| PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10807-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10807-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
A literal is an explicit numeric, character, string, or Boolean value not represented by an identifier. The numeric literal 135 and the string literal 'hello world' are examples. For more information, see "Literals".
Syntax

Description of the illustration boolean_literal.gif
Keyword and Parameter Description
A member of the PL/SQL character set. For more information, see "Character Set".
One of the numerals 0 .. 9.
A predefined Boolean value.
Usage Notes
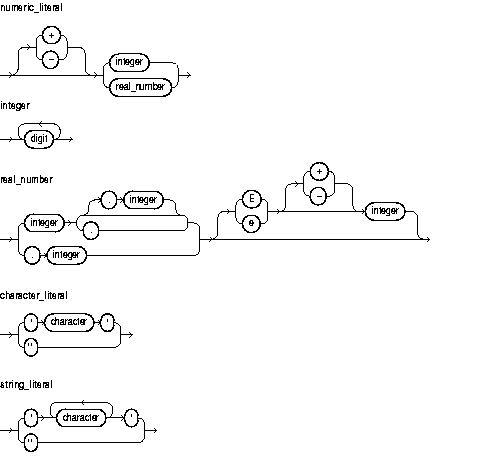
Two kinds of numeric literals can be used in arithmetic expressions: integers and reals. Numeric literals must be separated by punctuation. Spaces can be used in addition to the punctuation.
A character literal is an individual character enclosed by single quotes (apostrophes). Character literals include all the printable characters in the PL/SQL character set: letters, numerals, spaces, and special symbols.
PL/SQL is case sensitive within character literals. For example, PL/SQL considers the literals 'Q' and 'q' to be different.
A string literal is a sequence of zero or more characters enclosed by single quotes. The null string ('') contains zero characters. A string literal can hold up to 32,767 characters.
To represent an apostrophe within a string, enter two single quotes instead of one. For literals where doubling the quotes is inconvenient or hard to read, you can designate an escape character using the notation q'esc_char ... esc_char'. This escape character must not occur anywhere else inside the string.
PL/SQL is case sensitive within string literals. For example, PL/SQL considers the literals 'white' and 'White' to be different.
Trailing blanks are significant within string literals, so 'abc' and 'abc ' are different. Trailing blanks in a string literal are not trimmed during PL/SQL processing, although they are trimmed if you insert that value into a table column of type CHAR.
The Boolean values TRUE and FALSE cannot be inserted into a database column.
Examples
Several examples of numeric literals are:
25 6.34 7E2 25e-03 .1 1. +17 -4.4 -4.5D -4.6F
Several examples of character literals are:
'H' '&' ' ' '9' ']' 'g'
Several examples of string literals are:
'$5,000' '02-AUG-87' 'Don''t leave until you''re ready and I''m ready.' q'#Don't leave until you're ready and I'm ready.#'
Related Topics