| Oracle9i XML Database Developer's Guide - Oracle XML DB Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96620-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle9i XML Database Developer's Guide - Oracle XML DB Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96620-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter describes how Oracle Enterprise Manager can be used to manage Oracle XML DB. Oracle Enterprise Manager can be used to configure, create and manage Repository resources, and database objects such as XML schemas and XMLType tables.
It contains the following sections:
This chapter describes how to use Oracle Enterprise Manager (Enterprise Manager) to administer and manage Oracle XML DB.
Oracle Enterprise Manager is supplied with Oracle9i database software, both Enterprise and Standard Editions. To run the Enterprise Manager version that supports Oracle XML DB functionality, use Oracle9i Release 2 (9.2) or higher.
Oracle XML DB is installed by default when the Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) is used to create a new database. The following actions take place during Oracle XML DB installation:
http://www.oracle.com/xdb/xdbconfig.xsd
/sys/xdbconfig.xml conforming to the configuration XML schema. This resource contains default values for all Oracle XML DB parameters.
Oracle XML DB is typically used for its faster retrieval and search capabilities, access control, and versioning of XML documents. XML instance documents saved in the database can conform to an XML Schema. XML Schema is a schema definition language, also written in XML, that can be used to describe the structure and various other semantics of a conforming XML instance document.
Oracle XML DB provides a mechanism to register XML Schemas with the database.
Assuming that your XML schema document(s) already exists, registering the XML schema is your first task. Before you register the XML schema, you must know the following:
For most cases, it is assumed that you have XML schema annotated with information to automatically generate object types and object tables. Hence the Oracle9i database, as part of XML schema registration, automatically generates these objects.
Oracle XML DB is now ready for you to insert conforming XML documents.
With Enterprise Manager you can perform the following main Oracle XML DB administrative tasks:
See Figure 21-1 and Figure 21-2.
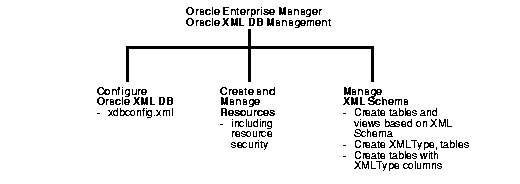
Oracle XML DB is managed through the configuration file, xdbconfig.xml. Through Enterprise Manager, you can view or configure this file's parameters. To access the Oracle XML DB configuration options, from the Enterprise Manager right hand window, select "Configure XML Database". See "Configuring Oracle XML DB with Enterprise Manager" .
To access the XML resource management options, select the XML Database object in the Navigator and click "Create a Resource" in the detail view. See "Creating and Managing Oracle XML DB Resources with Enterprise Manager" .
To access the XML schema management options, select the XML Database object in the Navigator and click "Create Table and Views Based on XML Schema" in the detail view. See "Managing XML Schema and Related Database Objects".
You can register, delete, view, generate (that is, reverse engineer) an XML schema and see its dependencies. You can also view an XML schema's contents and perform actions on its constituent elements.
XMLType, and look at the corresponding indexes.XMLType tables and columns, and look at the corresponding indexes. You can also specify LOB storage attributes on these columns.
You can create XMLType tables in CLOB or object-relational form, and specify constraints and LOB storage attributes on hidden XMLType columns.
XMLType.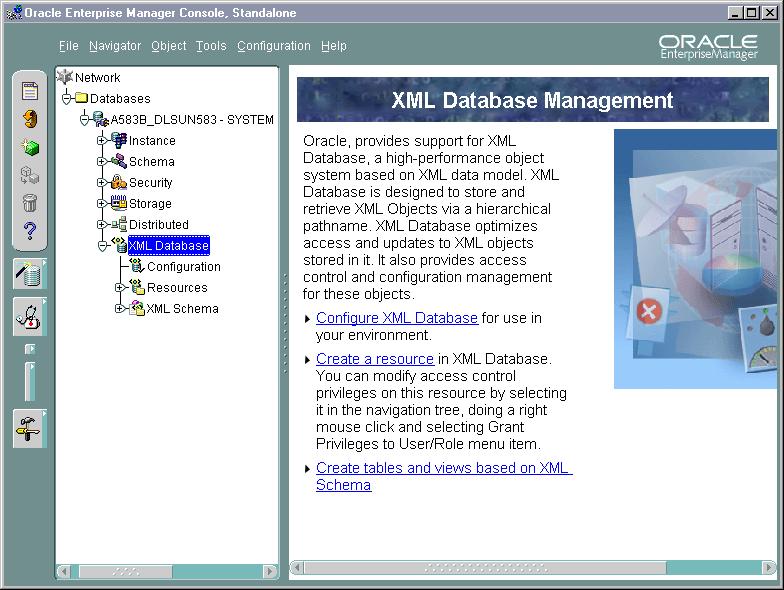
Text description of the illustration oem_xdb.jpg
See Figure 21-2. From the Enterprise Manager console you can quickly browse and manage Oracle XML DB objects.
From the XML Database Management detail view you can access the XML DB management functionality. From there you can select which task you need to perform.
Use the left-hand Navigator, to select the Oracle XML DB resources and database objects you need to view or modify.
Oracle XML DB configuration is an integral part of Oracle XML DB. It is used by protocols such as HTTP/WebDav or FTP, and any other components of Oracle XML DB that can be customized, such as, in the ACL based security.
