| Oracle® Database Gateway for VSAM User's Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B31054-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database Gateway for VSAM User's Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B31054-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This section describes the support methods that Oracle Connect for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways applies to normalize non-relational data. It includes the following topics:
See Also:
Oracle Database Gateway for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Installation and Configuration Guide for Microsoft Windows or Oracle Database Gateway for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Installation and Configuration Guide for UNIX for information on importing metadata into Oracle Studio for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways.Oracle Connect for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways exposes a purely relational front end through the HOA API. However, it connects to non-relational data sources, which include non-relational data models. As such, Oracle Connect for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways provides a logical mapping that exposes the non-relational constructs in a relational manner. The most prevalent problem in this domain is the issue of arrays, which is described in this section.
An array is a group of similar elements of the same size. Arrays contain a series of data elements that are of the same data type, which can be simple or complex (group). A specific element is defined and accessed by its position in the array, which is provided by an index.
Arrays are a convenient way to store a fixed amount of data that is accessed in an unpredictable fashion. They are not efficient, however, when you need to insert or delete individual elements of the array.
Before looking at the different methods of handling arrays, you should understand how metadata is represented in Oracle Studio for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways.
Figure 3-1 shows an example record with arrays and nested arrays.
See Also:
COBOL Copybook ExampleWhen you import this metadata into Oracle Studio for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways, the import process creates a data dictionary definition that is equivalent to the original structure, usually mapping the fields one to one. The import process also writes all primary and foreign key definitions to the ALL_CONSTRAINTS table.
Oracle Studio for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways represents the flattened view of the metadata on the table editor's Columns tab, as shown in Figure 3-2.
Figure 3-2 Representation of Metadata on the Columns tab in Oracle Studio for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways
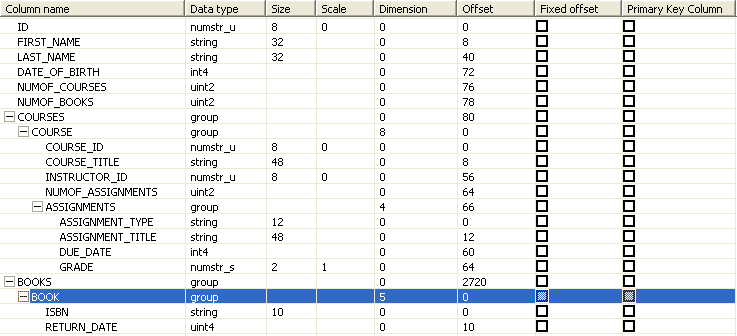
Table 3-1 describes the different columns shown in Figure 3-2.
The (+) to the left of a column indicates a group field. This type of field usually has a Dimension value. This value is not mandatory, but it optimizes the access to an array. You can click (+) to display the group members. In Figure 3-2, all groups are expanded.
Table 3-1 Metadata Column Tab Definition
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
|
Column name |
The name of the column. |
|
Data type |
The data type of the column. Selecting this field displays a drop-down box listing the possible data types. |
|
Size |
The size of the column for data types of a non-fixed size. |
|
Scale |
The information entered in this field depends on the data type: For decimal data types, this is the number of digits to the right of the decimal place. This number must not be greater than the number of digits. The default value is 0. For scaled data types, this is the total number of digits. The number must be negative. |
|
Dimension |
The maximum number of entries of an array. An array has a dimension other than zero. This value is not mandatory, but it optimizes the access to an array. |
|
Offset |
Not relevant for arrays. |
|
Fixed offset |
Not relevant for arrays. |
|
Primary Key Column |
The column is part of the table's primary key. |
The tree in the Metadata view displays a normalized view of the tables, as shown in Figure 3-3, where STUDENT_BOOK, STUDENT_COURSE, and STUDENT_COURSE_ASSIGNMENTS are virtual views and STUDENT_ST is a single table, also called sequential view.
The following SQL query on the Oracle data dictionary produces the result shown in Example 3-1. In this query, data source is the name of the data source from which the metadata was created. The result shows the metadata of the original table after virtual arrays were created.
