| PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10802-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10802-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
The UTL_HTTP package makes Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) callouts from SQL and PL/SQL. You can use it to access data on the Internet over HTTP.
When the package fetches data from a Web site using HTTPS, it requires Oracle Wallet Manager to set up an Oracle wallet. Non-HTTPS fetches do not require an Oracle wallet.
See Also:
|
This chapter contains the following topics:
With UTL_HTTP, you can write PL/SQL programs that communicate with Web (HTTP) servers. UTL_HTTP also contains a function that can be used in SQL queries. The package also supports HTTP over the Secured Socket Layer protocol (SSL), also known as HTTPS, directly or through an HTTP proxy. Other Internet-related data-access protocols (such as the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) or the Gopher protocol) are also supported using an HTTP proxy server that supports those protocols.
Use this PL/SQL record type to represent an HTTP request.
TYPE req IS RECORD ( url VARCHAR2(32767), method VARCHAR2(64), http_version VARCHAR2(64));
The information returned in REQ from the interface begin_request is for read only. Changing the field values in the record has no effect on the request.
There are other fields in REQ record type whose names begin with the prefix private_. The fields are private and are intended for use by implementation of the UTL_HTTP package. You should not modify the fields.
This PL/SQL record type is used to represent an HTTP response.
TYPE resp IS RECORD ( status_code PLS_INTEGER, reason_phrase VARCHAR2(256), http_version VARCHAR2(64));
The information returned in RESP from the interface get_response is read-only. There are other fields in the RESP record type whose names begin with the prefix private_. The fields are private and are intended for use by implementation of the UTL_HTTP package. You should not modify the fields.
The COOKIE type is the PL/SQL record type that represents an HTTP cookie. The COOKIE_TABLE type is a PL/SQL index-by-table type that represents a collection of HTTP cookies.
TYPE cookie IS RECORD ( name VARCHAR2(256), value VARCHAR2(1024), domain VARCHAR2(256), expire TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, path VARCHAR2(1024), secure BOOLEAN, version PLS_INTEGER, comment VARCHAR2(1024)); TYPE cookie_table IS TABLE OF cookie INDEX BY binary_integer;
Table 156-5 shows the fields for the COOKIE and COOKIE_TABLE record types.
PL/SQL programs do not usually examine or change the cookie information stored in the UTL_HTTP package. The cookies are maintained by the package transparently. They are maintained inside the UTL_HTTP package, and they last for the duration of the database session only. PL/SQL applications that require cookies to be maintained beyond the lifetime of a database session can read the cookies using get_cookies, store them persistently in a database table, and re-store the cookies back in the package using add_cookies in the next database session. All the fields in the cookie record, except for the comment field, must be stored. Do not alter the cookie information, which can result in an application error in the Web server or compromise the security of the PL/SQL and the Web server applications. See "Retrieving and Restoring Cookies".
Use the PL/SQL record type to represent the remote hosts and TCP/IP ports of a network connection that is kept persistent after an HTTP request is completed, according to the HTTP 1.1 protocol specification. The persistent network connection may be reused by a subsequent HTTP request to the same host and port. The subsequent HTTP request may be completed faster because the network connection latency is avoided. connection_table is a PL/SQL table of connection.
For a direct HTTP persistent connection to a Web server, the host and port fields contain the host name and TCP/IP port number of the Web server. The proxy_host and proxy_port fields are not set. For an HTTP persistent connection that was previously used to connect to a Web server using a proxy, the proxy_host and proxy_port fields contain the host name and TCP/IP port number of the proxy server. The host and port fields are not set, which indicates that the persistent connection, while connected to a proxy server, is not bound to any particular target Web server. An HTTP persistent connection to a proxy server can be used to access any target Web server that is using a proxy.
The ssl field indicates if Secured Socket Layer (SSL) is being used in an HTTP persistent connection. An HTTPS request is an HTTP request made over SSL. For an HTTPS (SSL) persistent connection connected using a proxy, the host and port fields contain the host name and TCP/IP port number of the target HTTPS Web server and the fields will always be set. An HTTPS persistent connection to an HTTPS Web server using a proxy server can only be reused to make another request to the same target Web server.
TYPE connection IS RECORD ( host VARCHAR2(256), port PLS_INTEGER, proxy_host VARCHAR2(256), proxy_port PLS_INTEGER, ssl BOOLEAN); TYPE connection_table IS TABLE OF connection INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
The UTL_HTTP package provides access to the HTTP protocol. The interfaces must be called in the order shown in Figure 156-1, or an exception will be raised.
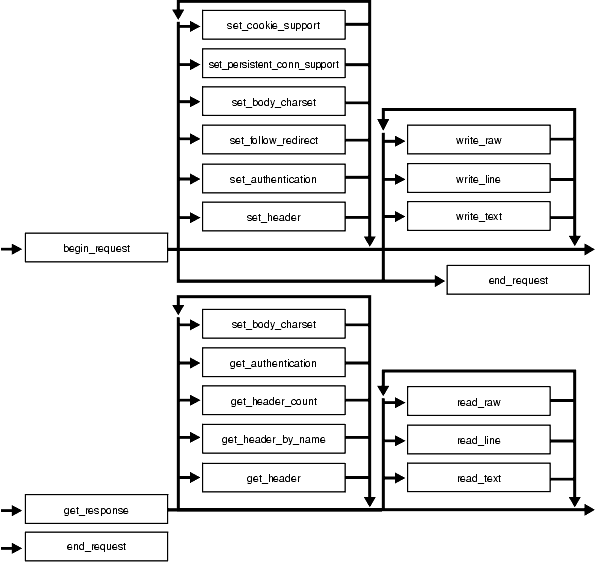
Text description of the illustration arpls006.gif
The following can be called at any time:
UTL_HTTP package in the current session
UTL_HTTP package in the current session
REQUEST and REQUEST_PIECES take a string uniform resource locator (URL), contact that site, and return the data (typically HTML) obtained from that site.
You should not expect REQUEST or REQUEST_PIECES to succeed in contacting a URL unless you can contact that URL by using a browser on the same machine (and with the same privileges, environment variables, and so on.)
If REQUEST or REQUEST_PIECES fails (for example, if it raises an exception, or if it returns an HTML-formatted error message, but you believe that the URL argument is correct), then try contacting that same URL with a browser to verify network availability from your machine. You may have a proxy server set in your browser that needs to be set with each REQUEST or REQUEST_PIECES call using the optional proxy parameter.
Session settings manipulate the configuration and default behavior of UTL_HTTP when HTTP requests are executed within a database user session. When a request is created, it inherits the default settings of the HTTP cookie support, follow-redirect, body character set, persistent-connection support, and transfer timeout of the current session. Those settings can be changed later by calling the request interface. When a response is created for a request, it inherits those settings from the request. Only the body character set can be changed later by calling the response interface.
The HTTP Requests group of subprograms begin an HTTP request, manipulate attributes, and send the request information to the Web server. When a request is created, it inherits the default settings of the HTTP cookie support, follow-redirect, body character set, persistent-connection support, and transfer timeout of the current session. The settings can be changed by calling the request interface.