Oracle XML DB configuration is stored as an XML schema based XML resource, xdbconfig.xml in the Oracle XML DB Repository. It conforms to the Oracle XML DB configuration XML schema stored at:
http://www.oracle.com/xdb/xdbconfig.xsd
This configuration XML schema is registered when Oracle XML DB is installed. The configuration property sheet has two tabs:
To configure items in Oracle XML DB, select the Configuration node under XML Database in the Navigator. See Figure 21-3 and See Figure 21-4.
The XML Database Parameters page displays a list of configuration parameters for the current XML database. You can also access this page from the XML Database Management main window > Configure XML Database.
When you click the Configuration node for the XML database in the Enterprise Manager Navigator, the XML DB Parameters page appears in the main panel to the right. The XML DB Parameters window lists the following information:
You can change the value of a parameter by clicking the Value field for the parameter and making the change. Click the Apply button to apply any changes you make. You can access a description of a parameter by clicking on the parameter in the list and then clicking the Description button at the bottom of the page. A text Description text box displays that describes in greater detail the parameter you selected. You can close the Description box by clicking again on the Description button.
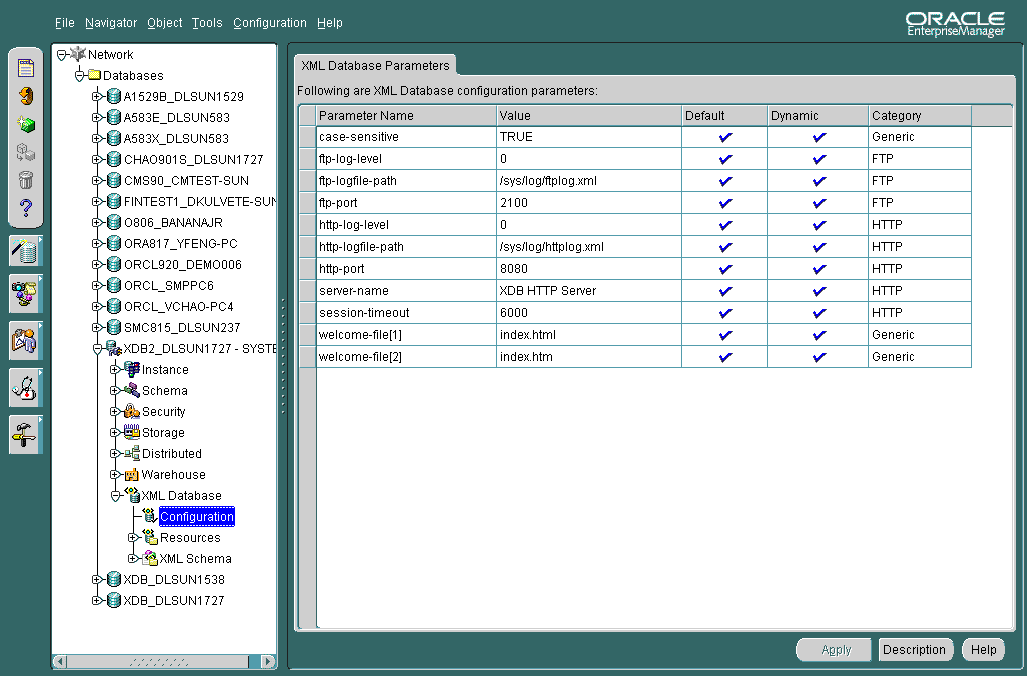
Text description of the illustration configuration.gif
Since Oracle XML DB provides support for standard Internet protocols (FTP and WebDAV/HTTP) as a means of accessing the Repository, Enterprise Manager provides you with related information:
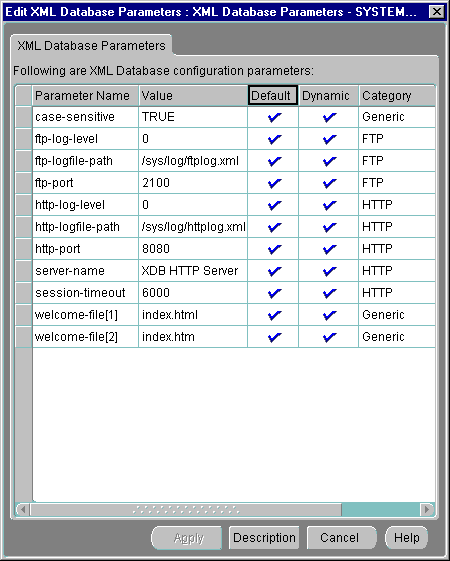
Text description of the illustration configuration_dlg.gif
With Enterprise Manager you can view and edit partial Oracle XML DB configuration parameters, in the following categories:
The Resources folder in the Enterprise Manager navigation tree is under the XML Database folder. It contains all the resources in the database regardless of the owner. Figure 21-5 shows a typical Resources tree.
When the Resources folder is selected in the Navigator, the right-hand side of the screen displays all the top level Oracle XML DB resources under root, their names, and their creation and modification dates. See Figure 21-6.