SQL> select TABLE_NAME,COLUMN_NAME,DATA_TYPE from ALL_TAB_COLUMNS@dg4[data_source] where table_name like 'STUDENT%';
Example 3-1 SQL Query Result
TABLE_NAME COLUMN_NAME DATA_TYPE ------------------------------ --------------------------- --------------------- STUDENT ID NUMBER STUDENT FIRST_NAME CHAR STUDENT LAST_NAME CHAR STUDENT DATE_OF_BIRTH CHAR STUDENT NUMOF_COURSES NUMBER STUDENT NUMOF_BOOKS NUMBER STUDENT_BOOK BOOK_ROWNUM NUMBER STUDENT_BOOK ISBN CHAR STUDENT_BOOK RETURN_DATE CHAR STUDENT_COURSE COURSE_ROWNUM NUMBER STUDENT_COURSE COURSE_ID NUMBER STUDENT_COURSE COURSE_TITLE CHAR STUDENT_COURSE INSTRUCTOR_ID NUMBER STUDENT_COURSE NUMOF_ASSIGNMENTS NUMBER STUDENT_COURSE_ASSIGNMENTS COURSE_ROWNUM NUMBER STUDENT_COURSE_ASSIGNMENTS ASSIGNMENTS_ROWNUM NUMBER STUDENT_COURSE_ASSIGNMENTS ASSIGNMENT_TYPE CHAR STUDENT_COURSE_ASSIGNMENTS ASSIGNMENT_TITLE CHAR STUDENT_COURSE_ASSIGNMENTS DUE_DATE CHAR STUDENT_COURSE_ASSIGNMENTS GRADE NUMBER STUDENT_ST __LEVEL VARCHAR2 STUDENT_ST __SEQUENCE NUMBER STUDENT_ST COURSE_ROWNUM NUMBER STUDENT_ST ASSIGNMENTS_ROWNUM NUMBER STUDENT_ST BOOK_ROWNUM NUMBER STUDENT_ST ID NUMBER STUDENT_ST FIRST_NAME CHAR STUDENT_ST LAST_NAME CHAR STUDENT_ST DATE_OF_BIRTH CHAR STUDENT_ST NUMOF_COURSES NUMBER STUDENT_ST NUMOF_BOOKS NUMBER STUDENT_ST COURSE_ID NUMBER STUDENT_ST COURSE_TITLE CHAR STUDENT_ST INSTRUCTOR_ID NUMBER STUDENT_ST NUMOF_ASSIGNMENTS NUMBER STUDENT_ST ASSIGNMENT_TYPE CHAR STUDENT_ST ASSIGNMENT_TITLE CHAR STUDENT_ST DUE_DATE CHAR STUDENT_ST GRADE NUMBER STUDENT_ST ISBN CHAR STUDENT_ST RETURN_DATE CHAR 41 rows selected.
Oracle Studio for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways lets you handle arrays by using the following methods:
Note:
Objects from virtual views and sequential flattening are described by Oracle Gateways as tables.See Chapter 4, "Setting the Array Handling Policy" for information on how to define array handling settings.
Exposing arrays as virtual views is a commonly used technique to handle arrays. It generates a virtual view for every array in the parent record that contains all the array members. Virtual views contain primary key fields from the parent to connect the parent and the virtual view. Optionally, they can also contain all fields from the parent table.
During the import process or when you set the virtual array policy on the table level, Oracle Studio for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways generates virtual views and names them by appending the array name to the parent name. When an array includes another array, the name of the resulting virtual table consists of the parent name, the array name, and the name of the nested array, as follows:
parentName_arrayName_nestedArrayName
For example, a parent table called STUDENT with an array called COURSE and a nested array called ASSIGNMENTS is represented by the virtual view STUDENT_COURSE_ASSIGNMENTS (see Figure 3-5).
The number of nested-array levels is not limited.
Virtual views include the following:
The array member columns from the original structure.
The fields from the parent's first unique key, or all parent fields, depending on the selection you make during the import process or when setting the virtual array policy on the table level.
If all parent fields are included in the virtual view, the parent's indexes are available in the view definition and can be used for efficient optimization strategies.
Note:
Inherited keys lose their uniqueness in the virtual view.If the view does not include all parent fields, the primary key fields (if the primary key is not the parent's first unique key).
If selected, a column called <array_name>_ROWNUM, which identifies the row in the array.
The unique key and <array_name>_ROWNUM columns are generated automatically. Together, they uniquely identify each row in the virtual view and form a unique key.
Figure 3-4 shows the STUDENT_BOOKS virtual view with the two array member columns (ISBN and RETURN_DATE) and the column that identifies the row in the array (BOOK_ROWNUM).
Oracle Studio for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways also maintains primary and foreign key definitions that connect between the parent table and the array tables. This allows graphical tools to easily match parent and array.
When working with virtual views, consider the following limitations:
Virtual views are read-only.
Virtual views do not support arrays within variants that have a selector field.
