| PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10802-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10802-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
DBMS_DEBUG is a PL/SQL interface to the PL/SQL debugger layer, Probe, in the Oracle server.
This API is primarily intended to implement server-side debuggers and it provides a way to debug server-side PL/SQL program units.
|
Note: The term program unit refers to a PL/SQL program of any type (procedure, function, package, package body, trigger, anonymous block, object type, or object type body). |
This chapter contains the following topics:
To debug server-side code, you must have two database sessions: one session to run the code in debug mode (the target session), and a second session to supervise the target session (the debug session).
The target session becomes available for debugging by making initializing calls with DBMS_DEBUG. This marks the session so that the PL/SQL interpreter runs in debug mode and generates debug events. As debug events are generated, they are posted from the session. In most cases, debug events require return notification: the interpreter pauses awaiting a reply.
Meanwhile, the debug session must also initialize itself using DBMS_DEBUG: This tells it which target session to supervise. The debug session may then call entry points in DBMS_DEBUG to read events that were posted from the target session and to communicate with the target session.
The following subprograms are run in the target session (the session that is to be debugged):
DBMS_DEBUG does not provide an interface to the PL/SQL compiler, but it does depend on debug information optionally generated by the compiler. Without debug information, it is not possible to examine or modify the values of parameters or variables.
A breakpoint status may have the following value:
Otherwise, the status is a mask of the following values:
breakpoint_status_active--a line breakpointbreakpoint_status_disabled--breakpoint is currently disabledbreakpoint_status_remote--a shadow breakpoint (a local representation of a remote breakpoint)| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The timeout value (used by both sessions).The smallest possible timeout is 1 second. If this value is set to 0, then a large value (3600) is used. |
This type is used by PRINT_BACKTRACE.
TYPE backtrace_table IS TABLE OF program_info INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
This type gives information about a breakpoint, such as its current status and the program unit in which it was placed.
TYPE breakpoint_info IS RECORD ( -- These fields are duplicates of 'program_info': Name VARCHAR2(30), Owner VARCHAR2(30), DbLink VARCHAR2(30), Line# BINARY_INTEGER, LibunitType BINARY_INTEGER, Status BINARY_INTEGER -- see breakpoint_status_* in following sections );
This type is used by SHOW_BREAKPOINTS.
TYPE breakpoint_table IS TABLE OF breakpoint_info INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
This type is used by GET_INDEXES to return the available indexes for an indexed table.
TYPE index_table IS table of BINARY_INTEGER INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
This type specifies a program location. It is a line number in a program unit. This is used for stack backtraces and for setting and examining breakpoints. The read-only fields are currently ignored by Probe for breakpoint operations. They are set by Probe only for stack backtraces.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
EntrypointName |
Null, unless this is a nested procedure or function. |
|
LibunitType |
Disambiguate among objects that share the same namespace (for example, procedure and package specifications). See the Libunit Types for more information. |
TYPE program_info IS RECORD ( -- The following fields are used when setting a breakpoint Namespace BINARY_INTEGER, -- See 'NAMESPACES' in following sections Name VARCHAR2(30), -- name of the program unit Owner VARCHAR2(30), -- owner of the program unit Dblink VARCHAR2(30), -- database link, if remote Line# BINARY_INTEGER, -- Read-only fields (set by Probe when doing a stack backtrace) LibunitType BINARY_INTEGER, EntrypointName VARCHAR2(30) );
This type gives context information about the running program.
TYPE runtime_info IS RECORD ( Line# BINARY_INTEGER, -- (duplicate of program.line#) Terminated BINARY_INTEGER, -- has the program terminated? Breakpoint BINARY_INTEGER, -- breakpoint number StackDepth BINARY_INTEGER, -- number of frames on the stack InterpreterDepth BINARY_INTEGER, -- <reserved field> Reason BINARY_INTEGER, -- reason for suspension Program program_info -- source location );
This type is used by SHOW_SOURCE.