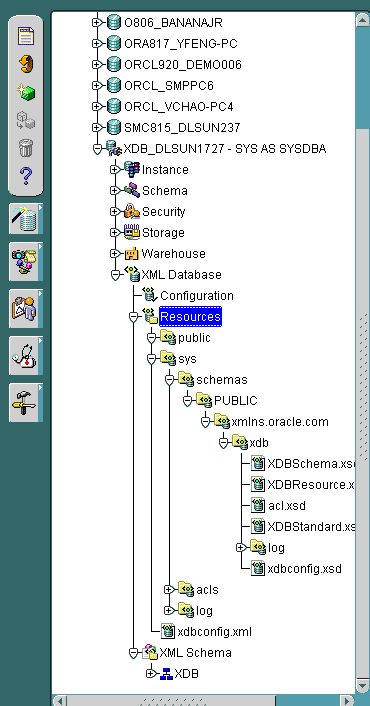
Text description of the illustration res_tree.gif
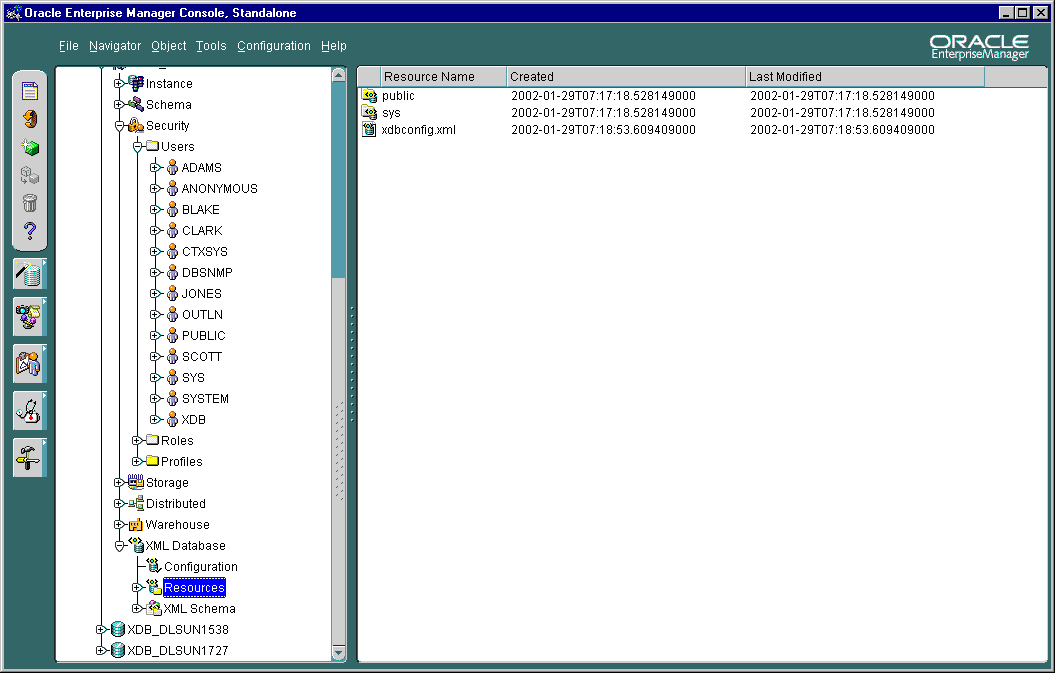
Text description of the illustration resources_rhs.gif
Once you select a resource sub-folder under the main Resources folder in the Navigator, you can see the resources "General Page" in the detail view, as shown in Figure 21-7.
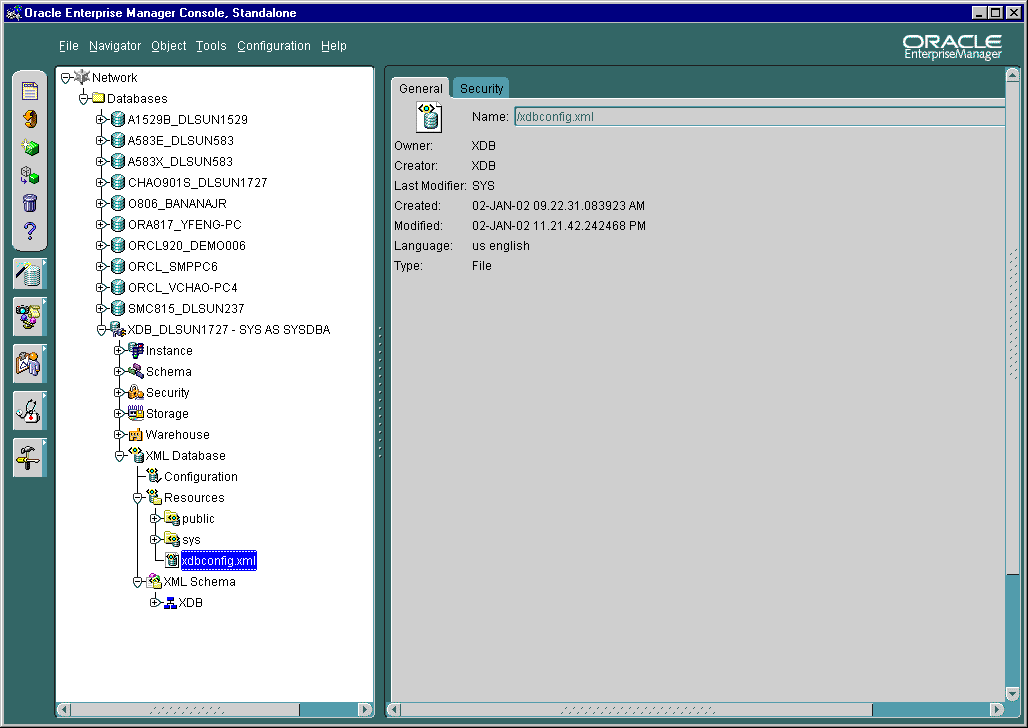
Text description of the illustration res_gen_page.gif
The Oracle XML DB Resources General page (also called the XML Resources Page) displays overview information about the resource container or resource file. When you select one of the Oracle XML DB resource containers or files in the Navigator, Enterprise Manager displays the Oracle XML DB Resources General page. This is a read-only page. It displays the following information:
Oracle XML DB Resources Security page changes the ACL associated with the XML DB resource container or file. Use the ACL files to restrict access to all XML DB resources. When you change the ACL file for the resource, you change the access privileges for the resource file. See Figure 21-8.