The HTTP Responses group of subprograms manipulate an HTTP response obtained from GET_RESPONSE and receive response information from the Web server. When a response is created for a request, it inherits settings of the HTTP cookie support, follow-redirect, body character set, persistent-connection support, and transfer timeout from the request. Only the body character set can be changed by calling the response interface.
The UTL_HTTP package provides subprograms to manipulate HTTP cookies.
The UTL_HTTP package provides subprograms to manipulate persistent connections.
The UTL_HTTP package provides subprograms to retrieve error information.
Table 156-6 lists the exceptions that the UTL_HTTP package interface can raise. By default, UTL_HTTP raises the exception request_failed when a request fails to execute. If the package is set to raise a detailed exception by set_detailed_excp_support, the rest of the exceptions will be raised directly (except for the exception end_of_body, which will be raised by read_text, read_line, and read_raw regardless of the setting).
For REQUEST and REQUEST_PIECES, the request_failed exception is raised when any exception occurs and detailed_exception is disabled.
The following examples demonstrate how to use UTL_HTTP.
SET serveroutput ON SIZE 40000 DECLARE req utl_http.req; resp utl_http.resp; value VARCHAR2(1024); BEGIN utl_http.set_proxy('proxy.my-company.com', 'corp.my-company.com'); req := utl_http.begin_request('http://www-hr.corp.my-company.com'); utl_http.set_header(req, 'User-Agent', 'Mozilla/4.0'); resp := utl_http.get_response(req); LOOP utl_http.read_line(resp, value, TRUE); dbms_output.put_line(value); END LOOP; utl_http.end_response(resp); EXCEPTION WHEN utl_http.end_of_body THEN utl_http.end_response(resp); END;
SET serveroutput ON SIZE 40000 DECLARE req utl_http.req; resp utl_http.resp; name VARCHAR2(256); value VARCHAR2(1024); BEGIN utl_http.set_proxy('proxy.my-company.com', 'corp.my-company.com'); req := utl_http.begin_request('http://www-hr.corp.my-company.com'); utl_http.set_header(req, 'User-Agent', 'Mozilla/4.0'); resp := utl_http.get_response(req); dbms_output.put_line('HTTP response status code: ' || resp.status_code); dbms_output.put_line('HTTP response reason phrase: ' || resp.reason_phrase); FOR i IN 1..utl_http.get_header_count(resp) LOOP utl_http.get_header(resp, i, name, value); dbms_output.put_line(name || ': ' || value); END LOOP; utl_http.end_response(resp); END;
SET serveroutput ON SIZE 40000 CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE get_page (url IN VARCHAR2, username IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, password IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, realm IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL) AS req utl_http.req; resp utl_http.resp; my_scheme VARCHAR2(256); my_realm VARCHAR2(256); my_proxy BOOLEAN; BEGIN -- Turn off checking of status code. We will check it by ourselves. utl_http.http_response_error_check(FALSE); req := utl_http.begin_request(url); IF (username IS NOT NULL) THEN utl_http.set_authentication(req, username, password); -- Use HTTP Basic Authen. Scheme END IF; resp := utl_http.get_response(req); IF (resp.status_code = utl_http.HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED) THEN utl_http.get_authentication(resp, my_scheme, my_realm, my_proxy); IF (my_proxy) THEN dbms_output.put_line('Web proxy server is protected.'); dbms_output.put('Please supplied the required ' || my_scheme || ' authentication username/password for realm ' || my_realm || ' for the proxy server.'); ELSE dbms_output.put_line('Web page ' || url || ' is protected.'); dbms_output.put('Please supplied the required ' || my_scheme || ' authentication username/password for realm ' || my_realm || ' for the Web page.'); END IF; utl_http.end_response(resp); RETURN; END IF; FOR i IN 1..utl_http.get_header_count(resp) LOOP utl_http.get_header(resp, i, name, value); dbms_output.put_line(name || ': ' || value); END LOOP; utl_http.end_response(resp); END;
CREATE TABLE my_cookies ( session_id INTEGER, name VARCHAR2(256), value VARCHAR2(1024), domain VARCHAR2(256), expire DATE, path VARCHAR2(1024), secure VARCHAR2(1), version INTEGER ); CREATE SEQUENCE session_id; SET serveroutput ON SIZE 40000 REM Retrieve cookies from UTL_HTTP CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION save_cookies RETURN PLS_INTEGER AS cookies utl_http.cookie_table; my_session_id PLS_INTEGER; secure VARCHAR2(1); BEGIN /* assume that some cookies have been set in previous HTTP requests. */ utl_http.get_cookies(cookies); select session_id.nextval into my_session_id from dual; FOR i in 1..cookies.count LOOP IF (cookies(i).secure) THEN secure := 'Y'; ELSE secure := 'N'; END IF; insert into my_cookies values (my_session_id, cookies(i).name, cookies(i).value, cookies(i).domain, cookies(i).expire, cookies(i).path, secure, cookies(i).version); END LOOP; RETURN my_session_id; END; / REM Retrieve cookies from UTL_HTTP CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE restore_cookies (this_session_id IN PLS_INTEGER) AS cookies utl_http.cookie_table; cookie utl_http.cookie; i PLS_INTEGER := 0; CURSOR c (c_session_id PLS_INTEGER) IS SELECT * FROM my_cookies WHERE session_id = c_session_id; BEGIN FOR r IN c(this_session_id) LOOP i := i + 1; cookie.name := r.name; cookie.value := r.value; cookie.domain := r.domain; cookie.expire := r.expire; cookie.path := r.path; IF (r.secure = 'Y') THEN cookie.secure := TRUE; ELSE cookie.secure := FALSE; END IF; cookie.version := r.version; cookies(i) := cookie; END LOOP; utl_http.clear_cookies; utl_http.add_cookies(cookies); END; /
| Subprogram | Description |
|---|---|
|
Begins a new HTTP request. | |
|
Ends the HTTP request. | |
|
Sets an HTTP request header. The request header is sent to the Web server as soon as it is set. | |
|
Sets HTTP authentication information in the HTTP request header. The Web server needs this information to authorize the request. | |
|
Sets the character set of the request body when the media type is | |
|
Enables or disables support for the HTTP cookies in the request. | |
|
Sets the maximum number of times | |
|
Enables or disables support for the HTTP 1.1 persistent-connection in the request. | |
|
Writes a text line in the HTTP request body and ends the line with new-line characters (CRLF as defined in | |
|
Writes some binary data in the HTTP request body. | |
|
Writes some text data in the HTTP request body. |
| Subprogram | Description |
|---|---|
|
Retrieves the detailed SQLCODE of the last exception raised. | |
|
Retrieves the detailed SQLERRM of the last exception raised. |
| Subprogram | Description |
|---|---|
|
Adds the cookies maintained by | |
|
Begins a new HTTP request. | |
|
Clears all cookies maintained by the UTL_HTTP package (see HTTP Cookies and HTTP Cookies Subprograms) | |
|
Closes an HTTP persistent connection maintained by the UTL_HTTP package in the current database session (see HTTP Persistent Connections and HTTP Persistent Connections Subprograms) | |
|
Closes a group of HTTP persistent connections maintained by the UTL_HTTP package in the current database session (see HTTP Persistent Connections and HTTP Persistent Connections Subprograms) | |
|
Ends the HTTP request (see HTTP Requests and HTTP Requests Subprograms) | |
|
Ends the HTTP response. It completes the HTTP request and response (see HTTP Responses and HTTP Responses Subprograms) | |
