Release 2 (9.2)
Part Number A96612-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle9i Supplied PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96612-01 |
|
Oracle lets you to write stored procedures and anonymous PL/SQL blocks that use dynamic SQL. Dynamic SQL statements are not embedded in your source program; rather, they are stored in character strings that are input to, or built by, the program at runtime. This enables you to create more general-purpose procedures. For example, dynamic SQL lets you create a procedure that operates on a table whose name is not known until runtime.
Additionally, DBMS_SQL enables you to parse any data manipulation language (DML) or data definition language (DDL) statement. Therefore, you can parse DDL statements directly using PL/SQL. For example, you might now choose to enter a DROP TABLE statement from within a stored procedure by using the PARSE procedure supplied with the DBMS_SQL package.
| See Also:
For more information on native dynamic SQL, see PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference. For a comparison of |
This chapter discusses the following topics:
The ability to use dynamic SQL from within stored procedures generally follows the model of the Oracle Call Interface (OCI).
PL/SQL differs somewhat from other common programming languages, such as C. For example, addresses (also called pointers) are not user-visible in PL/SQL. As a result, there are some differences between the Oracle Call Interface and the DBMS_SQL package. These differences include the following:
DBMS_SQL package uses bind by value.DBMS_SQL you must call VARIABLE_VALUE to retrieve the value of an OUT parameter for an anonymous block, and you must call COLUMN_VALUE after fetching rows to actually retrieve the values of the columns in the rows into your program.DBMS_SQL package does not provide CANCEL cursor procedures.NULLs are fully supported as values of a PL/SQL variable.A sample usage of the DBMS_SQL package follows. For users of the Oracle Call Interfaces, this code should seem fairly straightforward.
This example does not actually require the use of dynamic SQL, because the text of the statement is known at compile time. It does, however, illustrate the concepts of this package.
The DEMO procedure deletes all of the employees from the EMP table whose salaries are greater than the salary that you specify when you run DEMO.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE demo(salary IN NUMBER) AS cursor_name INTEGER; rows_processed INTEGER; BEGIN cursor_name := dbms_sql.open_cursor; DBMS_SQL.PARSE(cursor_name, 'DELETE FROM emp WHERE sal > :x', dbms_sql.native); DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(cursor_name, ':x', salary); rows_processed := dbms_sql.execute(cursor_name); DBMS_SQL.close_cursor(cursor_name); EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(cursor_name); END;
v6 constant INTEGER := 0; native constant INTEGER := 1; v7 constant INTEGER := 2;
TYPE varchar2s IS TABLE OF VARCHAR2(256) INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER; TYPE desc_rec IS RECORD ( col_type BINARY_INTEGER := 0, col_max_len BINARY_INTEGER := 0, col_name VARCHAR2(32) := '', col_name_len BINARY_INTEGER := 0, col_schema_name VARCHAR2(32) := '', col_schema_name_len BINARY_INTEGER := 0, col_precision BINARY_INTEGER := 0, col_scale BINARY_INTEGER := 0, col_charsetid BINARY_INTEGER := 0, col_charsetform BINARY_INTEGER := 0, col_null_ok BOOLEAN := TRUE); TYPE desc_tab IS TABLE OF desc_rec INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
type Number_Table IS TABLE OF NUMBER INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER; type Varchar2_Table IS TABLE OF VARCHAR2(2000) INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER; type Date_Table IS TABLE OF DATE INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER; type Blob_Table IS TABLE OF BLOB INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER; type Clob_Table IS TABLE OF CLOB INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER; type Bfile_Table IS TABLE OF BFILE INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER; type Urowid_Table IS TABLE OF UROWID INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
inconsistent_type exception; pragma exception_init(inconsistent_type, -6562);
This exception is raised by procedure COLUMN_VALUE or VARIABLE_VALUE when the type of the given OUT parameter (for where to put the requested value) is different from the type of the value.
To process a SQL statement, you must have an open cursor. When you call the OPEN_CURSOR function, you receive a cursor ID number for the data structure representing a valid cursor maintained by Oracle. These cursors are distinct from cursors defined at the precompiler, OCI, or PL/SQL level, and are used only by the DBMS_SQL package.