To specify a new ACL file:
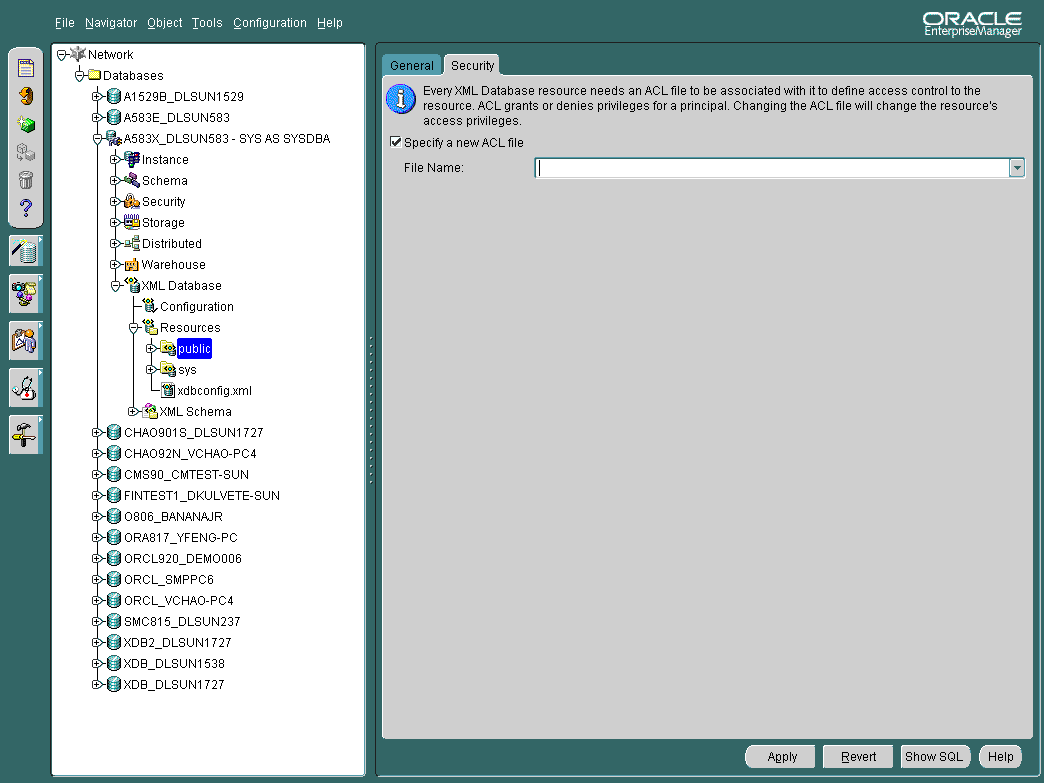
Text description of the illustration res_security_page.gif
Figure 21-9 shows the context-sensitive menu displayed when you select and right-click an individual Oracle XML DB resource object in the Navigator.
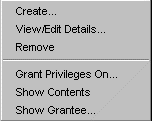
Text description of the illustration res_rmouse_menu.gif
You can perform the following Oracle XML DB tasks from the Enterprise Manager Content Menu:
Figure 21-10 shows how you can use the Create XML DB Resource dialog box to create an XML DB resource container or file. From the XML DB Resource dialog you can name the resource and then either create a new resource container or create a new resource file, designating the location of the file as either a local file, a file at a specified URL, or specifying the contents of the file.
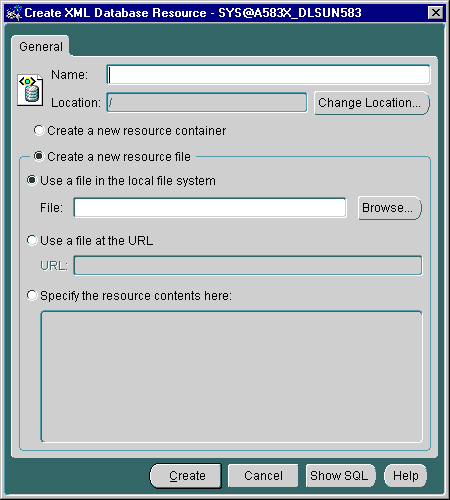
Text description of the illustration res_create.gif
Figure 21-11 shows the Grant Privileges On dialog box which assigns privileges on an Oracle XML DB resource to users or roles. You can grant multiple privileges to multiple users or roles. Grant Privileges On dialog box lists the available Oracle XML DB resource privileges in the Grant section at the top of the panel.