|
Retrieves the HTTP authentication information needed for the request to be accepted by the Web server as indicated in the HTTP response header (see HTTP Responses and HTTP Responses Subprograms) | |
|
Retrieves the default character set of the body of all future HTTP requests (see Session Settings and Session Settings Subprograms) | |
|
Returns the number of cookies currently maintained by the UTL_HTTP package set by all Web servers (see HTTP Cookies and HTTP Cookies Subprograms) | |
|
Retrieves the current cookie support settings (see Session Settings and Session Settings Subprograms) | |
|
Returns all the cookies currently maintained by the UTL_HTTP package set by all Web servers (see HTTP Cookies and HTTP Cookies Subprograms) | |
|
Checks if the | |
|
Retrieves the detailed SQLCODE of the last exception raised (see Error Conditions and Error Conditions Subprograms) | |
|
Retrieves the detailed SQLERRM of the last exception raised (see Error Conditions and Error Conditions Subprograms) | |
|
Retrieves the follow-redirect setting in the current session (see Session Settings and Session Settings Subprograms) | |
|
Returns the nth HTTP response header name and value returned in the response (see HTTP Responses and HTTP Responses Subprograms) | |
|
Returns the HTTP response header value returned in the response given the name of the header (see HTTP Responses and HTTP Responses Subprograms) | |
|
Returns the number of HTTP response headers returned in the response (see HTTP Responses and HTTP Responses Subprograms) | |
|
Returns the number of network connections currently kept persistent by the UTL_HTTP package to the Web servers (see HTTP Persistent Connections and HTTP Persistent Connections Subprograms) | |
|
Sees whether or not future HTTP requests will support the HTTP 1.1 persistent connection; sets the maximum number of persistent connections maintained in the current database user session (see Session Settings and Session Settings Subprograms) | |
|
Checks if the persistent connection support is enabled and gets the maximum number of persistent connections in the current session (see Session Settings and Session Settings Subprograms) | |
|
Returns all the network connections currently kept persistent by the UTL_HTTP package to the Web servers (see HTTP Persistent Connections and HTTP Persistent Connections Subprograms) | |
|
Retrieves the current proxy settings (see Session Settings and Session Settings Subprograms) | |
|
Reads the HTTP response. When the function returns, the status line and the HTTP response headers have been read and processed (see HTTP Responses and HTTP Responses Subprograms) | |
|
Checks if the response error check is set or no (see Session Settings and Session Settings Subprograms)t | |
|
Retrieves the current network transfer timeout value (see Session Settings and Session Settings Subprograms) | |
|
Reads the HTTP response body in text form until the end of line is reached and returns the output in the caller-supplied buffer (see HTTP Responses and HTTP Responses Subprograms) | |
|
Reads the HTTP response body in binary form and returns the output in the caller-supplied buffer (see HTTP Responses and HTTP Responses Subprograms) | |
|
Reads the HTTP response body in text form and returns the output in the caller-supplied buffer (see HTTP Responses and HTTP Responses Subprograms) | |
|
Returns up to the first 2000 bytes of the data retrieved from the given URL. This function can be used directly in SQL queries (see Simple HTTP Fetches and Simple HTTP Fetches in a Single Call Subprograms) | |
|
Returns a PL/SQL table of 2000-byte pieces of the data retrieved from the given URL (see Simple HTTP Fetches and Simple HTTP Fetches in a Single Call Subprograms) | |
|
Sets HTTP authentication information in the HTTP request header. The Web server needs this information to authorize the request (see HTTP Requests and HTTP Requests Subprograms) | |
|
Sets the default character set of the body of all future HTTP requests when the media type is | |
|
Sets the character set of the request body when the media type is | |
|
Sets the character set of the response body when the media type is "text" but the character set is not specified in the "Content-Type" header (see HTTP Responses, HTTP Responses Subprograms, Session Settings and Session Settings Subprograms) | |
|
Enables or disables support for the HTTP cookies in the request (see HTTP Requests and HTTP Requests Subprograms) | |
|
Sets whether or not future HTTP requests will support HTTP cookies; sets the maximum number of cookies maintained in the current database user session (see Session Settings and Session Settings Subprograms) | |
|
Sets the | |
|
Sets the maximum number of times | |
|
Sets the maximum number of times | |
|
Sets an HTTP request header. The request header is sent to the Web server as soon as it is set (see HTTP Requests and HTTP Requests Subprograms) | |
|
Enables or disables support for the HTTP 1.1 persistent-connection in the request (see HTTP Requests and HTTP Requests Subprograms) | |
|
Sets the proxy to be used for requests of HTTP or other protocols (see Session Settings and Session Settings Subprograms) | |
|
Sets whether or not | |
|
Sets the timeout value for | |
|
Sets the Oracle Wallet used for all HTTP requests over Secured Socket Layer (SSL), that is, HTTPS (see Session Settings and Session Settings Subprograms) | |
|
Writes a text line in the HTTP request body and ends the line with new-line characters (CRLF as defined in UTL_TCP) (see HTTP Requests and HTTP Requests Subprograms) | |
|
Writes some binary data in the HTTP request body (see HTTP Requests and HTTP Requests Subprograms) | |
|
Writes some text data in the HTTP request body (see HTTP Requests and HTTP Requests Subprograms) |
This procedure adds the cookies maintained by UTL_HTTP.
UTL_HTTP.ADD_COOKIES ( cookies IN cookie_table);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The cookies to be added. |
The cookies that the package currently maintains are not cleared before new cookies are added.
This functions begins a new HTTP request. UTL_HTTP establishes the network connection to the target Web server or the proxy server and sends the HTTP request line. The PL/SQL program continues the request by calling some other interface to complete the request. The URL may contain the username and password needed to authenticate the request to the server. The format is
scheme://[user[:password]@]host[:port]/[...]
UTL_HTTP.BEGIN_REQUEST ( url IN VARCHAR2, method IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT 'GET', http_version IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL) RETURN req;
The URL passed as an argument to this function is not examined for illegal characters, such as spaces, according to URL specification RFC 2396. You should escape those characters with the UTL_URL package to return illegal and reserved characters. URLs should consist of US-ASCII characters only. See Chapter 166, "UTL_URL" for a list of legal characters in URLs. Note that URLs should consist of US-ASCII characters only. The use of non-US-ASCII characters in a URL is generally unsafe.
An Oracle wallet must be set before accessing Web servers over HTTPS. See the set_wallet procedure on how to set up an Oracle wallet.
This procedure clears all cookies maintained by the UTL_HTTP package.
