| Oracle® Database Upgrade Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28300-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database Upgrade Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28300-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter provides an overview of the database upgrade process, as well as information about running multiple releases of Oracle Database.
This chapter covers the following topics:
This section includes an overview of the major steps required to upgrade an existing Oracle database to Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1). These procedures transform an existing Oracle Database system (including associated applications) into an Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) system. Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) is compatible with all earlier Oracle Database releases. Therefore, databases upgraded using the procedures described in this guide can work in the same manner as in earlier releases and, optionally, can leverage new Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) features and functions.
Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) supports the following tools and methods for upgrading a database to the new release:
Database Upgrade Assistant (DBUA)
Provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that guides you through the upgrade of a database. DBUA can be launched during installation with the Oracle Universal Installer, or you can launch DBUA as a standalone tool at any time in the future.
Note:
DBUA is the recommended method for performing a major release upgrade or patch release upgrade.Manual upgrade using SQL scripts and utilities
Provides a command-line upgrade of a database, using SQL scripts and utilities.
Export and Import utilities
Uses the Oracle Data Pump Export and Import utilities, available as of Oracle Database 10g Release 1 (10.1), or the original Export and Import utilities to perform a full or partial export from your database, followed by a full or partial import into a new Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) database. Export/Import can copy a subset of the data, leaving the database unchanged.
CREATE TABLE AS SQL statement
Copies data from a database into a new Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) database. Data copying can copy a subset of the data, leaving the database unchanged.
These tools and methods are described in more detail in "Choose an Upgrade Method".
The major steps in the upgrade process are illustrated in Figure 1-1.
Note:
The upgrade steps apply to all operating systems, with the possible exception of a few operating system-specific details identified in your operating system-specific Oracle documentation.The following list outlines the major steps performed during the upgrade process. Detailed instructions are provided in the appropriate chapters later in this guide.
Step 1: Prepare to Upgrade
Become familiar with the features of Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1).
Determine the upgrade path to the new release.
Choose an upgrade method.
Choose an Oracle home directory for the new release.
Develop a testing plan.
Prepare a backup strategy.
Step 2: Test the Upgrade Process
Perform a test upgrade using a test database. The test upgrade should be conducted in an environment created for testing and should not interfere with the actual production database.
Step 3: Test the Upgraded Test Database
Perform the tests you planned in Step 1 on the test database and on the test database that was upgraded to Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1).
Compare results, noting anomalies between test results on the test database and on the upgraded database.
Investigate ways to correct any anomalies you find and then implement the corrections.
Repeat Step 1, Step 2, and the first parts of Step 3, as necessary, until the test upgrade is completely successful and works with any required applications.
Chapter 2, "Preparing to Upgrade" provides detailed information about Steps 1 through 3.
Step 4: Prepare and Preserve the Production Database
Prepare the current production database as appropriate to ensure the upgrade to Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) is successful.
Schedule the downtime required for backing up and upgrading the production database.
Back up the current production database. Perform a full or an incremental backup, as necessary, to ensure your database is protected against data loss.
Step 5: Upgrade the Production Database
Upgrade the production database to Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1).
After the upgrade, perform a full backup of the production database and perform other post-upgrade tasks.
Chapter 3 describes Steps 4 and 5 when using DBUA or when performing a manual upgrade. Chapter 4 describes the backup procedure after the upgrade and other post-upgrade tasks.
Step 6: Tune and Adjust the New Production Database
Tune the Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) production database. The new production database should perform as well as, or better than, the database prior to the upgrade. Chapter 4, "After Upgrading to the New Release" describes these adjustments.
Determine which features of Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) you want to use and update your applications accordingly.
Develop new database administration procedures, as needed.
Do not upgrade production users to the new release until all applications have been tested and operate properly. Chapter 6, "Upgrading Your Applications" describes considerations for updating applications.
During the upgrade, consider running multiple releases of the database software so you can use the existing release as your production environment while you test the new release. See "Running Multiple Oracle Releases".
This guide describes moving between different releases of the Oracle Database server. Figure 1-2 describes what each part of a release number represents.