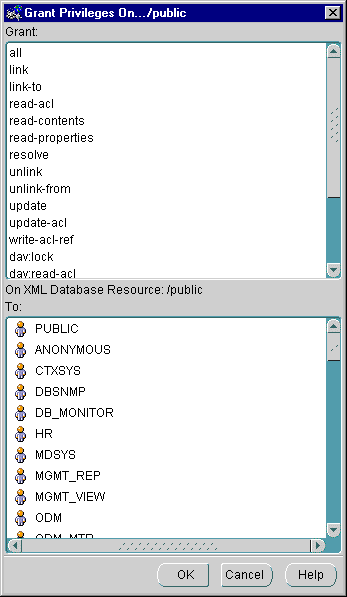
Text description of the illustration res_grant_dlg.gif
Figure 21-12 is an example of a Show Contents dialog box. It displays the contents of the selected resource file.
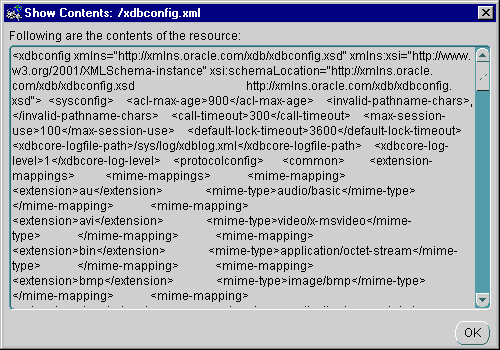
Text description of the illustration show_contents.gif
Figure 21-11 shows the Show Grantee of XML DB Resource dialog box. It displays a list of all granted privileges on a specified XML DB resource for the connected Enterprise Manager user. Show Grantee dialog box lists the connected Enterprise Manager user, privilege, and granted status of the privilege in tabular format.
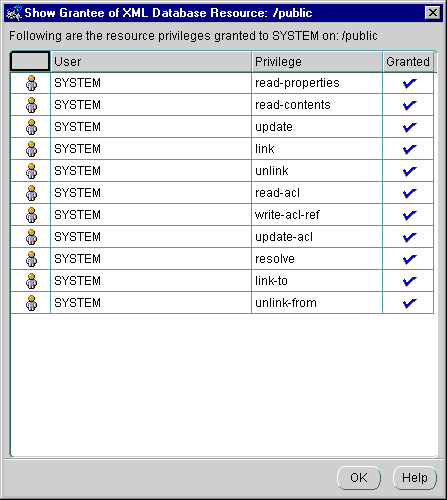
Text description of the illustration show_grantee.gif
From Enterprise Manager you can restrict access to all XML DB resources by means of ACLs. You can grant XML DB resource privileges to database user and database role separately using the existing Security/Users/user and Security/Roles/role interface, respectively.
You can access the Enterprise Manager security options in two main ways:
This section describes how to grant and revoke privileges for a "user", The same procedure applies when granting and revoking privileges for a "role". To grant privileges to a user follow these steps:
Conversely, you can revoke privileges by selecting them in the Granted list and clicking on the up arrow.
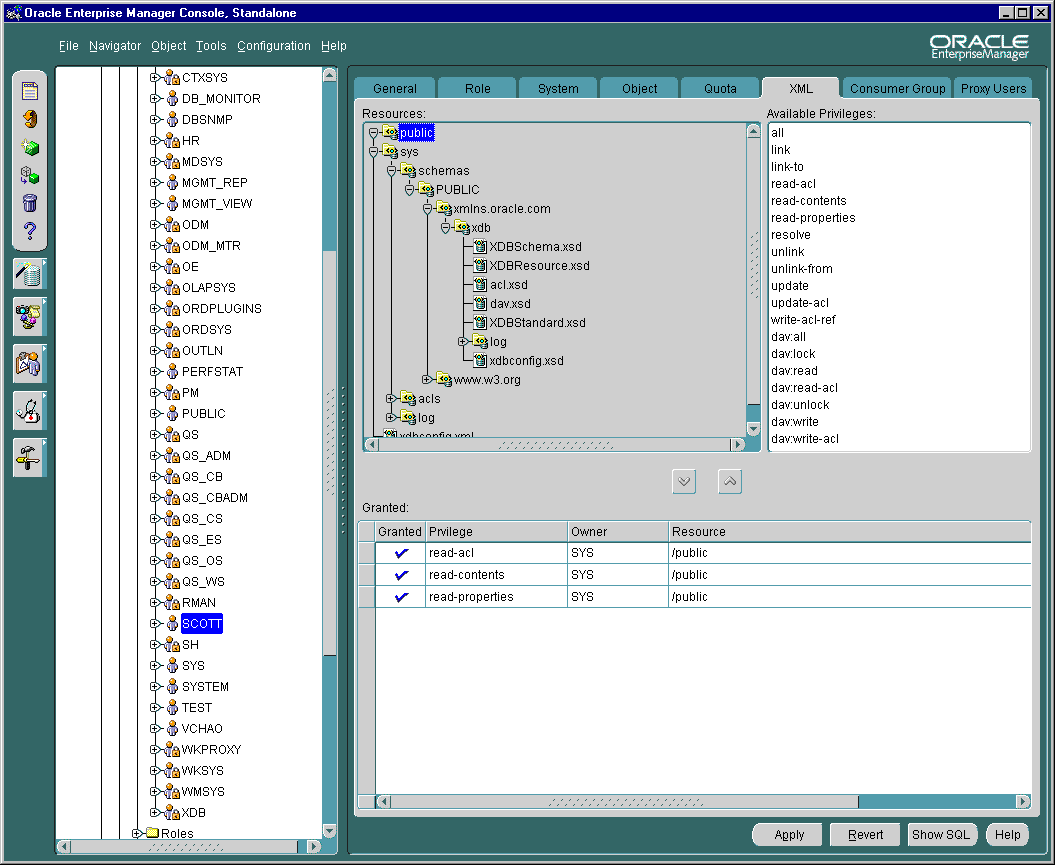
Text description of the illustration security_user.gif
The Resources list is a tree listing of resources located in Oracle XML DB Repository. You can navigate through the folder hierarchy to locate the resource on which you want to set privileges for the user or role you selected in Navigator. When you select a resource in the tree listing, its privileges appear in the Available Privileges list to the right.