TYPE vc2_table IS TABLE OF VARCHAR2(90) INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
These values are returned by the various functions called in the debug session (SYNCHRONIZE, CONTINUE, SET_BREAKPOINT, and so on). If PL/SQL exceptions worked across client/server and server/server boundaries, then these would all be exceptions rather than error codes.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Normal termination. |
Statuses returned by GET_VALUE and SET_VALUE:
Statuses returned by SET_VALUE:
Statuses returned by the breakpoint functions:
General error codes (returned by many of the DBMS_DEBUG subprograms):
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
|
i |
|
The following exceptions are raised by procedure SELF_CHECK:
There are two ways to ensure that debug information is generated: through a session switch, or through individual recompilation.
To set the session switch, enter the following statement:
ALTER SESSION SET PLSQL_DEBUG = true;
This instructs the compiler to generate debug information for the remainder of the session. It does not recompile any existing PL/SQL.
To generate debug information for existing PL/SQL code, use one of the following statements (the second recompiles a package or type body):
ALTER [PROCEDURE | FUNCTION | PACKAGE | TRIGGER | TYPE] <name> COMPILE DEBUG; ALTER [PACKAGE | TYPE] <name> COMPILE DEBUG BODY;
Figure 27-1 and Figure 27-2 illustrate the flow of operations in the session to be debugged and in the debugging session.
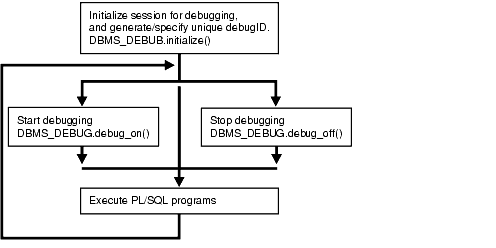
Text description of the illustration arpls001.gif
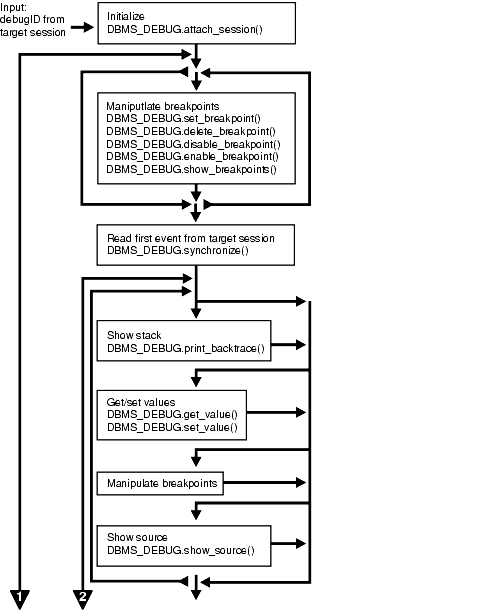
Text description of the illustration arpls003.gif
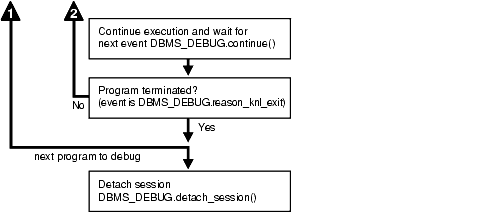
Text description of the illustration arpls004.gif
The interpreter pauses execution at the following times:
DBMS_DEBUG.CONTINUE in the breakflags parameter.There is no event for session termination. Therefore, it is the responsibility of the debug session to check and make sure that the target session has not ended. A call to DBMS_DEBUG.SYNCHRONIZE after the target session has ended causes the debug session to hang until it times out.
The diagram suggests that it is possible to set breakpoints prior to having a target session. This is true. In this case, Probe caches the breakpoint request and transmits it to the target session at first synchronization. However, if a breakpoint request is deferred in this fashion, then:
SET_BREAKPOINT does not set the breakpoint number (it can be obtained later from SHOW_BREAKPOINTS if necessary).SET_BREAKPOINT does not validate the breakpoint request. If the requested source line does not exist, then an error silently occurs at synchronization, and no breakpoint is set.To debug Probe, there are diagnostics parameters to some of the calls in DBMS_DEBUG. These parameters specify whether to place diagnostic output in the RDBMS tracefile. If output to the RDBMS tracefile is disabled, these parameters have no effect.