UTL_HTTP.CLEAR_COOKIES;
This procedure closes an HTTP persistent connection maintained by the UTL_HTTP package in the current database session.
UTL_HTTP.CLOSE_PERSISTENT_CONN ( conn IN connection);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The HTTP persistent connection to close |
This procedure closes a group of HTTP persistent connections maintained by the UTL_HTTP package in the current database session. This procedure uses a pattern-match approach to decide which persistent connections to close.
To close a group of HTTP persistent connection that share a common property (for example, all connections to a particular host, or all SSL connections), set the particular parameters and leave the rest of the parameters NULL. If a particular parameter is set to NULL when this procedure is called, that parameter will not be used to decide which connections to close.
For example, the following call to the procedure closes all persistent connections to foobar:
UTL_HTTP.CLOSE_PERSISTENT_CONNS(host => 'foobar');
And the following call to the procedure closes all persistent connections through the proxy www-proxy at TCP/IP port 80:
UTL_HTTP.CLOSE_PERSISTENT_CONNS(proxy_host => 'foobar', proxy_port => 80);
And the following call to the procedure closes all persistent connections:
UTL_HTTP.CLOSE_PERSISTENT_CONNS;
UTL_HTTP.CLOSE_PERSISTENT_CONNS ( host IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, port IN PLS_INTEGER DEFAULT NULL, proxy_host IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, proxy_port IN PLS_INTEGER DEFAULT NULL, ssl IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT NULL);
Connections to the same Web server at different TCP/IP ports are counted individually. The host names of the Web servers are identified as specified in the URL of the original HTTP requests. Therefore, fully qualified host names with domain names will be counted differently from the host names without domain names.
Note that the use of a NULL value in a parameter when this procedure is called means that the caller does not care about its value when the package decides which persistent connection to close. If you want a NULL value in a parameter to match only a NULL value of the parameter of a persistent connection (which is when you want to close a specific persistent connection), you should use the close_persistent_conn procedure that closes a specific persistent connection.
This procedure ends the HTTP request. To terminate the HTTP request without completing the request and waiting for the response, the program can call this procedure. Otherwise, the program should go through the normal sequence of beginning a request, getting the response, and closing the response. The network connection will always be closed and will not be reused.
UTL_HTTP.END_REQUEST ( r IN OUT NOCOPY req);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The HTTP request |
This procedure ends the HTTP response. It completes the HTTP request and response. Unless HTTP 1.1 persistent connection is used in this request, the network connection is also closed.
UTL_HTTP.END_RESPONSE ( r IN OUT NOCOPY resp);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The HTTP response. |
This procedure retrieves the HTTP authentication information needed for the request to be accepted by the Web server as indicated in the HTTP response header.
UTL_HTTP.GET_AUTHENTICATION( r IN OUT NOCOPY resp, scheme OUT VARCHAR2, realm OUT VARCHAR2, for_proxy IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE);
When a Web client is unaware that a document is protected, at least two HTTP requests are required for the document to be retrieved. In the first HTTP request, the Web client makes the request without supplying required authentication information; so the request is denied. The Web client can determine the authentication information required for the request to be authorized by calling get_authentication. The Web client makes the second request and supplies the required authentication information with set_authorization. If the authentication information can be verified by the Web server, the request will succeed and the requested document is returned. Before making the request, if the Web client knows that authentication information is required, it can supply the required authentication information in the first request, thus saving an extra request.
This procedure retrieves the default character set of the body of all future HTTP requests.
UTL_HTTP.GET_BODY_CHARSET ( charset OUT NOCOPY VARCHAR2);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The default character set of the body of all future HTTP requests |
This function returns the number of cookies currently maintained by the UTL_HTTP package set by all Web servers.
UTL_HTTP.GET_COOKIE_COUNT RETURN PLS_INTEGER;
This procedure retrieves the current cookie support settings.
UTL_HTTP.GET_COOKIE_SUPPORT ( enable OUT BOOLEAN, max_cookies OUT PLS_INTEGER, max_cookies_per_site OUT PLS_INTEGER);
This function returns all the cookies currently maintained by the UTL_HTTP package set by all Web servers.
UTL_HTTP.GET_COOKIES ( cookies IN OUT NOCOPY cookie_table);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The cookies returned |
This procedure checks if the UTL_HTTP package will raise a detailed exception or not.
UTL_HTTP.GET_DETAILED_EXCP_SUPPORT ( enable OUT BOOLEAN);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
This function retrieves the detailed SQLCODE of the last exception raised.
UTL_HTTP.GET_DETAILED_SQLCODE RETURN PLS_INTEGER;
This function retrieves the detailed SQLERRM of the last exception raised.
UTL_HTTP.GET_DETAILED_SQLERRM RETURN VARCHAR2;
This procedure retrieves the follow-redirect setting in the current session
.UTL_HTTP.GET_FOLLOW_REDIRECT ( max_redirects OUT PLS_INTEGER);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The maximum number of redirections for all future HTTP requests. |
This procedure returns the nth HTTP response header name and value returned in the response.
UTL_HTTP.GET_HEADER ( r IN OUT NOCOPY resp, n IN PLS_INTEGER, name OUT NOCOPY VARCHAR2, value OUT NOCOPY VARCHAR2);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The HTTP response. |
|
|
The nth header to return. |
|
|
The name of the HTTP response header. |
|
|
The value of the HTTP response header. |
If the response body returned by the remote Web server is encoded in chunked transfer encoding format, the trailer headers that are returned at the end of the response body will be added to the response, and the response header count will be updated. You can retrieve the additional headers after the end of the response body is reached and before you end the response.
This procedure returns the HTTP response header value returned in the response given the name of the header.
UTL_HTTP.GET_HEADER_BY_NAME( r IN OUT NOCOPY resp, name IN VARCHAR2, value OUT NOCOPY VARCHAR2, n IN PLS_INTEGER DEFAULT 1);
If the response body returned by the remote Web server is encoded in chunked transfer encoding format, the trailer headers that are returned at the end of the response body will be added to the response, and the response header count will be updated. You can retrieve the additional headers after the end of the response body is reached and before you end the response.
This function returns the number of HTTP response headers returned in the response.
UTL_HTTP.GET_HEADER_COUNT ( r IN OUT NOCOPY resp) RETURN PLS_INTEGER;
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The HTTP response |
If the response body returned by the remote Web server is encoded in chunked transfer encoding format, the trailer headers that are returned at the end of the response body will be added to the response, and the response header count will be updated. You can retrieve the additional headers after the end of the response body is reached and before you end the response.
This function returns the number of network connections currently kept persistent by the UTL_HTTP package to the Web servers.
UTL_HTTP.GET_PERSISTENT_CONN_COUNT RETURN PLS_INTEGER;
Connections to the same Web server at different TCP/IP ports are counted individually. The host names of the Web servers are identified as specified in the URL of the original HTTP requests. Therefore, fully qualified host names with domain names will be counted differently from the host names without domain names.