The Available Privileges list displays all privileges available for a resource. Click a privilege and then press the down arrow button to add the privilege to the Granted list. You can select consecutive privileges by clicking on the first privilege and then holding the Shift key down to select the last in the list. Also, you can select non-consecutive privileges by holding the Ctrl-key down while making selections.
Privileges can be either of the following:
The Granted list displays all privileges granted to the user or role for the resource selected in the Resources list. You can revoke a privilege by highlighting it and clicking the up arrow to remove it.
Privilege can be aggregate (contain other privileges) or atomic (cannot be subdivided). The following system privileges are supported:

Text description of the illustration res_grant_dlg.gif
| See Also:
Chapter 18, "Oracle XML DB Resource Security" for a list of supported system privileges. |
From the XML Database Management detail view, when you select "Create tables and views based on XML Schema" the "XML Schema Based Objects" page appears. With this you can:
XMLType tableXMLType columnsUnder the XML Schema folder, the tree lists all the XML schema owners. The example here is owner "XDB". See Figure 21-16:
http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBResource.xsd http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBSchema.xsd http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/XDBStandard.xsd
XMLType tables, tables with XMLType columns, and views. For example, Figure 21-16 shows top level elements servlet and LINK. The number and names of these elements are dictated by the relevant XML schema definition, which in this case is: http://xmlns.oracle.com/XDBStandard.xsd.XMLType Tables, Views, and User types.XDB" is an owner, and XDB owns a table called SERVLET.
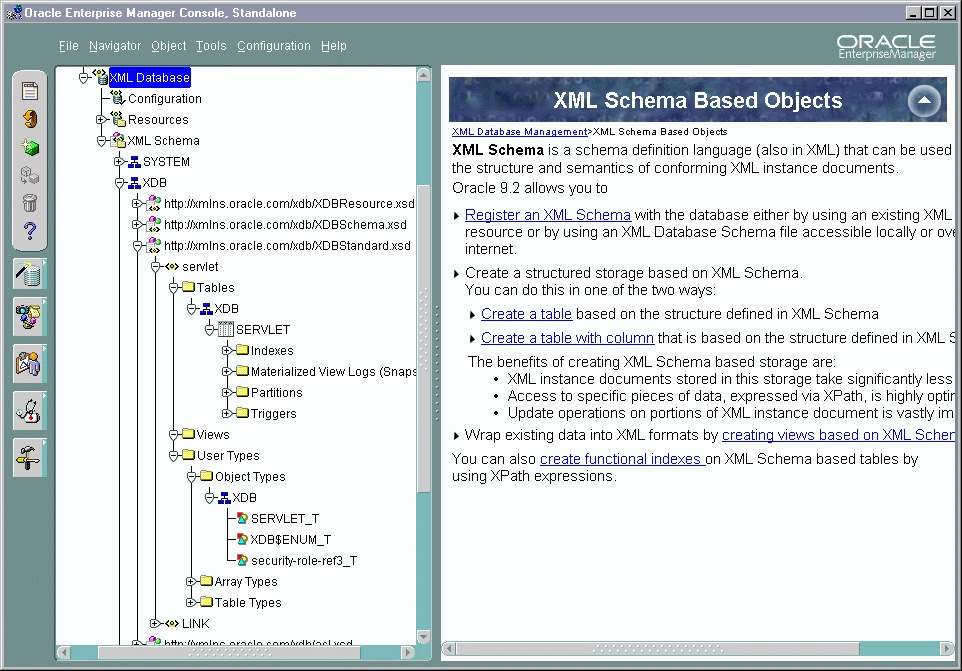
Text description of the illustration tree.gif
Text description of the illustration html2.gif
Registering an XML schema is one of the central, and often first, tasks before the you use Oracle XML DB. XML schema are registered using DBMS_XMLSCHEMA.registerSchema().
Figure 21-18 shows you how to register an XML schema.
From the GENERAL page, input the XML schema URL and select the Owner of the XML schema from the drop-down list.
Select either:
You can obtain the XML schema in one of four ways:
From the Options page you can select the following options:
See Figure 21-19. Press Create from either the General Tab or Options Tab to register this XML schema.