Every SQL statement must be parsed by calling the PARSE procedure. Parsing the statement checks the statement's syntax and associates it with the cursor in your program.
You can parse any DML or DDL statement. DDL statements are run on the parse, which performs the implied commit.
The execution flow of DBMS_SQL is shown in Figure 69-1.
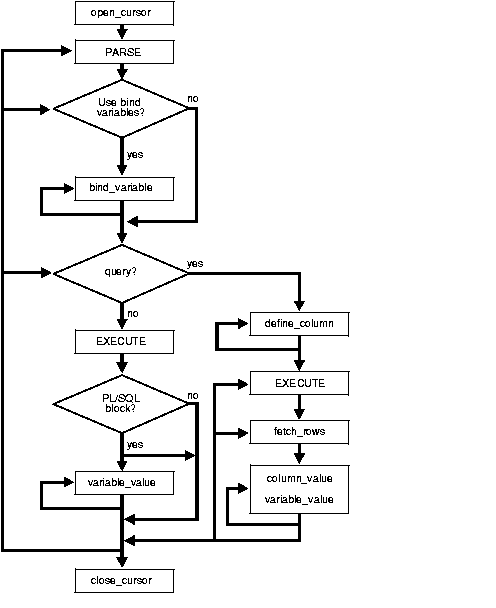
Many DML statements require that data in your program be input to Oracle. When you define a SQL statement that contains input data to be supplied at runtime, you must use placeholders in the SQL statement to mark where data must be supplied.
For each placeholder in the SQL statement, you must call one of the bind procedures, BIND_VARIABLE or BIND_ARRAY, to supply the value of a variable in your program (or the values of an array) to the placeholder. When the SQL statement is subsequently run, Oracle uses the data that your program has placed in the output and input, or bind, variables.
DBMS_SQL can run a DML statement multiple times -- each time with a different bind variable. The BIND_ARRAY procedure lets you bind a collection of scalars, each value of which is used as an input variable once for each EXECUTE. This is similar to the array interface supported by the OCI.
The columns of the row being selected in a SELECT statement are identified by their relative positions as they appear in the select list, from left to right. For a query, you must call one of the define procedures (DEFINE_COLUMN, DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG, or DEFINE_ARRAY) to specify the variables that are to receive the SELECT values, much the way an INTO clause does for a static query.
Use the DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG procedure to define LONG columns, in the same way that DEFINE_COLUMN is used to define non-LONG columns. You must call DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG before using the COLUMN_VALUE_LONG procedure to fetch from the LONG column.
Use the DEFINE_ARRAY procedure to define a PL/SQL collection into which you want to fetch rows in a single SELECT statement. DEFINE_ARRAY provides an interface to fetch multiple rows at one fetch. You must call DEFINE_ARRAY before using the COLUMN_VALUE procedure to fetch the rows.
Call the EXECUTE function to run your SQL statement.
The FETCH_ROWS function retrieves the rows that satisfy the query. Each successive fetch retrieves another set of rows, until the fetch is unable to retrieve anymore rows. Instead of calling EXECUTE and then FETCH_ROWS, you may find it more efficient to call EXECUTE_AND_FETCH if you are calling EXECUTE for a single execution.
For queries, call COLUMN_VALUE to determine the value of a column retrieved by the FETCH_ROWS call. For anonymous blocks containing calls to PL/SQL procedures or DML statements with returning clause, call VARIABLE_VALUE to retrieve the values assigned to the output variables when statements were run.
To fetch just part of a LONG database column (which can be up to two gigabytes in size), use the COLUMN_VALUE_LONG procedure. You can specify the offset (in bytes) into the column value, and the number of bytes to fetch.
When you no longer need a cursor for a session, close the cursor by calling CLOSE_CURSOR. If you are using an Oracle Open Gateway, then you may need to close cursors at other times as well. Consult your Oracle Open Gateway documentation for additional information.
If you neglect to close a cursor, then the memory used by that cursor remains allocated even though it is no longer needed.
Definer rights modules run under the privileges of the owner of the module. DBMS_SQL subprograms called from definer rights modules run with respect to the schema in which the module is defined.
Invoker rights modules run under the privileges of the invoker of the module. Therefore, DBMS_SQL subprograms called from invoker rights modules run under the privileges of the invoker of the module.