This procedure checks:
UTL_HTTP.GET_PERSISTENT_CONN_SUPPORT ( enable OUT BOOLEAN, max_conns OUT PLS_INTEGER);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
the maximum number of persistent connections maintained in the current session. |
This procedure returns all the network connections currently kept persistent by the UTL_HTTP package to the Web servers.
UTL_HTTP.get_persistent_conns ( connections IN OUT NOCOPY connection_table);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The network connections kept persistent |
Connections to the same Web server at different TCP/IP ports are counted individually. The host names of the Web servers are identified as specified in the URL of the original HTTP requests. Therefore, fully qualified host names with domain names will be counted differently from the host names without domain names.
This procedure retrieves the current proxy settings.
UTL_HTTP.GET_PROXY ( proxy OUT NOCOPY VARCHAR2, no_proxy_domains OUT NOCOPY VARCHAR2);
This function reads the HTTP response. When the function returns, the status line and the HTTP response headers have been read and processed. The status code, reason phrase, and the HTTP protocol version are stored in the response record. This function completes the HTTP headers section.
UTL_HTTP.GET_RESPONSE ( r IN OUT NOCOPY req) RETURN resp;
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The HTTP response |
This procedure checks if the response error check is set or not.
UTL_HTTP.GET_RESPONSE_ERROR_CHECK ( enable OUT BOOLEAN);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
UTL_HTTP.GET_TRANSFER_TIMEOUT ( timeout OUT PLS_INTEGER);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The network transfer timeout value in seconds. |
This procedure reads the HTTP response body in text form until the end of line is reached and returns the output in the caller-supplied buffer. The end of line is as defined in the function read_line of UTL_TCP. The end_of_body exception will be raised if the end of the HTTP response body is reached. Text data is automatically converted from the response body character set to the database character set.
UTL_HTTP.READ_LINE( r IN OUT NOCOPY resp, data OUT NOCOPY VARCHAR2 CHARACTER SET ANY_CS, remove_crlf IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The HTTP response. |
|
|
The HTTP response body in text form |
|
|
Removes the newline characters if set to |
The UTL_HTTP package supports HTTP 1.1 chunked transfer-encoding. When the response body is returned in chunked transfer-encoding format as indicated in the response header, the package automatically decodes the chunks and returns the response body in de-chunked format.
If transfer timeout is set in the request of this response, read_line waits for each data packet to be ready to read until timeout occurs. If it occurs, this procedure stops reading and returns all the data read successfully. If no data is read successfully, the transfer_timeout exception is raised. The exception can be handled and the read operation can be retried later.
If a partial multibyte character is found at the end of the response body, read_line stops reading and returns all the complete multibyte characters read successfully. If no complete character is read successfully, the partial_multibyte_char exception is raised. The exception can be handled and the bytes of that partial multibyte character can be read as binary by the read_raw procedure. If a partial multibyte character is seen in the middle of the response body because the remaining bytes of the character have not arrived and read timeout occurs, the transfer_timeout exception is raised instead. The exception can be handled and the read operation can be retried later.
When the "Content-Type" response header specifies the character set of the response body and the character set is unknown or unsupported by Oracle, the "ORA-01482: unsupported character set" exception is raised if you try to read the response body as text. You can either read the response body as binary using the READ_RAW procedure, or set the character set of the response body explicitly using the SET_BODY_CHARSET procedure and read the response body as text again.
This procedure reads the HTTP response body in binary form and returns the output in the caller-supplied buffer. The end_of_body exception will be raised if the end of the HTTP response body is reached.
UTL_HTTP.READ_RAW( r IN OUT NOCOPY resp, data OUT NOCOPY RAW, len IN PLS_INTEGER DEFAULT NULL);
The UTL_HTTP package supports HTTP 1.1 chunked transfer-encoding. When the response body is returned in chunked transfer-encoding format as indicated in the response header, the package automatically decodes the chunks and returns the response body in de-chunked format.
If transfer timeout is set in the request of this response, read_raw waits for each data packet to be ready to read until timeout occurs. If it occurs, read_raw stops reading and returns all the data read successfully. If no data is read successfully, the transfer_timeout exception is raised. The exception can be handled and the read operation can be retried later.
This procedure reads the HTTP response body in text form and returns the output in the caller-supplied buffer. The end_of_body exception will be raised if the end of the HTTP response body is reached. Text data is automatically converted from the response body character set to the database character set.
UTL_HTTP.READ_TEXT( r IN OUT NOCOPY resp, data OUT NOCOPY VARCHAR2 CHARACTER SET ANY_CS, len IN PLS_INTEGER DEFAULT NULL);
The UTL_HTTP package supports HTTP 1.1 chunked transfer-encoding. When the response body is returned in chunked transfer-encoding format as indicated in the response header, the package automatically decodes the chunks and returns the response body in de-chunked format.
If transfer timeout is set in the request of this response, read_text waits for each data packet to be ready to read until timeout occurs. If it occurs, this procedure stops reading and returns all the data read successfully. If no data is read successfully, the transfer_timeout exception is raised. The exception can be handled and the read operation can be retried later.
If a partial multibyte character is found at the end of the response body, read_text stops reading and returns all the complete multibyte characters read successfully. If no complete character is read successfully, the partial_multibyte_char exception is raised. The exception can be handled and the bytes of that partial multibyte character can be read as binary by the read_raw procedure. If a partial multibyte character is seen in the middle of the response body because the remaining bytes of the character have not arrived and read timeout occurs, the transfer_timeout exception is raised instead. The exception can be handled and the read operation can be retried later.
When the "Content-Type" response header specifies the character set of the response body and the character set is unknown or unsupported by Oracle, the "ORA-01482: unsupported character set" exception is raised if you try to read the response body as text. You can either read the response body as binary using the READ_RAW procedure, or set the character set of the response body explicitly using the SET_BODY_CHARSET procedure and read the response body as text again.
This function returns up to the first 2000 bytes of data retrieved from the given URL. This function can be used directly in SQL queries. The URL may contain the username and password needed to authenticate the request to the server. The format is
scheme://[user[:password]@]host[:port]/[...]
You can define a username/password for the proxy to be specified in the proxy string. The format is
[http://][user[:password]@]host[:port][/]
UTL_HTTP.REQUEST ( url IN VARCHAR2, proxy IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, wallet_path IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, wallet_password IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL) RETURN VARCHAR2;
pragma restrict_references (request, wnds, rnds, wnps, rnps);
The return type is a string of length 2000 or less, which contains up to the first 2000 bytes of the HTML result returned from the HTTP request to the argument URL.
INIT_FAILED REQUEST_FAILED
The URL passed as an argument to this function is not examined for illegal characters, for example, spaces, according to URL specification RFC 2396. The caller should escape those characters with the UTL_URL package. See the comments of the package for the list of legal characters in URLs. Note that URLs should consist of US-ASCII characters only. The use of non-US-ASCII characters in a URL is generally unsafe.
Please see the documentation of the function set_wallet on the use of an Oracle wallet, which is required for accessing HTTPS Web servers.
