Release 2 (9.2)
Part Number A96621-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle9i XML Developer's Kits Guide - XDK Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96621-01 |
|
This chapter contains the following sections:
XML Parser for PL/SQL is provided with Oracle9i and is also available for download from the OTN site: http://otn.oracle.com/tech/xml.
It is located at $ORACLE_HOME/xdk/plsql/parser
Appendix B, "XDK for PL/SQL: Specifications" lists the specifications and requirements for running the XML Parser for PL/SQL. It also includes syntax cheat sheets.
The XML Parser for PL/SQL makes developing XML applications with Oracle9i a simplified and standardized process. With the PL/SQL interface, Oracle shops familiar with PL/SQL can extend existing applications to take advantage of XML as needed.
Since the XML Parser for PL/SQL is implemented in PL/SQL and Java, it can run "out of the box" on the Oracle9i Java Virtual Machine.
XML Parser for PL/SQL supports the W3C XML 1.0 specification. The goal is to be 100% conformant. It can be used both as a validating or non-validating parser.
In addition, XML Parser for PL/SQL provides the two most common APIs you need for processing XML documents:
This makes writing custom applications that process XML documents straightforward in the Oracle9i environment, and means that a standards-compliant XML parser is part of the Oracle9i platform on every operating system where Oracle9i is ported.
Figure 20-1 shows the XML Parser for PL/SQL usage and parsing process diagram.
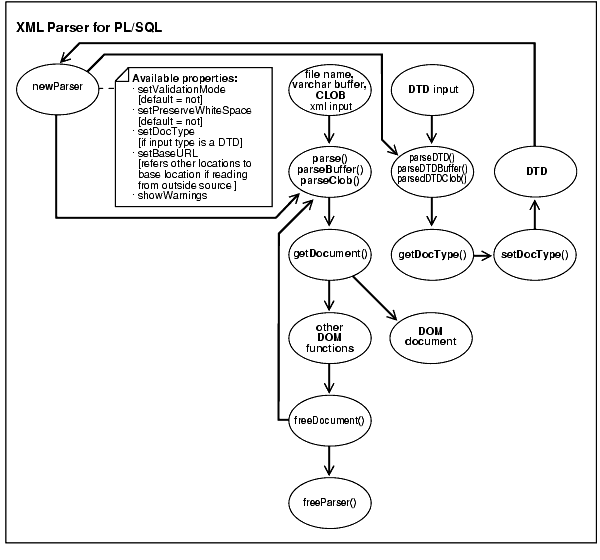
Table 20-1 lists available properties for the newParser procedure:
parse() if the XML input is a fileparseBuffer() if the XML input is an varchar bufferparserClob() if the XML input is a CLOBIf a DTD is also input, it is called by the following procedures:
For the XML Input: For an XML input, the parsed result from Parse(), ParserBuffer(), or ParserClob() procedures is sent to GetDocument().
getDocument() procedure performs the following:
freeDocument() function to free up the parser and parse the next XML inputfreeParser() to free up any temporary document structures created during the parsing processFor the DTD input: The parsed result from parseDTD(), parseDTDBuffer(), or parseDTDClob() is used by getDocType() function.
getDocType() then uses setDocType() to generate a DTD object.setDocType() to override the associated DTD.See Also:
|
The following is the default behavior for XML Parser for PLSQL XML:
The types and methods described in this manual are supplied with the PLSQL package xmlparser().
The $ORACLE_HOME/xdk/plsql/parser/sample/ directory contains two sample XML applications:
These show you how to use XML Parser for PL/SQL.
To run these sample programs carry out the following steps:
For example:
% sqlplus SQL> connect / as sysdba
For example, for user 'scott':
SQL> grant javauserpriv to scott; SQL> grant javasyspriv to scott;
You should see two messages that say "Grant succeeded." Contact your System Administrator, DBA, or Oracle support, if this does not occur.