The following subprograms may be called in either the target or the debug session:
The following subprograms may be called only in the target session:
The following subprograms should be run in the debug session only:
Exceptions that are declared in PL/SQL programs are known as user-defined exceptions. In addition, there are Oracle Errors (OERs) that are returned from the Oracle kernel. To tie the two mechanisms together, PL/SQL provides the exception_init pragma that turns a user-defined exception into an OER, so that a PL/SQL handler may be used for it, and so that the PL/SQL engine can return OERs to the Oracle kernel. As of the current release, the only information available about an OER is its number. If two user-defined exceptions are exception_init'd to the same OER, they are indistinguishable.
Program units on the server reside in different namespaces. When setting a breakpoint, specify the desired namespace.
Namespace_cursor contains cursors (anonymous blocks).Namespace_pgkspec_or_toplevel contains:
Namespace_pkg_body contains package bodies and type bodies.Namespace_trigger contains triggers.These values are used to disambiguate among objects in a given namespace. These constants are used in PROGRAM_INFO when Probe is giving a stack backtrace.
LibunitType_cursorLibunitType_procedureLibunitType_functionLibunitType_packageLibunitType_package_bodyLibunitType_triggerLibunitType_UnknownThese are values to use for the breakflags parameter to CONTINUE, in order to tell Probe what events are of interest to the client. These flags may be combined.
These are flags which may be passed as the info_requested parameter to SYNCHRONIZE, CONTINUE, and GET_RUNTIME_INFO.
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Get the current depth of the stack. |
|
|
Get the breakpoint number. |
|
|
Get program unit information. |
After CONTINUE is run, the program either runs to completion or breaks on some line.
This procedure notifies the debug session about the target program.
DBMS_DEBUG.ATTACH_SESSION ( debug_session_id IN VARCHAR2, diagnostics IN BINARY_INTEGER := 0);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Debug ID from a call to |
|
|
Generate diagnostic output if nonzero. |
This function passes the given breakflags (a mask of the events that are of interest) to Probe in the target process. It tells Probe to continue execution of the target process, and it waits until the target process runs to completion or signals an event.
If info_requested is not NULL, then calls GET_RUNTIME_INFO.
DBMS_DEBUG.CONTINUE ( run_info IN OUT runtime_info, breakflags IN BINARY_INTEGER, info_requested IN BINARY_INTEGER := NULL) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Information about the state of the program. |
|
|
Mask of events that are of interest. See "Breakflags" . |
|
|
Which information should be returned in |
| Return | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Timed out before the program started running. |
|
|
Other communication error. |
|
Caution: There must be a debug session waiting if immediate is |
This procedure notifies the target session that debugging should no longer take place in that session. It is not necessary to call this function before ending the session.
DBMS_DEBUG.DEBUG_OFF;
The server does not handle this entrypoint specially. Therefore, it attempts to debug this entrypoint.
This procedure marks the target session so that all PL/SQL is run in debug mode. This must be done before any debugging can take place.
DBMS_DEBUG.DEBUG_ON ( no_client_side_plsql_engine BOOLEAN := TRUE, immediate BOOLEAN := FALSE);
This function deletes a breakpoint.
DBMS_DEBUG.DELETE_BREAKPOINT ( breakpoint IN BINARY_INTEGER) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Breakpoint number from a previous call to |
This function deletes an OER breakpoint.
DBMS_DEBUG.DELETE_OER_BREAKPOINT ( oer IN PLS_INTEGER) RETURN PLS_INTEGER;
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The OER (positive 4-byte number) to delete. |
This procedure stops debugging the target program. This procedure may be called at any time, but it does not notify the target session that the debug session is detaching itself, and it does not terminate execution of the target session. Therefore, care should be taken to ensure that the target session does not hang itself.
DBMS_DEBUG.DETACH_SESSION;
This function makes an existing breakpoint inactive but leaves it in place.
DBMS_DEBUG.DISABLE_BREAKPOINT ( breakpoint IN BINARY_INTEGER) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Breakpoint number from a previous call to |
| Returns | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
No such breakpoint exists. |
|
|
Cannot disable an unused breakpoint. |
This function is the reverse of disabling. This enables a previously disabled breakpoint.