When a module has AUTHID set to current_user, the unqualified names are resolved with respect to the invoker's schema.
income is an invoker rights stored procedure in USER1's schema, and USER2 has been granted EXECUTE privilege on it.
CREATE PROCEDURE income(amount number) AUTHID current_user IS c number; n number; BEGIN c:= dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, 'insert into accts(''income'', :1)', dbms_sql.native); dbms_sql.bind_variable(c, '1', amount); n := dbms_sql.execute(c); dbms_sql.close_cursor(c); END;
If USER1 calls USER1.income, then USER1's privileges are used, and name resolution of unqualified names is done with respect to USER1's schema.
If USER2 calls USER1.income, then USER2's privileges are used, and name resolution of unqualified names (such as accts) is done with respect to USER2's schema.
Any DBMS_SQL subprograms called from an anonymous PL/SQL block are run using the privileges of the current user.
If you are using dynamic SQL to process a query, then you must perform the following steps:
SELECT statement by calling DEFINE_COLUMN, DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG, or DEFINE_ARRAY.SELECT statement by calling EXECUTE.FETCH_ROWS (or EXECUTE_AND_FETCH) to retrieve the rows that satisfied your query.COLUMN_VALUE or COLUMN_VALUE_LONG to determine the value of a column retrieved by the FETCH_ROWS call for your query. If you used anonymous blocks containing calls to PL/SQL procedures, then you must call VARIABLE_VALUE to retrieve the values assigned to the output variables of these procedures.This section provides example procedures that make use of the DBMS_SQL package.
The following sample procedure is passed a SQL statement, which it then parses and runs:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE exec(STRING IN varchar2) AS cursor_name INTEGER; ret INTEGER; BEGIN cursor_name := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DDL statements are run by the parse call, which performs the implied commit.
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(cursor_name, string, DBMS_SQL.native); ret := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(cursor_name); DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(cursor_name); END;
Creating such a procedure enables you to perform the following operations:
For example, after creating this procedure, you could make the following call:
exec('create table acct(c1 integer)');
You could even call this procedure remotely, as shown in the following example. This lets you perform remote DDL.
exec@hq.com('CREATE TABLE acct(c1 INTEGER)');
The following sample procedure is passed the names of a source and a destination table, and copies the rows from the source table to the destination table. This sample procedure assumes that both the source and destination tables have the following columns:
id of type NUMBER name of type VARCHAR2(30) birthdate of type DATE
This procedure does not specifically require the use of dynamic SQL; however, it illustrates the concepts of this package.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE copy ( source IN VARCHAR2, destination IN VARCHAR2) IS id_var NUMBER; name_var VARCHAR2(30); birthdate_var DATE; source_cursor INTEGER; destination_cursor INTEGER; ignore INTEGER; BEGIN -- Prepare a cursor to select from the source table: source_cursor := dbms_sql.open_cursor; DBMS_SQL.PARSE(source_cursor, 'SELECT id, name, birthdate FROM ' || source, DBMS_SQL.native); DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN(source_cursor, 1, id_var); DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN(source_cursor, 2, name_var, 30); DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN(source_cursor, 3, birthdate_var); ignore := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(source_cursor); -- Prepare a cursor to insert into the destination table: destination_cursor := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR; DBMS_SQL.PARSE(destination_cursor, 'INSERT INTO ' || destination || ' VALUES (:id_bind, :name_bind, :birthdate_bind)', DBMS_SQL.native); -- Fetch a row from the source table and insert it into the destination table: LOOP IF DBMS_SQL.FETCH_ROWS(source_cursor)>0 THEN -- get column values of the row DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(source_cursor, 1, id_var); DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(source_cursor, 2, name_var); DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(source_cursor, 3, birthdate_var); -- Bind the row into the cursor that inserts into the destination table. You -- could alter this example to require the use of dynamic SQL by inserting an -- if condition before the bind. DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(destination_cursor, ':id_bind', id_var); DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(destination_cursor, ':name_bind', name_var); DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(destination_cursor, ':birthdate_bind', birthdate_var); ignore := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(destination_cursor); ELSE -- No more rows to copy: EXIT; END IF; END LOOP; -- Commit and close all cursors: COMMIT; DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(source_cursor); DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(destination_cursor); EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN IF DBMS_SQL.IS_OPEN(source_cursor) THEN DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(source_cursor); END IF; IF DBMS_SQL.IS_OPEN(destination_cursor) THEN DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(destination_cursor); END IF; RAISE; END; /
This series of examples shows how to use bulk array binds (table items) in the SQL DML statements DELETE, INSERT, and UPDATE.