Figure 1-2 Example of an Oracle Release Number
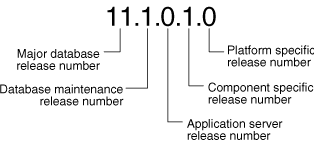
Note:
Starting with Oracle Database9i Release 2 (9.2), maintenance releases of Oracle Database are denoted by a change to the second digit of a release number. In previous releases, the third digit indicated a particular maintenance release.See Also:
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for more information about Oracle release numbersWhen a statement is made in this guide about a major database release number, the statement applies to all releases within that major database release. References to Oracle Database include release 1 (11.1); references to Oracle Database 10g include Oracle Database 10g Release 1 (10.1) and Oracle Database 10g Release 2 (10.2); references to Oracle9i include release 1 (9.0.1) and release 2 (9.2).
Similarly, when a statement is made in this guide about a maintenance release, the statement applies to all component-specific (also referred to as patchset releases) and platform-specific releases within that maintenance release. So, a statement about Oracle Database9i Release 2 (9.2) applies to release 9.2.0.1, release 9.2.0.2, and all other platform-specific releases within release 2 (9.2).
You can run different releases of Oracle Database on the same computer at the same time. However, you must observe the following conditions when using multiple releases:
An Oracle Database release must be installed in a new Oracle home that is separate from previous releases of Oracle.
There cannot be more than one release for each Oracle home. Oracle recommends that you adopt an Optimal Flexible Architecture (OFA) when creating multiple Oracle homes. See "Using Optimal Flexible Architecture (OFA)" for more information.
Caution:
It is not possible to install Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) products into an existing Oracle home of a prior major release. This feature was available only for certain previous releases and has not been continued.Each database server can access only a database that is consistent with its release number.
For example, if you have Oracle9i and Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) installed on the same computer, then the Oracle9i database server can access Oracle9i databases but not Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) databases, and the Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) database server can access Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) databases but not Oracle9i databases.
See Also:
Your operating system-specific Oracle documentation for more information about running multiple releases of Oracle on your operating system. Restrictions might apply on some operating systems.The following sections provide general information about running multiple releases of Oracle Database.
You can install Oracle8i, Oracle9i, and Oracle Database 10g databases in multiple (separate) Oracle homes on the same computer and have Oracle8i, Oracle9i, and Oracle Database 10g clients connecting to any or all of the databases.
You can install Oracle8i, Oracle9i, Oracle Database 10g, and Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) databases in multiple (separate) Oracle homes on separate computers and have Oracle8i, Oracle9i, Oracle Database 10g, and Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) clients connecting to any or all of the databases.
You can upgrade an Oracle8i, Oracle9i, or Oracle Database 10g database to Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) and have Oracle8i, Oracle9i, Oracle Database 10g, and Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) clients connecting to the upgraded database.
You can upgrade any or all of your Oracle8i, Oracle9i, or Oracle Database 10g clients to Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1). The Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) client can be used to access your Oracle8i, Oracle9i, Oracle Database 10g, and Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) databases.
Oracle recommends the Optimal Flexible Architecture (OFA) standard for your Oracle Database installations. The OFA standard is a set of configuration guidelines for efficient and reliable Oracle databases that require little maintenance.
OFA provides the following benefits:
Organizes large amounts of complicated software and data on disk to avoid device bottlenecks and poor performance
Facilitates routine administrative tasks, such as software and data backup functions, which are often vulnerable to data corruption
Alleviates switching among multiple Oracle databases
Adequately manages and administers database growth
Helps to eliminate fragmentation of free space in the data dictionary, isolates other fragmentation, and minimizes resource contention.
If you are not currently using the OFA standard, then switching to the OFA standard involves modifying your directory structure and relocating your database files.
See Also:
Your operating system-specific Oracle documentation for more information about OFA
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for information about relocating database files
If you are installing 64-bit Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) software but were previously using a 32-bit Oracle Database installation, then the database is automatically converted to 64-bit during a patch release or major release upgrade to Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1).
You must increase initialization parameters affecting the system global area, such as sga_target and shared_pool_size, to support 64-bit operation.
See Also:
Your platform-specific installation guide for additional informationA rolling upgrade upgrades different databases or different instances of the same database (in an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment) one at a time, without stopping the database. Depending on the method you choose, you can perform a rolling upgrade of the Oracle Database software version, apply patchsets, or apply individual patches (sometimes referred to as one-off patches), incurring little or no database downtime.
Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) provides the following methods for performing rolling upgrades:
Oracle Data Guard and logical standby databases
Using SQL Apply and logical standby databases, you can upgrade Oracle Database software and patchsets with little or no database downtime. For example, you can upgrade the Oracle Database software from patchset release 10.1.0.n to the next database 10.1.0.(n+1) patchset release, or upgrade Oracle Database 10g Release 1 (10.1) to Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1).
See Also:
"Upgrading Standby Databases" for more information.Using Streams source and destination databases, you can upgrade to a new version of Oracle Database software, migrate an Oracle database to a different operating system or character set, upgrade user-created applications, and apply Oracle Database patches. These maintenance operations use the features of Oracle Streams to achieve little or no database down time.
Oracle Real Application Clusters rolling upgrades with the OPatch Utility
Using the OPatch command-line utility, you can perform rolling patch upgrades with Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC), incurring little or no database downtime. Note that the OPatch utility can only be used to apply individual patches, not patchset releases. See Oracle Universal Installer and OPatch User's Guide for more information about the OPatch utility.
The advantage of a Oracle RAC rolling upgrade is that it enables at least some instances of the Oracle RAC installation to be available during the scheduled outage required for patch upgrades. Only the Oracle RAC instance that is currently being patched must be brought down; the other instances can continue to remain available. This means that the effect on the application downtime required for such scheduled outages is further minimized. The Oracle OPatch utility enables you to apply the patch successively to the different instances of the Oracle RAC installation.
Oracle Clusterware rolling upgrades using the Oracle Universal Installer (OUI)
Using the Oracle Universal Installer (OUI) that is downloaded with the patch update, you can perform rolling upgrades to upgrade Oracle Clusterware or Oracle Cluster Ready Services. You can perform a rolling upgrade to apply patchset releases.
The advantage of an Oracle Clusterware rolling upgrade is that it enables at least some instances of the Oracle RAC installation to be available during the scheduled outage required for patchset upgrades. Only the node that is currently being patched must be brought down; the other instances remain available. This means that the effect on the application downtime required for such scheduled outages is further minimized. OUI enables you to apply the patchset successively to the different instances of the Oracle Clusterware installation.
See Also:
The "How to Perform Oracle Clusterware Rolling Upgrades" discussion in your platform-specific Oracle Clusterware installation guides for step-by-step instructions to help you upgrade your Oracle Clusterware. Also, see Oracle Universal Installer and OPatch User's Guide for information about using OUI.Automatic Storage Management (ASM) Rolling Upgrades
Starting with Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1), you can perform a rolling upgrade of Oracle Automatic Storage Management software from Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1) to a later release. ASM rolling upgrades enable you to independently upgrade or patch clustered ASM nodes without affecting database availability, thus providing greater uptime. During a rolling upgrade, all of the features of a clustered ASM environment continue to function even while one or more of the nodes in the cluster are running on different software versions. This feature provides greater availability and enables you to upgrade ASM software from one release to the next more gracefully.
See Also:
Your platform-specific Oracle Clusterware installation guide for instructions on how to perform a rolling upgrade, and the Oracle Database Storage Administrator's Guide for more information about ASMIf you have a Standard Edition database at a release prior to Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1), then you can change it to an Enterprise Edition database by installing the Enterprise Edition and following the normal upgrade procedures, as described in this manual.
To change your existing Oracle Database 11g Standard Edition database to an Enterprise Edition database, follow these steps:
Ensure that the release number of your Standard Edition server software is the same release as the Enterprise Edition server software.
For example, if your Standard Edition server software is release 11.1.0.6, then you should upgrade to release 11.1.0.6 of the Enterprise Edition.
Shut down your database.
If your operating system is Windows, then stop all Oracle services, including the OracleServiceSID Oracle service, where SID is the instance name.
Deinstall the Standard Edition server software.
Install the Enterprise Edition server software using the Oracle Universal Installer.
Select the same Oracle home that was used for the de-installed Standard Edition. During the installation, be sure to select the Enterprise Edition. When prompted, choose Software Only from the Database Configuration screen.
Start up your database.
Your database is now upgraded to the Enterprise Edition.
In order to upgrade Oracle Database 10g Express Edition (Oracle Database XE) to Oracle Database 11g, you need to install Oracle Database 11g on the same system as Oracle Database XE and use Database Upgrade Assistant to perform the upgrade.