DBMS_DEBUG.ENABLE_BREAKPOINT ( breakpoint IN BINARY_INTEGER) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Breakpoint number from a previous call to |
| Return | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Success. |
|
|
No such breakpoint exists. |
|
|
Cannot enable an unused breakpoint. |
This procedure executes SQL or PL/SQL code in the target session. The target session is assumed to be waiting at a breakpoint (or other event). The call to DBMS_DEBUG.EXECUTE occurs in the debug session, which then asks the target session to execute the code.
DBMS_DEBUG.EXECUTE ( what IN VARCHAR2, frame# IN BINARY_INTEGER, bind_results IN BINARY_INTEGER, results IN OUT NOCOPY dbms_debug_vc2coll, errm IN OUT NOCOPY VARCHAR2);
This example executes a SQL statement. It returns no results.
DECLARE
coll sys.dbms_debug_vc2coll; -- results (unused)
errm VARCHAR2(100);
BEGIN
dbms_debug.execute('insert into emp(ename,empno,deptno) ' ||
'values(''LJE'', 1, 1)',
-1, 0, coll, errm);
END;
This example executes a PL/SQL block, and it returns no results. The block is an autonomous transaction, which means that the value inserted into the table becomes visible in the debug session.
DECLARE
coll sys.dbms_debug_vc2coll;
errm VARCHAR2(100);
BEGIN
dbms_debug.execute(
'DECLARE PRAGMA autonomous_transaction; ' ||
'BEGIN ' ||
' insert into emp(ename, empno, deptno) ' ||
' values(''LJE'', 1, 1); ' ||
' COMMIT; ' ||
'END;',
-1, 0, coll, errm);
END;
This example executes a PL/SQL block, and it returns some results.
DECLARE
coll sys.dbms_debug_vc2coll;
errm VARCHAR2(100);
BEGIN
dbms_debug.execute(
'DECLARE ' ||
' pp SYS.dbms_debug_vc2coll := SYS.dbms_debug_vc2coll(); ' ||
' x PLS_INTEGER; ' ||
' i PLS_INTEGER := 1; ' ||
'BEGIN ' ||
' SELECT COUNT(*) INTO x FROM emp; ' ||
' pp.EXTEND(x * 6); ' ||
' FOR c IN (SELECT * FROM emp) LOOP ' ||
' pp(i) := ''Ename: '' || c.ename; i := i+1; ' ||
' pp(i) := ''Empno: '' || c.empno; i := i+1; ' ||
' pp(i) := ''Job: '' || c.job; i := i+1; ' ||
' pp(i) := ''Mgr: '' || c.mgr; i := i+1; ' ||
' pp(i) := ''Sal: '' || c.sal; i := i+1; ' ||
' pp(i) := null; i := i+1; ' ||
' END LOOP; ' ||
' :1 := pp;' ||
'END;',
-1, 1, coll, errm);
each := coll.FIRST;
WHILE (each IS NOT NULL) LOOP
dosomething(coll(each));
each := coll.NEXT(each);
END LOOP;
END;
Given a name of a variable or parameter, this function returns the set of its indexes, if it is an indexed table. An error is returned if it is not an indexed table.
DBMS_DEBUG.GET_INDEXES ( varname IN VARCHAR2, frame# IN BINARY_INTEGER, handle IN program_info, entries OUT index_table) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
| Return | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
- The package is not instantiated. - The user does not have privileges to debug the package. - The object does not exist in the package. |
When source does not fit in the buffer provided by that version of the SHOW_SOURCE Procedures which produce a formatted buffer, this procedure provides additional source.
DBMS_DEBUG.GET_MORE_SOURCE ( buffer IN OUT VARCHAR2, buflen IN BINARY_INTEGER, piece# IN BINARY_INTEGER);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The buffer. |
|
|
The length of the buffer. |
|
|
A value between 2 and the value returned in the parameter pieces from the call to the relevant version of the SHOW_SOURCE Procedures. |
This procedure should be called only after the version of SHOW_SOURCE that returns a formatted buffer.
This function finds line and entrypoint information about a program so that a debugger can determine the source lines at which it is possible to place breakpoints.