Now, connect again as the user under which the PL/SQL parser was loaded in step 1. For example, for user 'scott' with password 'tiger':
SQL> connect scott/tiger
To run domsample carry out the following steps:
SQL> @domsample
The domsample.sql script defines a procedure domsample with the following syntax:
domsample(dir varchar2, inpfile varchar2, errfile varchar2)
where:
On Unix, you can could do the following:
SQL>execute domsample('/private/scott', 'family.xml', 'errors.txt');
On Windows NT, you can do the following:
SQL>execute domsample('c:\xml\sample', 'family.xml', 'errors.txt');
where family.xml is provided as a test case
To run xslsample, carry out these steps:
xslsample.sql script under SQL*Plus (if SQL*Plus is not up, first start it up, connecting as the user running this sample):
SQL>@xslsample
xslsample.sql script defines a procedure xslsample with the following syntax:
xslsample ( dir varchar2, xmlfile varchar2, xslfile varchar2, resfile varchar2, errfile varchar2 )
where:
xslsample procedure inside SQL*Plus by supplying appropriate arguments for 'dir', 'xmlfile', 'xslfile', and 'errfile'.
For example:
family.xml and iden.xslParsing XML document c:\/family.xml Parsing XSL document c:\/iden.xsl XSL Root element information Qualified Name: xsl:stylesheet Local Name: stylesheet Namespace: http://www.w3.org/XSL/Transform/1.0 Expanded Name: http://www.w3.org/XSL/Transform/1.0:stylesheet A total of 1 XSL instructions were found in the stylesheet Processing XSL stylesheet Writing transformed document
family.out should contain the following:
<family lastname="Smith"> <member memberid="m1">Sarah</member> <member memberid="m2">Bob</member> <member memberid="m3" mom="m1" dad="m2">Joanne</member> <member memberid="m4" mom="m1" dad="m2">Jim</member> </family>
You might see a delay in getting the output when executing the procedure for the first time. This is because Oracle JVM performs various initialization tasks before it can execute a Java Stored Procedure (JSP). Subsequent invocations should run quickly.
If you get errors, ensure the directory name is specified as a complete path on the file system
Otherwise, report the problem on the XML discussion forum at http://otn.oracle.com
This XML file inputs domsample.sql.
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?> <!DOCTYPE family SYSTEM "family.dtd"> <family lastname="Smith"> <member memberid="m1">Sarah</member> <member memberid="m2">Bob</member> <member memberid="m3" mom="m1" dad="m2">Joanne</member> <member memberid="m4" mom="m1" dad="m2">Jim</member> </family>
This DTD file is referenced by XML file, family.xml.
<!ELEMENT family (member*)> <!ATTLIST family lastname CDATA #REQUIRED> <!ELEMENT member (#PCDATA)> <!ATTLIST member memberid ID #REQUIRED> <!ATTLIST member dad IDREF #IMPLIED> <!ATTLIST member mom IDREF #IMPLIED>
-- This file demonstrates a simple use of the parser and DOM API. -- The XML file that is given to the application is parsed and the -- elements and attributes in the document are printed. -- It shows you how to set the parser options. set serveroutput on; create or replace procedure domsample(dir varchar2, inpfile varchar2, errfile varchar2) is p xmlparser.parser; doc xmldom.DOMDocument; -- prints elements in a document procedure printElements(doc xmldom.DOMDocument) is nl xmldom.DOMNodeList; len number; n xmldom.DOMNode; begin -- get all elements nl := xmldom.getElementsByTagName(doc, '*'); len := xmldom.getLength(nl); -- loop through elements for i in 0..len-1 loop n := xmldom.item(nl, i); dbms_output.put(xmldom.getNodeName(n) || ' '); end loop; dbms_output.put_line(''); end printElements; -- prints the attributes of each element in a document procedure printElementAttributes(doc xmldom.DOMDocument) is nl xmldom.DOMNodeList; len1 number; len2 number; n xmldom.DOMNode; e xmldom.DOMElement; nnm xmldom.DOMNamedNodeMap; attrname varchar2(100); attrval varchar2(100); begin -- get all elements nl := xmldom.getElementsByTagName(doc, '*'); len1 := xmldom.getLength(nl); -- loop through elements for j in 0..len1-1 loop n := xmldom.item(nl, j); e := xmldom.makeElement(n); dbms_output.put_line(xmldom.getTagName(e) || ':'); -- get all attributes of element nnm := xmldom.getAttributes(n); if (xmldom.isNull(nnm) = FALSE) then len2 := xmldom.getLength(nnm); -- loop through attributes for i in 0..len2-1 loop n := xmldom.item(nnm, i); attrname := xmldom.getNodeName(n); attrval := xmldom.getNodeValue(n); dbms_output.put(' ' || attrname || ' = ' || attrval); end loop; dbms_output.put_line(''); end if; end loop; end printElementAttributes; begin -- new parser p := xmlparser.newParser; -- set some characteristics xmlparser.setValidationMode(p, FALSE); xmlparser.setErrorLog(p, dir || '/' || errfile); xmlparser.setBaseDir(p, dir); -- parse input file xmlparser.parse(p, dir || '/' || inpfile); -- get document doc := xmlparser.getDocument(p); -- Print document elements dbms_output.put('The elements are: '); printElements(doc); -- Print document element attributes dbms_output.put_line('The attributes of each element are: '); printElementAttributes(doc); -- deal with exceptions exception when xmldom.INDEX_SIZE_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Index Size error'); when xmldom.DOMSTRING_SIZE_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'String Size error'); when xmldom.HIERARCHY_REQUEST_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Hierarchy request error'); when xmldom.WRONG_DOCUMENT_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Wrong doc error'); when xmldom.INVALID_CHARACTER_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Invalid Char error'); when xmldom.NO_DATA_ALLOWED_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Nod data allowed error'); when xmldom.NO_MODIFICATION_ALLOWED_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'No mod allowed error'); when xmldom.NOT_FOUND_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Not found error'); when xmldom.NOT_SUPPORTED_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Not supported error'); when xmldom.INUSE_ATTRIBUTE_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'In use attr error'); end domsample; / show errors;
-- This file demonstates a simple use of XSLT transformation capabilities. -- The XML and XSL files that are given to the application are parsed, -- the transformation specified is applied and the transformed document is -- written to a specified result file. -- It shows you how to set the parser options. set serveroutput on; create or replace procedure xslsample(dir varchar2, xmlfile varchar2, xslfile varchar2, resfile varchar2, errfile varchar2) is p xmlparser.Parser; xmldoc xmldom.DOMDocument; xmldocnode xmldom.DOMNode; proc xslprocessor.Processor; ss xslprocessor.Stylesheet; xsldoc xmldom.DOMDocument; docfrag xmldom.DOMDocumentFragment; docfragnode xmldom.DOMNode; xslelem xmldom.DOMElement; nspace varchar2(50); xslcmds xmldom.DOMNodeList; begin -- new parser p := xmlparser.newParser; -- set some characteristics xmlparser.setValidationMode(p, FALSE); xmlparser.setErrorLog(p, dir || '/' || errfile); xmlparser.setPreserveWhiteSpace(p, TRUE); xmlparser.setBaseDir(p, dir); -- parse xml file dbms_output.put_line('Parsing XML document ' || dir || '/' || xmlfile); xmlparser.parse(p, dir || '/' || xmlfile); -- get document xmldoc := xmlparser.getDocument(p); -- parse xsl file dbms_output.put_line('Parsing XSL document ' || dir || '/' || xslfile); xmlparser.parse(p, dir || '/' || xslfile); -- get document xsldoc := xmlparser.getDocument(p); xslelem := xmldom.getDocumentElement(xsldoc); nspace := xmldom.getNamespace(xslelem); -- print out some information about the stylesheet dbms_output.put_line('XSL Root element information'); dbms_output.put_line('Qualified Name: ' || xmldom.getQualifiedName(xslelem)); dbms_output.put_line('Local Name: ' || xmldom.getLocalName(xslelem)); dbms_output.put_line('Namespace: ' || nspace); dbms_output.put_line('Expanded Name: ' || xmldom.getExpandedName(xslelem)); xslcmds := xmldom.getChildrenByTagName(xslelem, '*', nspace); dbms_output.put_line('A total of ' || xmldom.getLength(xslcmds) || ' XSL instructions were found in the stylesheet'); -- make