Unless response error check is turned on, this function does not raise an exception when a 4xx or 5xx response is received from the Web server. Instead, it returns the formatted error message from the Web server:
<HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE>Error Message</TITLE> </HEAD> <BODY> <H1>Fatal Error 500</H1> Can't Access Document: http://home.nothing.comm. <P> <B>Reason:</B> Can't locate remote host: home.nothing.comm. <P> <P><HR> <ADDRESS><A HREF="http://www.w3.org"> CERN-HTTPD3.0A</A></ADDRESS> </BODY> </HTML>
SQLPLUS> SELECT utl_http.request('http://www.my-company.com/') FROM dual; UTL_HTTP.REQUEST('HTTP://WWW.MY-COMPANY.COM/') <html> <head><title>My Company Home Page</title> <!--changed Jan. 16, 19 1 row selected.
If you are behind a firewall, include the proxy parameter. For example, from within the Oracle firewall, where there might be a proxy server named www-proxy.my-company.com:
SQLPLUS> SELECT utl_http.request('http://www.my-company.com', 'www-proxy.us.my-company.com') FROM dual;
This function returns a PL/SQL table of 2000-byte pieces of the data retrieved from the given URL. You can define a username/password for the proxy to be specified in the proxy string. The format is
[http://][user[:password]@]host[:port][/]
type html_pieces is table of varchar2(2000) index by binary_integer; UTL_HTTP.REQUEST_PIECES ( url IN VARCHAR2, max_pieces IN NATURAL DEFAULT 32767, proxy IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, wallet_path IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, wallet_password IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL) RETURN html_pieces;
pragma restrict_references (request_pieces, wnds, rnds, wnps, rnps);
REQUEST_PIECES returns a PL/SQL table of type UTL_HTTP.HTML_PIECES. Each element of that PL/SQL table is a string of maximum length 2000. The elements of the PL/SQL table returned by REQUEST_PIECES are successive pieces of the data obtained from the HTTP request to that URL.
INIT_FAILED REQUEST_FAILED
The URL passed as an argument to this function will not be examined for illegal characters, for example, spaces, according to URL specification RFC 2396. The caller should escape those characters with the UTL_URL package. See the comments of the package for the list of legal characters in URLs. Note that URLs should consist of US-ASCII characters only. The use of non-US-ASCII characters in a URL is generally unsafe.
Each entry of the PL/SQL table (the "pieces") returned by this function may not be filled to their fullest capacity. The function may start filling the data in the next piece before the previous "piece" is totally full.
Please see the documentation of the function set_wallet on the use of an Oracle wallet, which is required for accessing HTTPS Web servers.
Unless response error check is turned on, this function does not raise an exception when a 4xx or 5xx response is received from the Web server. Instead, it returns the formatted error message from the Web server:
<HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE>Error Message</TITLE> </HEAD> <BODY> <H1>Fatal Error 500</H1> Can't Access Document: http://home.nothing.comm. <P> <B>Reason:</B> Can't locate remote host: home.nothing.comm. <P> <P><HR> <ADDRESS><A HREF="http://www.w3.org"> CERN-HTTPD3.0A</A></ADDRESS> </BODY> </HTML>
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON DECLARE x utl_http.html_pieces; len PLS_INTEGER; BEGIN x := utl_http.request_pieces('http://www.oracle.com/', 100); dbms_output.put_line(x.count || ' pieces were retrieved.'); dbms_output.put_line('with total length '); IF x.count < 1 THEN dbms_output.put_line('0'); ELSE len := 0; FOR i in 1..x.count LOOP len := len + length(x(i)); END LOOP; dbms_output.put_line(i); END IF; END; / -- Output Statement processed. 4 pieces were retrieved. with total length 7687
This procedure sets HTTP authentication information in the HTTP request header. The Web server needs this information to authorize the request.
UTL_HTTP.SET_AUTHENTICATION( r IN OUT NOCOPY req, username IN VARCHAR2, password IN VARCHAR2, scheme IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT 'Basic', for_proxy IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE);
Only the HTTP Basic Authentication scheme is supported.
This procedure is overloaded. The description of different functionalities is located alongside the syntax declarations.
Sets the default character set of the body of all future HTTP requests when the media type is text and the character set is not specified in the Content-Type header. Following the HTTP protocol standard specification, if the media type of a request or a response is text, but the character set information is missing in the Content-Type header, the character set of the request or response body should default to ISO-8859-1. A response created for a request inherits the default body character set of the request instead of the body character set of the current session. The default body character set is ISO-8859-1 in a database user session. The default body character set setting affects only future requests and has no effect on existing requests. After a request is created, the body character set can be changed by using the other SET_BODY_CHARSET procedure that operates on a request:
UTL_HTTP.SET_BODY_CHARSET ( charset IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL);
Sets the character set of the request body when the media type is text but the character set is not specified in the Content-Type header. According to the HTTP protocol standard specification, if the media type of a request or a response is "text" but the character set information is missing in the Content-Type header, the character set of the request or response body should default to "ISO-8859-1". Use this procedure to change the default body character set a request inherits from the session default setting:
UTL_HTTP.SET_BODY_CHARSET( r IN OUT NOCOPY req, charset IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL);
Sets the character set of the response body when the media type is "text" but the character set is not specified in the "Content-Type" header. For each the HTTP protocol standard specification, if the media type of a request or a response is "text" but the character set information is missing in the "Content-Type" header, the character set of the request or response body should default to "ISO-8859-1". Use this procedure to change the default body character set a response inherits from the request:
UTL_HTTP.SET_BODY_CHARSET( r IN OUT NOCOPY resp, charset IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL);
This procedure is overloaded. The description of different functionalities is located alongside the syntax declarations.
This procedure
Enables or disables support for the HTTP cookies in the request. Use this procedure to change the cookie support setting a request inherits from the session default setting:
UTL_HTTP.SET_COOKIE_SUPPORT( r IN OUT NOCOPY REQ, enable IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE);
Sets whether or not future HTTP requests will support HTTP cookies, and the maximum number of cookies maintained in the current database user session:
UTL_HTTP.SET_COOKIE_SUPPORT ( enable IN BOOLEAN, max_cookies IN PLS_INTEGER DEFAULT 300, max_cookies_per_site IN PLS_INTEGER DEFAULT 20);
If cookie support is enabled for an HTTP request, all cookies saved in the current session and applicable to the request are returned to the Web server in the request in accordance with HTTP cookie specification standards. Cookies set in the response to the request are saved in the current session for return to the Web server in the subsequent requests if cookie support is enabled for those requests. If the cookie support is disabled for an HTTP request, no cookies are returned to the Web server in the request and the cookies set in the response to the request are not saved in the current session, although the Set-Cookie HTTP headers can still be retrieved from the response.
Cookie support is enabled by default for all HTTP requests in a database user session. The default setting of the cookie support (enabled versus disabled) affects only the future requests and has no effect on the existing ones. After your request is created, the cookie support setting may be changed by using the other set_cookie_support procedure that operates on a request.
The default maximum number of cookies saved in the current session is 20 for each site and 300 total.