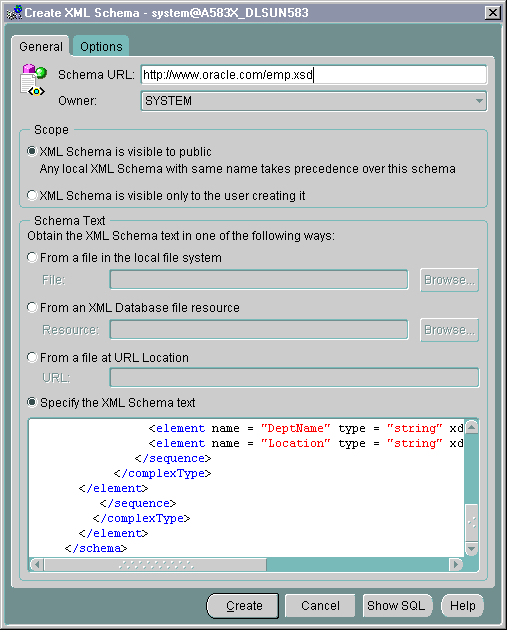
Text description of the illustration xschema1.gif
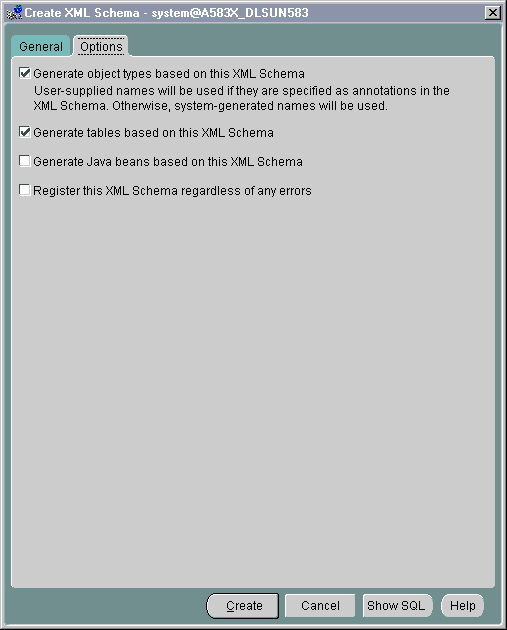
Text description of the illustration xschema2.gif
This section describes how to use Oracle Enterprise Manager to create XMLType tables, views, and indexes.
You have two main options when creating tables:
To create an XMLType view, see "Creating a View Based on XML Schema".
To create function-based indexes see "Creating a Function-Based Index Based on XPath Expressions".
From the Create Table property sheet, enter the desired name of the table you are creating on the General page. Select the table owner from the drop-down list "Schema". Leave Tablespace at the default setting. Select "XMLType" table.
Under the lower "Schema" option, select the XML schema owner, from the drop-down list.
Under "XML Schema", select the actual XML schema from the drop-down list.
Under "Element", select the required element to from the XMLType table, from the drop-down list.
Specify the storage:
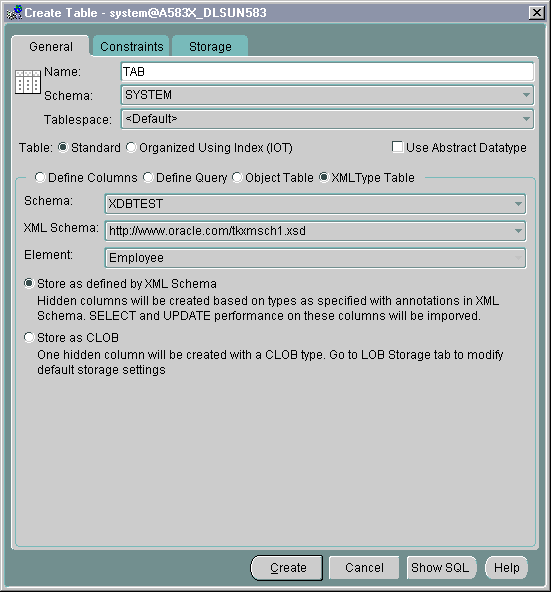
Text description of the illustration xtab1.gif
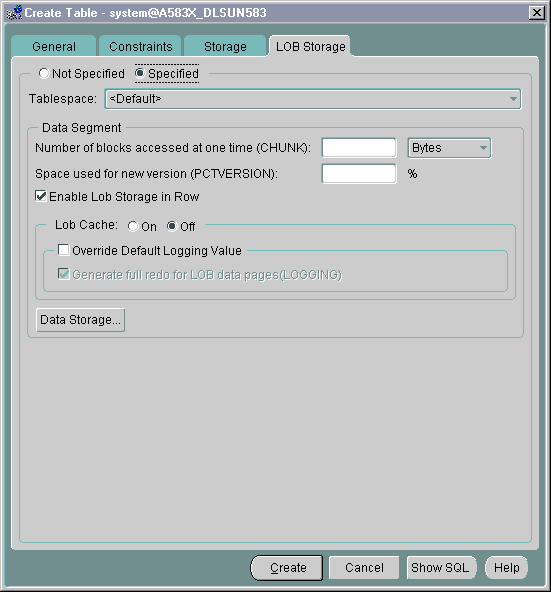
Text description of the illustration xtab2.gif
See Figure 21-22 shows the Create Table General page. To create a table with XMLType columns follow these steps:
XMLType from the drop-down list. The XMLType Options dialog window appears. See Figure 21-23.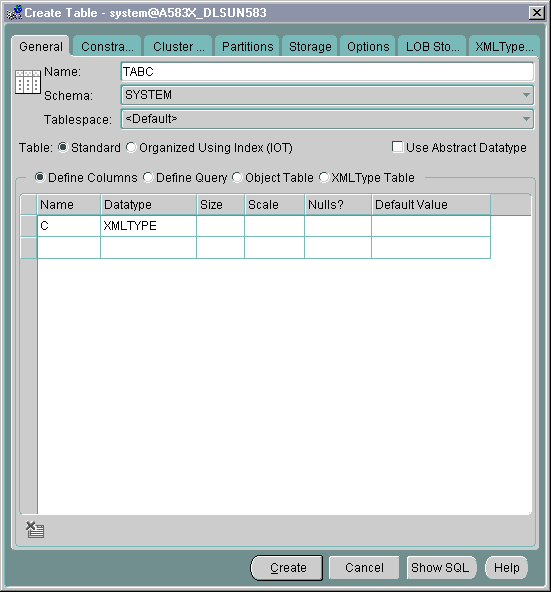
Text description of the illustration xtcol1.gif
XMLType column, whether it is XML schema-based or non-schema-based.