stylesheet ss := xslprocessor.newStylesheet(xsldoc, dir || '/' || xslfile); -- process xsl proc := xslprocessor.newProcessor; xslprocessor.showWarnings(proc, true); xslprocessor.setErrorLog(proc, dir || '/' || errfile); dbms_output.put_line('Processing XSL stylesheet'); docfrag := xslprocessor.processXSL(proc, ss, xmldoc); docfragnode := xmldom.makeNode(docfrag); dbms_output.put_line('Writing transformed document'); xmldom.writeToFile(docfragnode, dir || '/' || resfile); -- deal with exceptions exception when xmldom.INDEX_SIZE_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Index Size error'); when xmldom.DOMSTRING_SIZE_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'String Size error'); when xmldom.HIERARCHY_REQUEST_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Hierarchy request error'); when xmldom.WRONG_DOCUMENT_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Wrong doc error'); when xmldom.INVALID_CHARACTER_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Invalid Char error'); when xmldom.NO_DATA_ALLOWED_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Nod data allowed error'); when xmldom.NO_MODIFICATION_ALLOWED_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'No mod allowed error'); when xmldom.NOT_FOUND_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Not found error'); when xmldom.NOT_SUPPORTED_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'Not supported error'); when xmldom.INUSE_ATTRIBUTE_ERR then raise_application_error(-20120, 'In use attr error'); end xslsample; / show errors;
When I try to use the oraxsl I get the following: Exception in thread main:
java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError" oracle/xml/parser/v2/oraxsl.
How do I fix this?
Answer: If you are running outside the database you need to make sure the xmlparserv2.jar is explicitly in your CLASS_PATH, not simply its directory. If from the database you need to make sure it has been properly loaded and that JServer initialized.
I cannot get the element value using the PL/SQL XMLDOM. Here is the code fragment:
...nl := xmldom.getElementsByTagName(doc, '*'); len := xmldom.getLength(nl) ;-- loop through elements for i in 0..len-1 loop n := xmldom.item(nl, i); elename := xmldom.getNodeName(n); eleval := xmldom.getNodeValue(n); ...elename is Ok, but eleval is NULL.
Associating with a text node does not seem to work, or I am not doing it correctly? I receive a compile error, as in this example:
...t xmldom.DOMText; ...t := xmldom.makeText(n); eleval := xmldom.getNodeValue(t);
What am I doing wrong?
Answer: To get the text node value associated with the element node, you must perform additional node navigation through xmldom.getFirstChild(n).
To illustrate, change printElements() in DOMSample.sql as follows:
begin -- get all elements nl := xmldom.getElementsByTagName(doc, '*'); len := xmldom.getLength(nl); -- loop through elements for i in 0..len-1 loop n := xmldom.item(nl, i); dbms_output.put(xmldom.getNodeName(n)); -- get the text node associated with the element node n := xmldom.getFirstChild(n); if xmldom.getNodeType(n) = xmldom.TEXT_NODE then dbms_output.put('=' | | xmldom.getNodeValue(n)); end if; dbms_output.put(' '); end loop; dbms_output.put_line(''); end printElements;
This produces the following output, listing the elements:
family member=Sarah member=Bob member=Joanne member=Jim
The attributes of each element are:
family:familylastname val=Smithmember:membermemberid val=m1member:membermemberid val=m2member:membermemberid val=m3 mom val=m1 dad val=m2member:membermemberid val=m4 mom val=m1 dad val=m2
I downloaded XDK for PL/SQL but it requires OAS. Do you have any idea how to run this in an IIS environment?
Answer: If you're going to use IIS, it would be better to use the XML Parser for Java version 2. You'll also need Oracle9i.
I am having problems parsing a DTD file contained in a CLOB. I used the xmlparser.parseDTDClob API, provided by the XML Parser for PL/SQL.
I received the following error:
"ORA-29531: no method parseDTD in class oracle/xml/parser/plsql/XMLParserCover".