In a DELETE statement, for example, you could bind in an array in the WHERE clause and have the statement be run for each element in the array:
declare stmt varchar2(200); dept_no_array dbms_sql.Number_Table; c number; dummy number; begin dept_no_array(1) := 10; dept_no_array(2) := 20; dept_no_array(3) := 30; dept_no_array(4) := 40; dept_no_array(5) := 30; dept_no_array(6) := 40; stmt := 'delete from emp where deptno = :dept_array'; c := dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, stmt, dbms_sql.native); dbms_sql.bind_array(c, ':dept_array', dept_no_array, 1, 4); dummy := dbms_sql.execute(c); dbms_sql.close_cursor(c); exception when others then if dbms_sql.is_open(c) then dbms_sql.close_cursor(c); end if; raise; end; /
In the preceding example, only elements 1 through 4 are used as specified by the bind_array call. Each element of the array potentially deletes a large number of employees from the database.
Here is an example of a bulk INSERT statement:
declare stmt varchar2(200); empno_array dbms_sql.Number_Table; empname_array dbms_sql.Varchar2_Table; c number; dummy number; begin for i in 0..9 loop empno_array(i) := 1000 + i; empname_array(I) := get_name(i); end loop; stmt := 'insert into emp values(:num_array, :name_array)'; c := dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, stmt, dbms_sql.native); dbms_sql.bind_array(c, ':num_array', empno_array); dbms_sql.bind_array(c, ':name_array', empname_array); dummy := dbms_sql.execute(c); dbms_sql.close_cursor(c); exception when others then if dbms_sql.is_open(c) then dbms_sql.close_cursor(c); end if; raise; end; /
When the execute takes place, all 10 of the employees are inserted into the table.
Finally, here is an example of an bulk UPDATE statement.
declare stmt varchar2(200); emp_no_array dbms_sql.Number_Table; emp_addr_array dbms_sql.Varchar2_Table; c number; dummy number; begin for i in 0..9 loop emp_no_array(i) := 1000 + i; emp_addr_array(I) := get_new_addr(i); end loop; stmt := 'update emp set ename = :name_array where empno = :num_array'; c := dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, stmt, dbms_sql.native); dbms_sql.bind_array(c, ':num_array', empno_array); dbms_sql.bind_array(c, ':name_array', empname_array); dummy := dbms_sql.execute(c); dbms_sql.close_cursor(c); exception when others then if dbms_sql.is_open(c) then dbms_sql.close_cursor(c); end if; raise; end; /
When the EXECUTE call happens, the addresses of all employees are updated at once. The two collections are always stepped in unison. If the WHERE clause returns more than one row, then all those employees get the address the addr_array happens to be pointing to at that time.
The following examples show how to use the DEFINE_ARRAY procedure:
declare c number; d number; n_tab dbms_sql.Number_Table; indx number := -10; begin c := dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, 'select n from t order by 1', dbms_sql); dbms_sql.define_array(c, 1, n_tab, 10, indx); d := dbms_sql.execute(c); loop d := dbms_sql.fetch_rows(c); dbms_sql.column_value(c, 1, n_tab); exit when d != 10; end loop; dbms_sql.close_cursor(c); exception when others then if dbms_sql.is_open(c) then dbms_sql.close_cursor(c); end if; raise; end; /
Each time the preceding example does a FETCH_ROWS call, it fetches 10 rows that are kept in DBMS_SQL buffers. When the COLUMN_VALUE call is run, those rows move into the PL/SQL table specified (in this case n_tab), at positions -10 to -1, as specified in the DEFINE statements. When the second batch is fetched in the loop, the rows go to positions 0 to 9; and so on.
A current index into each array is maintained automatically. This index is initialized to "indx" at EXECUTE and keeps getting updated every time a COLUMN_VALUE call is made. If you reexecute at any point, then the current index for each DEFINE is re-initialized to "indx".