XMLType column, from the drop-down list.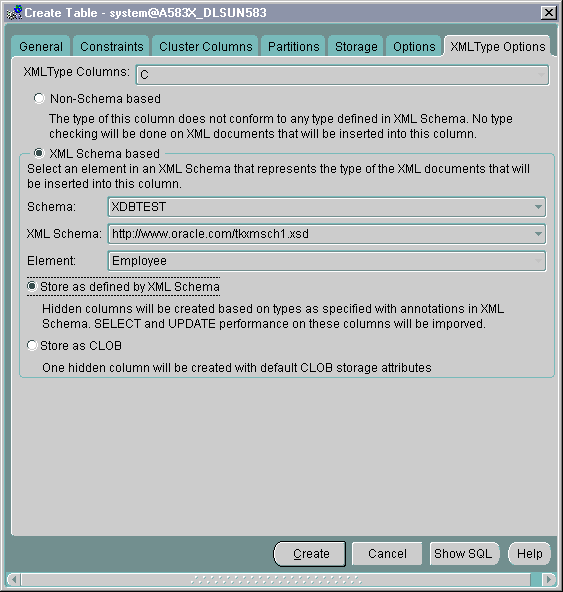
Text description of the illustration xtcol2.gif
Figure 21-24 shows the Create View General page. To create a view based on an XML schema, follow these steps:
From here you can select Force mode
XMLType view, select the "As Object" option. Select "XMLType" not "Object Type".XMLType column, from the drop-down list.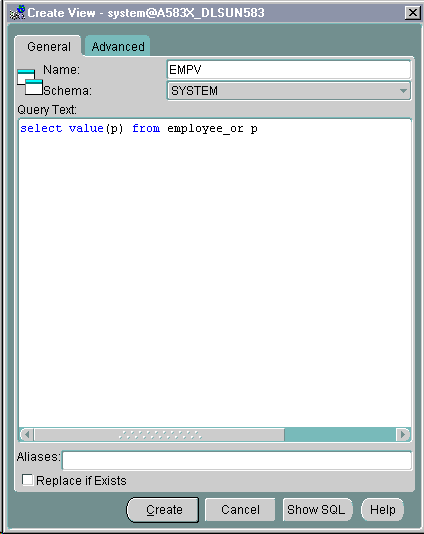
Text description of the illustration xview1.gif
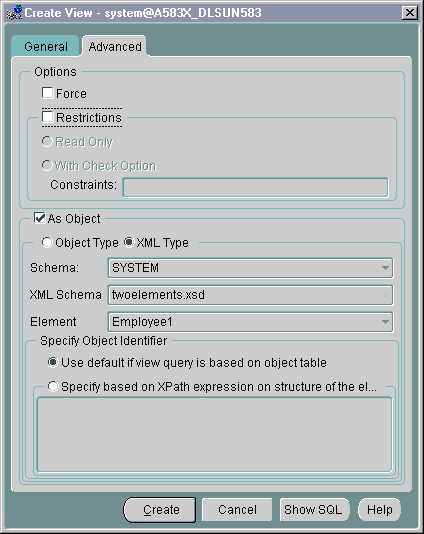
Text description of the illustration xview2.gif
See Figure 21-26 shows the Create Index General page. To create a function-based index based on an XPath expression follow these steps:
XMLType table or table with XMLType column from the drop-down list.
You can also enter an alias for a column expression. You can specify this alias inside your function-based index statement.
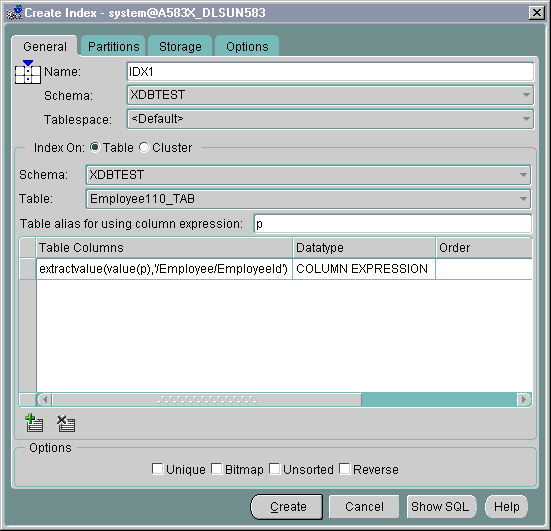
Text description of the illustration xindex1.gif