The procedure xmlparser.parseDTDClob calls a Java Stored Procedure xmlparsercover.parseDTDClob, which in turn calls another Java Stored Procedure xmlparsercover.parseDTD.
I have confirmed that the class file, oracle.xml.parser.plsql.XMLParserCover, has been loaded into the database, and that it has been published. So the error message does not make sense. The procedure used to call xmlparser.parseDTDClob is:
create or replace procedure parse_my_dtd as p xmlparser.parser; l_clob clob; begin p := xmlparser.newParser; select content into l_clob from dca_documents where doc_id = 1; xmlparser.parseDTDClob(p,l_clob,'site_template'); end; API Documentation for xmlparser.parseDTDClob: parseDTDClob PURPOSE Parses the DTD stored in the given clob SYNTAX PROCEDURE parseDTDClob(p Parser, dtd CLOB, root VARCHAR2); PARAMETERS p (IN)- parser instance dtd (IN)- dtd clob to parse root (IN)- name of the root element RETURNS Nothing COMMENTS
Any changes to the default parser behavior should be made before calling this procedure. An application error is raised if parsing failed, for some reason. Description of the table dca_documents:
DOC_ID NOT NULL NUMBER DOC_NAME NOT NULL VARCHAR2(350) DOC_TYPE VARCHAR2(30) DESCRIPTION VARCHAR2(4000) MIME_TYPE VARCHAR2(48) CONTENT NOT NULL CLOB CREATED_BY NOT NULL VARCHAR2(30) CREATED_ON NOT NULL DATE UPDATED_BY NOT NULL VARCHAR2(30) UPDATED_ON NOT NULL DATE
The contents of the DTD:
<!ELEMENT site_template (component*)> <!ATTLIST site_template template_id CDATA #REQUIRED> <!ATTLIST site_template template_name CDATA #REQUIRED> <!ELEMENT component (#PCDATA)> <!ATTLIST component component_id ID #REQUIRED> <!ATTLIST component parent_id ID #REQUIRED> <!ATTLIST component component_name ID #REQUIRED>
Answer: This is a known issue in release 1.0.1 of the XML Parser for PL/SQL. Here is the workaround.
First, make a backup of ./plsqlxmlparser_1.0.1/lib/sql/xmlparsercover.sql
Then, in line 18 of xmlparsercover.sql, change the string oracle.xml.parser.plsql.XMLParserCover.parseDTD to oracle.xml.parser.plsql.XMLParserCover.parseDTDClob
Verify that Line 18 now reads:
procedure parseDTDClob(id varchar2, DTD CLOB, root varchar2, err in out varchar2) is language java name 'oracle.xml.parser.plsql.XMLParserCover.parseDTDClob(java.lang.String, oracle.sql.CLOB, java.lang.String, java.lang.String[])';
Save the file, then rerun xmlparsercover.sql in SQL*Plus. Assuming you've loaded XMLParser version 2 release 2.0.2.6 into the database, this should solve your problem.
I have just started using XML Parser for PL/SQL. I am have trouble getting the text between the begin tag and the end tag into a local variable. Do you have examples?
Answer: You just have to use the following:
selectSingleNode("pattern"); getNodeValue()
Remember, if you are trying to get value from a Element node, you have to move down to the #text child node, for example, getFirstChild.getNodeValue()
Suppose you need to get the text contained between the starting and ending tags of a xmldom.DOMNode n. The following two lines will suffice.
n_child:=xmldom.getFirstChild(n); text_value:=xmldom.getNodeValue(n_child));
n_child is of type xmldom.DOMNode.
text_value is of type varchar2.
We are using the XML Parser for PLSQL and are trying to parse an XML document. We are getting a Java security error:
ORA-29532: Java call terminated by uncaught Java exception: java.lang.SecurityException ORA-06512: at "NSEC.XMLPARSERCOVER", line 0 ORA-06512: at "NSEC.XMLPARSER", line 79 ORA-06512: at "NSEC.TEST1_XML line 36 ORA-06512: at line 5
Do we need to grant to user? The syntax appears correct. We also get the error when we run the demo.