In this way the entire result of the query is fetched into the table. When FETCH_ROWS cannot fetch 10 rows, it returns the number of rows actually fetched (if no rows could be fetched, then it returns zero) and exits the loop.
Here is another example of using the DEFINE_ARRAY procedure:
Consider a table MULTI_TAB defined as:
create table multi_tab (num number, dat1 date, var varchar2(24), dat2 date)
To select everything from this table and move it into four PL/SQL tables, you could use the following simple program:
declare c number; d number; n_tab dbms_sql.Number_Table; d_tab1 dbms_sql.Date_Table; v_tab dbms_sql.Varchar2_Table; d_tab2 dbms_sql.Date_Table; indx number := 10; begin c := dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, 'select * from multi_tab order by 1', dbms_sql); dbms_sql.define_array(c, 1, n_tab, 5, indx); dbms_sql.define_array(c, 2, d_tab1, 5, indx); dbms_sql.define_array(c, 3, v_tab, 5, indx); dbms_sql.define_array(c, 4, d_tab2, 5, indx); d := dbms_sql.execute(c); loop d := dbms_sql.fetch_rows(c); dbms_sql.column_value(c, 1, n_tab); dbms_sql.column_value(c, 2, d_tab1); dbms_sql.column_value(c, 3, v_tab); dbms_sql.column_value(c, 4, d_tab2); exit when d != 5; end loop; dbms_sql.close_cursor(c); /*
The four tables can be used for anything. One usage might be to use BIND_ARRAY to move the rows to another table by using a query such as 'INSERT into SOME_T values (:a, :b, :c, :d);
*/ exception when others then if dbms_sql.is_open(c) then dbms_sql.close_cursor(c); end if; raise; end; /
This can be used as a substitute to the SQL*Plus DESCRIBE call by using a SELECT * query on the table that you want to describe.
declare c number; d number; col_cnt integer; f boolean; rec_tab dbms_sql.desc_tab; col_num number; procedure print_rec(rec in dbms_sql.desc_rec) is begin dbms_output.new_line; dbms_output.put_line('col_type = ' || rec.col_type); dbms_output.put_line('col_maxlen = ' || rec.col_max_len); dbms_output.put_line('col_name = ' || rec.col_name); dbms_output.put_line('col_name_len = ' || rec.col_name_len); dbms_output.put_line('col_schema_name = ' || rec.col_schema_name); dbms_output.put_line('col_schema_name_len = ' || rec.col_schema_name_len); dbms_output.put_line('col_precision = ' || rec.col_precision); dbms_output.put_line('col_scale = ' || rec.col_scale); dbms_output.put('col_null_ok = '); if (rec.col_null_ok) then dbms_output.put_line('true'); else dbms_output.put_line('false'); end if; end; begin c := dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, 'select * from scott.bonus', dbms_sql); d := dbms_sql.execute(c); dbms_sql.describe_columns(c, col_cnt, rec_tab); /* * Following loop could simply be for j in 1..col_cnt loop. * Here we are simply illustrating some of the PL/SQL table * features. */ col_num := rec_tab.first; if (col_num is not null) then loop print_rec(rec_tab(col_num)); col_num := rec_tab.next(col_num); exit when (col_num is null); end loop; end if; dbms_sql.close_cursor(c); end; /
The RETURNING clause was added to DML statements in Oracle 8.0.3. With this clause, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements can return values of expressions. These values are returned in bind variables.
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE is used to bind these outbinds if a single row is inserted, updated, or deleted. If multiple rows are inserted, updated, or deleted, then DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY is used. DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE must be called to get the values in these bind variables.