If you lower the maximum total number of cookies or the maximum number of cookies for each Web site, the oldest cookies will be purged first to reduce the number of cookies to the lowered maximum. HTTP cookies saved in the current session last for the duration of the database session only; there is no persistent storage for the cookies. Cookies saved in the current session are not cleared if you disable cookie support.
See "Examples" for how to use get_cookies and add_cookies to retrieve, save, and restore cookies.
This procedure sets the UTL_HTTP package to raise a detailed exception. By default, UTL_HTTP raises the request_failed exception when an HTTP request fails. Use GET_DETAILED_SQLCODE and GET_DETAILED_SQLEERM for more detailed information about the error.
UTL_HTTP.SET_DETAILED_EXCP_SUPPORT ( enable IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Asks |
This procedure sets the maximum number of times UTL_HTTP follows the HTTP redirect instruction in the HTTP response to this request, or future requests, in the GET_RESPONSE function.
Use this procedure to set the maximum number of redirections:
UTL_HTTP.SET_FOLLOW_REDIRECT ( max_redirects IN PLS_INTEGER DEFAULT 3);
Use this procedure to change the maximum number of redirections a request inherits from the session default setting:
UTL_HTTP.SET_FOLLOW_REDIRECT( r IN OUT NOCOPY req, max_redirects IN PLS_INTEGER DEFAULT 3);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The HTTP request |
|
|
The maximum number of redirects. Set to zero to disable redirects. |
If max_redirects is set to a positive number, the GET_RESPONSE Function will automatically follow the redirected URL for the HTTP response status code 301, 302, and 307 for the HTTP HEAD and GET methods, and 303 for all HTTP methods, and retry the HTTP request (the request method will be changed to HTTP GET for the status code 303) at the new location. It follows the redirection until the final, non-redirect location is reached, or an error occurs, or the maximum number of redirections has been reached (to prevent an infinite loop). The URL and method fields in the REQ record will be updated to the last redirected URL and the method used to access the URL. Set the maximum number of redirects to zero to disable automatic redirection.
While it is set not to follow redirect automatically in the current session, it is possible to specify individual HTTP requests to follow redirect instructions the function follow_redirect and vice versa.
The default maximum number of redirections in a database user session is 3. The default value affects only future requests and has no effect on existing requests.
The SET_FOLLOW_REDIRECT procedure must be called before GET_RESPONSE for any redirection to take effect.
This procedure sets an HTTP request header. The request header is sent to the Web server as soon as it is set.
UTL_HTTP.SET_HEADER ( r IN OUT NOCOPY req, name IN VARCHAR2, value IN VARCHAR2);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The HTTP request |
|
|
The name of the HTTP request header |
|
|
The value of the HTTP request header |
Multiple HTTP headers with the same name are allowed in the HTTP protocol standard. Therefore, setting a header does not replace a prior header with the same name.
If the request is made using HTTP 1.1, UTL_HTTP sets the Host header automatically for you.
When you set the Content-Type header with this procedure, UTL_HTTP looks for the character set information in the header value. If the character set information is present, it is set as the character set of the request body. It can be overridden later by using the set_body_charset procedure.
When you set the Transfer-Encoding header with the value chunked, UTL_HTTP automatically encodes the request body written by the WRITE_TEXT, WRITE_LINE and WRITE_RAW procedures. Note that some HTTP-1.1-based Web servers or CGI programs do not support or accept the request body encoding in the HTTP 1.1 chunked transfer-encoding format.
This procedure enables or disables support for the HTTP 1.1 persistent-connection in the request.
UTL_HTTP.SET_PERSISTENT_CONN_SUPPORT( r IN OUT NOCOPY req, enable IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The HTTP request |
|
|
TRUE to keep the network connection persistent. FALSE otherwise. |
If the persistent-connection support is enabled for an HTTP request, the package will keep the network connections to a Web server or the proxy server open in the package after the request is completed properly for a subsequent request to the same server to reuse for each HTTP 1.1 protocol specification. With the persistent connection support, subsequent HTTP requests may be completed faster because the network connection latency is avoided. If the persistent-connection support is disabled for a request, the package will always send the HTTP header "Connection: close" automatically in the HTTP request and close the network connection when the request is completed. This setting has no effect on HTTP requests that follows HTTP 1.0 protocol, for which the network connections will always be closed after the requests are completed.
When a request is being made, the package attempts to reuse an existing persistent connection to the target Web server (or proxy server) if one is available. If none is available, a new network connection will be initiated. The persistent-connection support setting for a request affects only whether the network connection should be closed after a request completes.
Use this procedure to change the persistent-connection support setting a request inherits from the session default setting.
Users should note that while the use of persistent connections in UTL_HTTP may reduce the time it takes to fetch multiple Web pages from the same server, it consumes precious system resources (network connections) in the database server. Also, excessive use of persistent connections may reduce the scalability of the database server when too many network connections are kept open in the database server. Network connections should be kept open only if they will be used immediately by subsequent requests and should be closed immediately when they are no longer needed. Set the default persistent connection support as disabled in the session, and enable persistent connection in individual HTTP requests as shown in "Examples".
The default value of the maximum number of persistent connections in a database session is zero. To truly enable persistent connections, you must also set the maximum number of persistent connections to a positive value or no connections will be kept persistent.
DECLARE TYPE vc2_table IS TABLE OF VARCHAR2(256) INDEX BY binary_integer; paths vc2_table; UTL_HTTP.fetch_pages(paths IN vc2_table) AS url_prefix VARCHAR2(256) := 'http://www.my-company.com/'; req utl_http.req; resp utl_http.resp; data VARCHAR2(1024); BEGIN FOR i IN 1..paths.count LOOP req := utl_http.begin_request(url_prefix || paths(i)); -- Use persistent connection except for the last request IF (i < paths.count) THEN utl_http.set_persistent_conn_support(req, TRUE); END IF; resp := utl_http.get_response(req); BEGIN LOOP utl_http.read_text(resp, data); -- do something with the data END LOOP; EXCEPTION WHEN utl_http.end_of_body THEN NULL; END; utl_http.end_response(resp); END LOOP; END; BEGIN utl_http.set_persistent_conn_support(FALSE, 1); paths(1) := '...'; paths(2) := '...'; ... fetch_pages(paths); END;
This procedure sets the proxy to be used for requests of the HTTP or other protocols, excluding those for hosts that belong to the domain specified in no_proxy_domains.no_proxy_domains is a comma-, semi-colon-, or space-separated list of domains or hosts for which HTTP requests should be sent directly to the destination HTTP server instead of going through a proxy server.
UTL_HTTP.SET_PROXY ( proxy IN VARCHAR2, no_proxy_domains IN VARCHAR2);
The proxy may include an optional TCP/IP port number at which the proxy server listens. The syntax is [http://]host[:port][/], for example, www-proxy.my-company.com:80. If the port is not specified for the proxy, port 80 is assumed.
Optionally, a port number can be specified for each domain or host. If the port number is specified, the no-proxy restriction is only applied to the request at the port of the particular domain or host, for example, corp.my-company.com, eng.my-company.com:80. When no_proxy_domains is NULL and the proxy is set, all requests go through the proxy. When the proxy is not set, UTL_HTTP sends requests to the target Web servers directly.