DBMS_DEBUG.GET_LINE_MAP ( program IN program_info, maxline OUT BINARY_INTEGER, number_of_entry_points OUT BINARY_INTEGER, linemap OUT RAW) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
| Return | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A successful completion. |
|
|
The program unit exists, but has no debug info. |
|
|
No such program unit exists. |
This function returns information about the current program. It is only needed if the info_requested parameter to SYNCHRONIZE or CONTINUE was set to 0.
DBMS_DEBUG.GET_RUNTIME_INFO ( info_requested IN BINARY_INTEGER, run_info OUT runtime_info) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Which information should be returned in |
|
|
Information about the state of the program. |
This procedure returns the current timeout behavior. This call is made in the target session.
DBMS_DEBUG.GET_TIMEOUT_BEHAVIOUR RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The OER (a 4-byte positive number). |
| Return | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A successful completion. |
info_getOerInfo CONSTANT PLS_INTEGER:= 32;
Less functionality is supported on OER breakpoints than on code breakpoints. In particular, note that:
delete_oer_breakpoint.This function gets a value from the currently-running program. There are two overloaded GET_VALUE functions.
DBMS_DEBUG.GET_VALUE ( variable_name IN VARCHAR2, frame# IN BINARY_INTEGER, scalar_value OUT VARCHAR2, format IN VARCHAR2 := NULL) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
This form of GET_VALUE is for fetching package variables. Instead of a frame#, it takes a handle, which describes the package containing the variable.
DBMS_DEBUG.GET_VALUE ( variable_name IN VARCHAR2, handle IN program_info, scalar_value OUT VARCHAR2, format IN VARCHAR2 := NULL) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
This example illustrates how to get the value with a given package PACK in schema SCOTT, containing variable VAR:
DECLARE
handle dbms_debug.program_info;
resultbuf VARCHAR2(500);
retval BINARY_INTEGER;
BEGIN
handle.Owner := 'SCOTT';
handle.Name := 'PACK';
handle.namespace := dbms_debug.namespace_pkgspec_or_toplevel;
retval := dbms_debug.get_value('VAR', handle, resultbuf, NULL);
END;
This function initializes the target session for debugging.
DBMS_DEBUG.INITIALIZE ( debug_session_id IN VARCHAR2 := NULL, diagnostics IN BINARY_INTEGER := 0) RETURN VARCHAR2;
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Name of session ID. If |
|
|
Indicates whether to dump diagnostic output to the tracefile. 1 = print diagnostics |
The newly-registered debug session ID (debugID)
You cannot use DBMS_DEBUG and the JDWP-based debugging interface simultaneously. This call will either fail with an ORA-30677 error if the session is currently being debugged with the JDWP-based debugging interface or, if the call succeeds, any further use of the JDWP-based interface to debug this session will be disallowed.
Calls to DBMS_DEBUG will succeed only if either the caller or the specified debug role carries the DEBUG CONNECT SESSION privilege. Failing that, an ORA-1031 error will be raised. Other exceptions are also possible if a debug role is specified but the password does not match, or if the calling user has not been granted the role, or the role is application-enabled and this call does not originate from within the role-enabling package.
The CREATE ANY PROCEDURE privilege does not affect the visibility of routines through the debugger. A privilege DEBUG for each object has been introduced with a corresponding DEBUG ANY PROCEDURE variant. These are required in order to see routines owned by users other than the session's login user.
Authentication of the debug role and the check for DEBUG CONNECT SESSION privilege will be done in the context of the caller to this routine. If the caller is a definer's rights routine or has been called from one, only privileges granted to the defining user, the debug role, or PUBLIC will be used to check for DEBUG CONNECT SESSION. If this call is from within a definer's rights routine, the debug role, if specified, must be one that has been granted to that definer, but it need not also have been granted to the session login user or be enabled in the calling session at the time the call is made.
The checks made by the debugger after this call is made looking for the DEBUG privilege on individual procedures will be done in the context of the session's login user, the roles that were enabled at session level at the moment this call was made (even if those roles were not available within a definer's rights environment of the call), and the debug role.
This procedure pings the target session to prevent it from timing out. Use this procedure when execution is suspended in the target session, for example at a breakpoint.
If the timeout_behaviour is set to retry_on_timeout then this procedure is not necessary.