|
Note: This is similar to |
i) Single row insert
create or replace procedure single_Row_insert (c1 number, c2 number, r out number) is c number; n number; begin c := dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, 'insert into tab values (:bnd1, :bnd2) ' || 'returning c1*c2 into :bnd3', 2); dbms_sql.bind_variable(c, 'bnd1', c1); dbms_sql.bind_variable(c, 'bnd2', c2); dbms_sql.bind_variable(c, 'bnd3', r); n := dbms_sql.execute(c); dbms_sql.variable_value(c, 'bnd3', r); -- get value of outbind variable dbms_Sql.close_Cursor(c); end; /
ii) Single row update
create or replace procedure single_Row_update (c1 number, c2 number, r out number) is c number; n number; begin c := dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, 'update tab set c1 = :bnd1, c2 = :bnd2 ' || 'where rownum < 2' || 'returning c1*c2 into :bnd3', 2); dbms_sql.bind_variable(c, 'bnd1', c1); dbms_sql.bind_variable(c, 'bnd2', c2); dbms_sql.bind_variable(c, 'bnd3', r); n := dbms_sql.execute(c); dbms_sql.variable_value(c, 'bnd3', r);-- get value of outbind variable dbms_Sql.close_Cursor(c); end; /
iii) Single row delete
create or replace procedure single_Row_Delete (c1 number, c2 number, r out number) is c number; n number; begin c := dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, 'delete from tab ' || 'where rownum < 2 ' || 'returning c1*c2 into :bnd3', 2); dbms_sql.bind_variable(c, 'bnd1', c1); dbms_sql.bind_variable(c, 'bnd2', c2); dbms_sql.bind_variable(c, 'bnd3', r); n := dbms_sql.execute(c); dbms_sql.variable_value(c, 'bnd3', r);-- get value of outbind variable dbms_Sql.close_Cursor(c); end; /
iv) Multi-row insert
create or replace procedure multi_Row_insert (c1 dbms_sql.number_table, c2 dbms_sql.number_table, r out dbms_sql.number_table) is c number; n number; begin c := dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, 'insert into tab values (:bnd1, :bnd2) ' || 'returning c1*c2 into :bnd3', 2); dbms_sql.bind_array(c, 'bnd1', c1); dbms_sql.bind_array(c, 'bnd2', c2); dbms_sql.bind_array(c, 'bnd3', r); n := dbms_sql.execute(c); dbms_sql.variable_value(c, 'bnd3', r);-- get value of outbind variable dbms_Sql.close_Cursor(c); end; /
v) Multi row Update.
create or replace procedure multi_Row_update (c1 number, c2 number, r out dbms_Sql.number_table) is c number; n number; begin c := dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, 'update tab set c1 = :bnd1 where c2 = :bnd2 ' || 'returning c1*c2 into :bnd3', 2); dbms_sql.bind_variable(c, 'bnd1', c1); dbms_sql.bind_variable(c, 'bnd2', c2); dbms_sql.bind_array(c, 'bnd3', r); n := dbms_sql.execute(c); dbms_sql.variable_value(c, 'bnd3', r);-- get value of outbind variable dbms_Sql.close_Cursor(c); end; /
vi) Multi-row delete
create or replace procedure multi_row_delete (c1 dbms_Sql.number_table, r out dbms_sql.number_table) is c number; n number; begin c := dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, 'delete from tab where c1 = :bnd1' || 'returning c1*c2 into :bnd2', 2); dbms_sql.bind_array(c, 'bnd1', c1); dbms_sql.bind_array(c, 'bnd2', r); n := dbms_sql.execute(c); dbms_sql.variable_value(c, 'bnd2', r);-- get value of outbind variable dbms_Sql.close_Cursor(c); end; /
vii) Out-bind in bulk PL/SQL
create or replace foo (n number, square out number) is begin square := n * n; end;/ create or replace procedure bulk_plsql (n dbms_sql.number_Table, square out dbms_sql.number_table) is c number; r number; begin c := dbms_sql.open_cursor; dbms_sql.parse(c, 'begin foo(:bnd1, :bnd2); end;', 2); dbms_sql.bind_array(c, 'bnd1', n); dbms_Sql.bind_Array(c, 'bnd2', square); r := dbms_sql.execute(c); dbms_Sql.variable_Value(c, 'bnd2', square); end; /
|
Note:
|
If you are using dynamic SQL to process an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE, then you must perform the following steps:
INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement by calling EXECUTE.returning clause, then you must call VARIABLE_VALUE to retrieve the values assigned to the output variables.There are additional functions in the DBMS_SQL package for obtaining information about the last referenced cursor in the session. The values returned by these functions are only meaningful immediately after a SQL statement is run. In addition, some error-locating functions are only meaningful after certain DBMS_SQL calls. For example, you call LAST_ERROR_POSITION immediately after a PARSE.
|
 Copyright © 2000, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|