You can define a username/password for the proxy to be specified in the proxy string. The format is
[http://][user[:password]@]host[:port][/]
If proxy settings are set when the database server instance is started, the proxy settings in the environment variables http_proxy and no_proxy are assumed. Proxy settings set by this procedure override the initial settings.
This procedure sets whether or not get_response raises an exception when the Web server returns a status code that indicates an error--a status code in the 4xx or 5xx ranges. For example, when the requested URL is not found in the destination Web server, a 404 (document not found) response status code is returned.
UTL_HTTP.SET_RESPONSE_ERROR_CHECK ( enable IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
If the status code indicates an error--a 4xx or 5xx code--and this procedure is enabled, get_response will raise the HTTP_CLIENT_ERROR or HTTP_SERVER_ERROR exception. If SET_RESPONSE_ERROR_CHECK is set to FALSE, get_response will not raise an exception when the status code indicates an error.
Response error check is turned off by default.
The get_response function can raise other exceptions when SET_RESPONSE_ERROR_CHECK is set to FALSE.
This procedure sets the default time out value for all future HTTP requests that the UTL_HTTP package should attempt while reading the HTTP response from the Web server or proxy server. This time out value may be used to avoid the PL/SQL programs from being blocked by busy Web servers or heavy network traffic while retrieving Web pages from the Web servers.
UTL_HTTP.SET_TRANSFER_TIMEOUT ( timeout IN PLS_INTEGER DEFAULT 60);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The network transfer timeout value in seconds. |
The default value of the time out is 60 seconds.
This procedure sets the Oracle wallet used for all HTTP requests over Secured Socket Layer (SSL), namely HTTPS. When the UTL_HTTP package communicates with an HTTP server over SSL, the HTTP server presents its digital certificate, which is signed by a certificate authority, to the UTL_HTTP package for identification purpose. The Oracle wallet contains the list of certificate authorities that are trusted by the user of the UTL_HTTP package. An Oracle wallet is required to make an HTTPS request.
UTL_HTTP.SET_WALLET ( path IN VARCHAR2, password IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL);
To set up an Oracle wallet, use the Oracle Wallet Manager to create a wallet. In order for the HTTPS request to succeed, the certificate authority that signs the certificate of the remote HTTPS Web server must be a trust point set in the wallet.
When a wallet is created, it is populated with a set of well-known certificate authorities as trust points. If the certificate authority that signs the certificate of the remote HTTPS Web server is not among the trust points, or the certificate authority has new root certificates, you should obtain the root certificate of that certificate authority and install it as a trust point in the wallet using Oracle Wallet Manager
| See Also:
Oracle Advanced Security Administrator's Guide for more information on Wallet Manager |
This procedure writes a text line in the HTTP request body and ends the line with new-line characters (CRLF as defined in UTL_TCP). As soon as some data is sent as the HTTP request body, the HTTP request headers section is completed. Text data is automatically converted from the database character set to the request body character set.
UTL_HTTP.WRITE_LINE( r IN OUT NOCOPY req, data IN VARCHAR2 CHARACTER SET ANY_CS);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The HTTP request |
|
|
The text line to send in the HTTP request body |
An HTTP client must always let the remote Web server know the length of the request body it is sending. If the amount of data is known beforehand, you can set the Content-Length header in the request, where the length of the content is measured in bytes instead of characters. If the length of the request body is not known beforehand, you can send the request body using the HTTP 1.1 chunked transfer-encoding format. The request body is sent in chunks, where the length of each chunk is sent before the chunk is sent. The UTL_HTTP package performs chunked transfer-encoding on the request body transparently when the Transfer-Encoding: chunked header is set. Note that some HTTP-1.1-based Web servers or CGI programs do not support or accept the request body encoding in the HTTP 1.1 chunked transfer-encoding format. See the set_header procedure for details.
If you send the Content-Length header, you should note that the length specified in the header should be the byte-length of the textual request body after it is converted from the database character set to the request body character set. When either one of the two character sets is a multibyte character set, the precise byte-length of the request body in the request body character set cannot be known beforehand. In this case, you can perform the character set conversion explicitly, determine the byte-length of the results, send the Content-Length header, and the results using the write_raw procedure to avoid the automatic character set conversion. Or, if the remove Web server or CGI programs allow, you can send the request body using the HTTP 1.1 chunked transfer-encoding format, where UTL_HTTP handles the length of the chunks transparently.
This procedure writes some binary data in the HTTP request body. As soon as some data is sent as the HTTP request body, the HTTP request headers section is completed.
UTL_HTTP.WRITE_RAW( r IN OUT NOCOPY req, data IN RAW);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The HTTP request |
|
|
The binary data to send in the HTTP request body |
An HTTP client must always let the remote Web server know the length of the request body it is sending. If the amount of data is known beforehand, you can set the Content-Length header in the request, where the length of the content is measured in bytes instead of characters. If the length of the request body is not known beforehand, you can send the request body using the HTTP 1.1 chunked transfer-encoding format. The request body is sent in chunks, where the length of each chunk is sent before the chunk is sent. UTL_HTTP performs chunked transfer-encoding on the request body transparently when the Transfer-Encoding: chunked header is set. Note that some HTTP-1.1-based Web servers or CGI programs do not support or accept the request body encoding in the HTTP 1.1 chunked transfer-encoding format. See the set_header procedure for details.
This procedure writes some text data in the HTTP request body. As soon as some data is sent as the HTTP request body, the HTTP request headers section is completed. Text data is automatically converted from the database character set to the request body character set.
UTL_HTTP.WRITE_TEXT( r IN OUT NOCOPY req, data IN VARCHAR2 CHARACTER SET ANY_CS);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The HTTP request |
|
|
The text data to send in the HTTP request body |
An HTTP client must always let the remote Web server know the length of the request body it is sending. If the amount of data is known beforehand, you can set the Content-Length header in the request, where the length of the content is measured in bytes instead of characters. If the length of the request body is not known beforehand, you can send the request body using the HTTP 1.1 chunked transfer-encoding format. The request body is sent in chunks, where the length of each chunk is sent before the chunk is sent. UTL_HTTP performs chunked transfer-encoding on the request body transparently when the Transfer-Encoding: chunked header is set. Note that some HTTP-1.1-based Web servers or CGI programs do not support or accept the request body encoding in the HTTP 1.1 chunked transfer-encoding format. See the set_header procedure for details.
If you send the Content-Length header, you should note that the length specified in the header should be the byte-length of the textual request body after it is converted from the database character set to the request body character set. When either one of the two character sets is a multibyte character set, the precise byte-length of the request body in the request body character set cannot be known beforehand. In this case, you can perform the character set conversion explicitly, determine the byte-length of the results, send the Content-Length header, and the results using the write_raw procedure to avoid the automatic character set conversion. Or, if the remove Web server or CGI programs allow, you can send the request body using the HTTP 1.1 chunked transfer-encoding format, where UTL_HTTP handles the length of the chunks transparently.