DBMS_DEBUG.PING;
Oracle will display the no_target_program exception if there is no target program or if the target session is not currently waiting for input from the debug session.
Timeout options for the target session are registered with the target session by calling set_timeout_behaviour.
retry_on_timeout - Retry. Timeout has no effect. This is like setting the timeout to an infinitely large value.continue_on_timeout - Continue execution, using same event flags.nodebug_on_timeout - Turn debug-mode OFF (in other words, call debug_off) and then continue execution. No more events will be generated by this target session unless it is re-initialized by calling debug_on.abort_on_timeout - Continue execution, using the abort_execution flag, which should cause the program to terminate immediately. The session remains in debug-mode.retry_on_timeout CONSTANT BINARY_INTEGER:= 0;
continue_on_timeout CONSTANT BINARY_INTEGER:= 1;
nodebug_on_timeout CONSTANT BINARY_INTEGER:= 2;
abort_on_timeout CONSTANT BINARY_INTEGER:= 3;
This procedure prints a backtrace listing of the current execution stack. This should only be called if a program is currently running.
There are two overloaded PRINT_BACKTRACE procedures.
DBMS_DEBUG.PRINT_BACKTRACE ( listing IN OUT VARCHAR2); DBMS_DEBUG.PRINT_BACKTRACE ( backtrace OUT backtrace_table);
This procedure returns a list of the packages that have been instantiated in the current session.
DBMS_DEBUG.PRINT_INSTANTIATIONS ( pkgs IN OUT NOCOPY backtrace_table, flags IN BINARY_INTEGER);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The instantiated packages |
|
|
Bitmask of options: |
no_target_program - target session is not currently executing
On return, pkgs contains a program_info for each instantiation. The valid fields are: Namespace, Name, Owner, and LibunitType.
In addition, Line# contains a bitmask of:
This procedure returns the version number of DBMS_DEBUG on the server.
DBMS_DEBUG.PROBE_VERSION ( major out BINARY_INTEGER, minor out BINARY_INTEGER);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Major version number. |
|
|
Minor version number: increments as functionality is added. |
This procedure performs an internal consistency check. SELF_CHECK also runs a communications test to ensure that the Probe processes are able to communicate.
If SELF_CHECK does not return successfully, then an incorrect version of DBMS_DEBUG was probably installed on this server. The solution is to install the correct version (pbload.sql loads DBMS_DEBUG and the other relevant packages).
DBMS_DEBUG.SELF_CHECK ( timeout IN binary_integer := 60);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The timeout to use for the communication test. Default is 60 seconds. |
All of these exceptions are fatal. They indicate a serious problem with Probe that prevents it from working correctly.
This function sets a breakpoint in a program unit, which persists for the current session. Execution pauses if the target program reaches the breakpoint.
DBMS_DEBUG.SET_BREAKPOINT ( program IN program_info, line# IN BINARY_INTEGER, breakpoint# OUT BINARY_INTEGER, fuzzy IN BINARY_INTEGER := 0, iterations IN BINARY_INTEGER := 0) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
|
Note: The |
Return Values
| Return | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A successful completion. |
|
|
Cannot set a breakpoint at that line. |
|
|
No such program unit exists. |
This function sets an OER breakpoint.
DBMS_DEBUG.SET_OER_BREAKPOINT ( oer IN PLS_INTEGER) RETURN PLS_INTEGER;
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The OER (positive 4-byte number) to delete. |
| Return | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A successful completion. |
|
|
No such OER breakpoint exists. |
This function sets the timeout value and returns the new timeout value.
DBMS_DEBUG.SET_TIMEOUT ( timeout BINARY_INTEGER) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The timeout to use for communication between the target and debug sessions. |
This procedure tells Probe what to do with the target session when a timeout occurs. This call is made in the target session.
DBMS_DEBUG.SET_TIMEOUT_BEHAVIOUR ( behaviour IN PLS_INTEGER);
unimplemented - the requested behavior is not recognized
The default behavior (if this procedure is not called) is continue_on_timeout, since it allows a debugger client to reestablish control (at the next event) but does not cause the target session to hang indefinitely.
This function sets a value in the currently-running program. There are two overloaded SET_VALUE functions.
