorphic view is a single view, so you must use predicates to obtain the set of objects of a particular type.
Evolution: If a new subtype is added, a subview can be added to a view hierarchy without changing existing view definitions. With a polymorphic view, the single view definition must be modified by adding another UNION branch.
DML Statements: In a view hierarchy, each subview can be either inherently updatable or can have its own INSTEAD OF trigger. With a polymorphic view, only one INSTEAD OF trigger can be defined for a given operation on the view.
This section discusses the SQLJ object type.
According to the Information Technology - SQLJ - Part 2 document (SQLJ Standard), a SQLJ object type is a database object type designed for Java. A SQLJ object type maps to a Java class. Once the mapping is registered through the extended SQL CREATE TYPE command (a DDL statement), the Java application can insert or select the Java objects directly into or from the database through an Oracle JDBC driver. This enables the user to deploy the same class in the client, through JDBC, and in the server, through SQL method dispatch.
The extended SQL CREATE TYPE command:
Populates the database catalog with the external names for attributes, functions, and the Java class. Also, dependencies between the Java class and its corresponding SQLJ object type are maintained.
Validates the existence of the Java class and validates that it implements the interface corresponding to the value of the USING clause.
Validates the existence of the Java fields (as specified in the EXTERNAL NAME clause) and whether these fields are compatible with corresponding SQL attributes.
Generates an internal class to support constructors, external variable names, and external functions that return self as a result.
The SQLJ object type is a special case of SQL object type in which all methods are implemented in a Java class(es). The mapping between a Java class and its corresponding SQL type is managed by the SQLJ object type specification. That is, the SQLJ Object type specification cannot have a corresponding type body specification.
Also, the inheritance rules among SQLJ object types specify the legal mapping between a Java class hierarchy and its corresponding SQLJ object type hierarchy. These rules ensure that the SQLJ Type hierarchy contains a valid mapping. That is, the supertype or subtype of a SQLJ object type has to be another SQLJ object type.
The custom object type is the Java interface for accessing SQL object type. A SQL object type may include methods that are implemented in languages such as PLSQL, Java, and C. Methods implemented in Java in a given SQL object type can belong to different unrelated classes. That is, the SQL object type does not map to a specific Java class.
In order for the client to access these objects, JPub can be used to generate the corresponding Java class. Furthermore, the user has to augment the generated classes with the code of the corresponding methods. Alternatively, the user can create the class corresponding to the SQL object type.
At runtime, the JDBC user has to register the correspondence between a SQL Type name and its corresponding Java class in a map.
The following table summarizes the differences between SQLJ object types and custom object types.
Table 8-1 Differences Between SQLJ and Custom Object Types
| Feature | SQLJ Object Type Behavior | Custom Object Type Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Typecodes | Use the OracleTypes.JAVA_STRUCT typecode to register a SQLJ object type as a SQL OUT parameter. The OracleTypes.JAVA_STRUCT typecode is also used in the _SQL_TYPECODE field of a class implementing the ORAData or SQLData interface. |
Use the OracleTypes.STRUCT typecode to register a custom object type as a SQL OUT parameter. The OracleTypes.STRUCT typecode is also used in the _SQL_TYPECODE field of a class implementing the ORAData or SQLData interface. |
| Creation | Create a Java class implementing the SQLData or ORAData and ORADataFactory interfaces first and then load the Java class into the database. Next, you issue the extended SQL CREATE TYPE command for SQLJ object type. |
Issue the extended SQL CREATE TYPE command for a custom object type and then create the SQLData or ORAData Java wrapper class using JPublisher or do this manually. |
| Method Support | Supports external names, constructor calls, and calls for member functions with side effects. | There is no default class for implementing type methods as Java methods. Some methods may also be implemented in SQL. |
| Type Mapping | Type mapping is automatically done by the extended SQL CREATE TYPE command. However, the SQLJ object type must have a defining Java class on the client. |
Register the correspondence between SQL and Java in a type map. Otherwise, the type is materialized as oracle.sql.STRUCT. |
| Inheritance | There are rules for mapping SQL hierarchy to a Java class hierarchy. See the Oracle Database SQL Reference for a complete description of these rules. | There are no mapping rules. |
This section discusses miscellaneous tips.
If a column or table is of type T, Oracle adds a hidden column for each attribute of type T and, if the column or table is substitutable, for each attribute of every subtype of T, to store attribute data. A hidden typeid column is added as well, to keep track of the type of the object instance in a row.
The number of columns in a table is limited to 1,000. A type hierarchy with a number of total attributes approaching 1,000 puts you at risk of running up against this limit when using substitutable columns of a type in the hierarchy. To avoid problems as a result of this, consider one of the following options for dealing with a hierarchy that has a large number of total attributes:
Use views
Use REFs
Break up the hierarchy