| Oracle9i SQL Reference Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96540-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle9i SQL Reference Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96540-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
You can write user-defined functions in PL/SQL or Java to provide functionality that is not available in SQL or SQL built-in functions. User-defined functions can appear in a SQL statement anywhere SQL functions can appear, that is, wherever an expression can occur.
For example, user-defined functions can be used in the following:
SELECT statementWHERE clauseCONNECT BY, START WITH, ORDER BY, and GROUP BY clausesVALUES clause of an INSERT statementSET clause of an UPDATE statementuser_defined_function::=
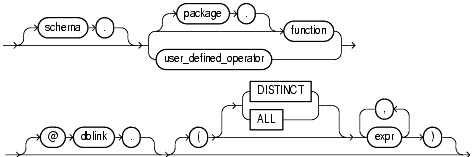
The optional expression list must match attributes of the function, package, or operator.
The DISTINCT and ALL keywords are valid only with a user-defined aggregate function.
See Also:
|
User-defined functions must be created as top-level functions or declared with a package specification before they can be named within a SQL statement.
To use a user function in a SQL expression, you must own or have EXECUTE privilege on the user function. To query a view defined with a user function, you must have SELECT privileges on the view. No separate EXECUTE privileges are needed to select from the view.
See Also:
|
Within a SQL statement, the names of database columns take precedence over the names of functions with no parameters. For example, if the Human Resources manager creates the following two objects in the hr schema:
CREATE TABLE new_emps (new_sal NUMBER, ...); CREATE FUNCTION new_sal RETURN NUMBER IS BEGIN ... END;
then in the following two statements, the reference to new_sal refers to the column new_emps.new_sal:
SELECT new_sal FROM new_emps; SELECT new_emps.new_sal FROM new_emps;
To access the function new_sal, you would enter:
SELECT hr.new_sal FROM new_emps;
Here are some sample calls to user functions that are allowed in SQL expressions:
circle_area (radius) payroll.tax_rate (empno) hr.employees.tax_rate (dependent, empno)@remote
To call the tax_rate user function from schema hr, execute it against the ss_no and sal columns in tax_table, and place the results in the variable income_tax, specify the following:
SELECT hr.tax_rate (ss_no, sal) INTO income_tax FROM tax_table WHERE ss_no = tax_id;
If only one of the optional schema or package names is given, then the first identifier can be either a schema name or a package name. For example, to determine whether PAYROLL in the reference PAYROLL.TAX_RATE is a schema or package name, Oracle proceeds as follows:
PAYROLL package in the current schema.PAYROLL package is not found, then look for a schema name PAYROLL that contains a top-level TAX_RATE function. If no such function is found, then return an error.PAYROLL package is found in the current schema, then look for a TAX_RATE function in the PAYROLL package. If no such function is found, then return an error.You can also refer to a stored top-level function using any synonym that you have defined for it.