DBMS_DEBUG.SET_VALUE ( frame# IN binary_integer, assignment_statement IN varchar2) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER; DBMS_DEBUG.SET_VALUE ( handle IN program_info, assignment_statement IN VARCHAR2) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
In some cases, the PL/SQL compiler uses temporaries to access package variables, and does not guarantee to update such temporaries. It is possible, although unlikely, that modification to a package variable using SET_VALUE might not take effect for a line or two.
To set the value of SCOTT.PACK.var to 6:
DECLARE handle dbms_debug.program_info; retval BINARY_INTEGER; BEGIN handle.Owner := 'SCOTT'; handle.Name := 'PACK'; handle.namespace := dbms_debug.namespace_pkgspec_or_toplevel; retval := dbms_debug.set_value(handle, 'var := 6;'); END;
There are two overloaded procedures that return a listing of the current breakpoints. There are three overloaded SHOW_BREAKPOINTS procedures.
DBMS_DEBUG.SHOW_BREAKPOINTS ( listing IN OUT VARCHAR2); DBMS_DEBUG.SHOW_BREAKPOINTS ( listing OUT breakpoint_table); DBMS_DEBUG.SHOW_BREAKPOINTS ( code_breakpoints OUT breakpoint_table, oer_breakpoints OUT oer_table);
The procedure gets the source code. There are two overloaded SHOW_SOURCE procedures.
DBMS_DEBUG.SHOW_FRAME_SOURCE ( first_line IN BINARY_INTEGER, last_line IN BINARY_INTEGER, source IN OUT NOCOPY vc2_table, frame_num IN BINARY_INTEGER);
SHOW_SOURCE can also be used.The procedure gets the source code. There are two overloaded SHOW_SOURCE procedures.
DBMS_DEBUG.SHOW_SOURCE ( first_line IN BINARY_INTEGER, last_line IN BINARY_INTEGER, source OUT vc2_table); DBMS_DEBUG.SHOW_SOURCE ( first_line IN BINARY_INTEGER, last_line IN BINARY_INTEGER, window IN BINARY_INTEGER, print_arrow IN BINARY_INTEGER, buffer IN OUT VARCHAR2, buflen IN BINARY_INTEGER, pieces OUT BINARY_INTEGER);
An indexed table of source-lines. The source lines are stored starting at first_line. If any error occurs, then the table is empty.
The best way to get the source code (for a program that is being run) is to use SQL. For example:
DECLARE
info DBMS_DEBUG.runtime_info;
BEGIN
-- call DBMS_DEBUG.SYNCHRONIZE, CONTINUE,
-- or GET_RUNTIME_INFO to fill in 'info'
SELECT text INTO <buffer> FROM all_source
WHERE owner = info.Program.Owner
AND name = info.Program.Name
AND line = info.Line#;
END;
However, this does not work for nonpersistent programs (for example, anonymous blocks and trigger invocation blocks). For nonpersistent programs, call SHOW_SOURCE. There are two flavors: one returns an indexed table of source lines, and the other returns a packed (and formatted) buffer.
The second overloading of SHOW_SOURCE returns the source in a formatted buffer, complete with line-numbers. It is faster than the indexed table version, but it does not guarantee to fetch all the source.
If the source does not fit in bufferlength (buflen), then additional pieces can be retrieved using the GET_MORE_SOURCE procedure (pieces returns the number of additional pieces that need to be retrieved).
This function waits until the target program signals an event. If info_requested is not NULL, then it calls GET_RUNTIME_INFO.
DBMS_DEBUG.SYNCHRONIZE ( run_info OUT runtime_info, info_requested IN BINARY_INTEGER := NULL) RETURN BINARY_INTEGER;
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Structure in which to write information about the program. By default, this includes information about what program is running and at which line execution has paused. |
|
|
Optional bit-field in which to request information other than the default (which is See "Information Flags". |
| Return | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A successful completion. |
|
|
Timed out before the program started execution. |
|
|
Other communication error. |
This procedure returns TRUE if the target session is currently executing a stored procedure, or FALSE if it is not.
DBMS_DEBUG.TARGET_PROGRAM_RUNNING RETURN BOOLEAN;