Including all parent fields in the virtual view greatly reduces the need for performing join operations because this in itself is an implicit join. In general, the query processor can devise efficient access strategies because Oracle Connect for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways copies all relevant indexes from the parent to the virtual view.
Oracle Studio for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways indicates virtual views by using a different colored icon in the Metadata view, as shown in Figure 3-5.
Performing a bulk load of complex data from a non-relational system to a relational database requires a carefully thought-out algorithm that keeps I/O operations at a minimum.
In a bulk load scenario, a method such as Virtual Views requires a full scan of the physical file for every single array. An efficient method of performing this task presents a kind of row-wise normalization, called sequential flattening. This method reads all data in the physical file in a single scan.
Sequential flattening replaces arrays in a non-relational system by a sequence of rows. It maps all the record fields of the non-relational file to a single table that contains both parent and child records. In this way, sequential flattening enables the reception of a stream of data by using a single SELECT statement.
The sequentially flattened view of a complex table is referred to as a single table or sequential view. You can choose to create a sequential view in Oracle Studio for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways by selecting the Generate sequential view check box during the Metadata Model Selection step of the Metadata Import procedure. The single table is read-only.
See Also:
Oracle Database Gateway for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Installation and Configuration Guide for Microsoft Windows or Oracle Database Gateway for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Installation and Configuration Guide for UNIX for details on importing metadata into Oracle Studio for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways.The flattened table is called <table>_ST, where <table> is the name of the parent table and ST indicates a single table. For example, if a parent table is called STUDENT, the single table, or sequential view, is called STUDENT_ST.
The structure of the single table is identical to the original table's structure, except that Oracle Connect for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways removes all array dimensions and adds some control fields. When reading a record, Oracle Connect for IMS, VSAM, and Adabas Gateways performs a tree traversal of the parent and its array hierarchy. Each record in the resulting recordset deals with a specific array member; other arrays are nulled out.
The sequentially flattened single table includes the following columns:
The parent fields, that is the non-repeating fields.
The array fields for all arrays within the parent.
For each array, an optional column called <array_name>_ROWNUM, which identifies the row in the array. This column is generated automatically for the array.
The sequentially flattened single table includes a record (row) for each array record.
See Figure 3-1 for an illustration of arrays and nested arrays.
Figure 3-6 shows the metadata that sequential flattening produces for a data source with three arrays (COURSE, ASSIGNMENTS, and BOOK) in the SQL View window. The window presents read-only information about each of the columns in the table.
The following table describes the information presented in this window.
Table 3-2 SQL View Window
| Information Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
Name |
The name of the column. |
|
Data Type |
The data type supported by that column. For example, string or integer. |
|
Size |
Indicates the maximum size allowable for the data in the column. The size is in standard units for the data type. For example, a string with size 40 can have no more than forty characters. |
|
Scale |
Indicates the number of digits allowed after the decimal point for a numeric value. |
|
Precision |
Indicates the total number of digits allowed for a numeric value in the column. If the value has a scale of one or more, then the total number of digits allowed before the decimal point is the precision value minus the scale value. For example, a value with precision 4 and scale 2 can be no larger than 99.99. |
|
Nullable |
Indicates whether the column can have a null value. If |
Figure 3-7 shows the actual single table after running a SELECT clause. It contains a column for each row in the preceding SQL view.
A SQL describe of this single table produces the following result:
Name Null? Type ----------------------------------------- ------------------ ------------------ __LEVEL NOT NULL VARCHAR2(64) __SEQUENCE NOT NULL NUMBER(11) COURSE_ROWNUM NUMBER(10) ASSIGNMENTS_ROWNUM NUMBER(10) BOOK_ROWNUM NUMBER(10) ID NOT NULL NUMBER(8) FIRST_NAME NOT NULL CHAR(32) LAST_NAME NOT NULL CHAR(32) DATE_OF_BIRTH NOT NULL CHAR(8) NUMOF_COURSES NOT NULL NUMBER(10) NUMOF_BOOKS NOT NULL NUMBER(10) COURSE_ID NUMBER(8) COURSE_TITLE CHAR(48) INSTRUCTOR_ID NUMBER(8) NUMOF_ASSIGNMENTS NUMBER(10) ASSIGNMENT_TYPE CHAR(12) ASSIGNMENT_TITLE CHAR(48) DUE_DATE CHAR(8) GRADE NUMBER(2,1) ISBN CHAR(10) RETURN_DATE CHAR(8)
This table shows all the columns of the single table.