Answer: If the document you are parsing contains a doctype which has a System URI with a protocol like file:/// or http:/// then you need to grant an appropriate privilege to your current database user to be able to "reach out of the database", so to speak, and open a stream on the file or URL.CONNECT SYSTEM/MANAGER. The following code should do it:
GRANT JAVAUSERPRIV, JAVASYSPRIV TO youruser;
I have downloaded and installed the plxmlparser_V1_0_1.tar.gz. The readme said to use loadjava to upload xmlparserv2.jar and plsql.jar in order. I tried to load xmlparserv2.jar using the following command:
loadjava -user test/test -r -v xmlparserv2.jar
to upload the jar file into Oracle8i. After much of the uploading, I got the following error messages:
identical: oracle/xml/parser/v2/XMLConstants is unchanged from previously loaded fileidentical: org/xml/sax/Locator is unchanged from previously loaded fileloading : META-INF/MANIFEST.MFcreating : META-INF/MANIFEST.MFError while creating resource META-INF/MANIFEST.MF ORA-29547: Java system class not available: oracle/aurora/rdbms/Compilerloading : oracle/xml/parser/v2/mesg/XMLErrorMesg_en_US.propertiescreating : oracle/xml/parser/v2/mesg/XMLErrorMesg_en_US.propertiesError while creating ...
Then I removed -r from the previous command:
loadjava -user test/test -v xmlparserv2.jar
I still got errors but it's down to four:
.identical: org/xml/sax/Locator is unchanged from previously loaded fileloading : META-INF/MANIFEST.MFcreating : META-INF/MANIFEST.MFError while creating ...
I think I have installed the JServer on the database correctly.
Answer: The JServer option is not properly installed if you're getting errors like this during loadjava. You need to run INITJVM.SQL and INITDBJ.SQL to get the JavaVM properly installed. Usually these are in the ./javavm subdirectory of your Oracle Home.
I am trying to execute domsample on dom1151. This is an example that is provided with the XML Parser for PL/SQL. The XML file family.xml is present in the directory /hrwork/log/pqpd115CM/out.
I am getting the following error:
Usage of domsample is domsample(dir, inpfile, errfile) SQL> begin domsample('/hrwork/log/pqpd115CM/out','family.xml','errors.txt'); end; / Error generated : begin * ERROR at line 1: ORA-20100: Error occurred while parsing: No such file or directory ORA-06512: at "APPS.XMLPARSER", line 22 ORA-06512: at "APPS.XMLPARSER", line 69 ORA-06512: at "APPS.DOMSAMPLE", line 80 ORA-06512: at line 2
Answer: From your description it sounds like you have not completed all of the steps in the sample and Readme without errors. After confirming that the xmlparserv2.jar is loaded, carefully complete the steps again.
In an Oracle8i database, we have CLOBs which contain well-formed XML documents up to 1 MB in size.
We want the ability to extract only part of the CLOB (XML document), modify it, and replace it back in the database rather than processing the entire document.
Second, we want this process to run entirely on the database tier.
Which products or tools are needed for this? This may be possible with the JVM which comes with Oracle9i. There also may be some PL/SQL tools available to achieve this by means of stored procedures.
Answer: You can do this by using either of the following:
XML Parser for PLSQL has methods such as the following:
xmlparser.parseCLOB()xslProcessor.selectNodes(), to find what part of the doc you are looking forxmldom.* methods to manipulate the content of the XML documentxmldom.writeToCLOB() to write it backIf you wanted to do fine-detail updates on the text of the CLOB, you would have to use DBMS_LOB.* routines, but this would be tricky unless the changes being made to the content don't involve any increase or decrease in the number of characters.
We are parsing a 50Mb XML file. We have upped the java_pool_size to 150Mb with a shared_pool_size of 200Mb. We get the following "out of memory" errors in the Oracle XML parser:
last entry at 2000-04-26 10:59:27.042: VisiBroker for Java runtime caught exception: java.lang.OutOfMemoryError at oracle.xml.parser.v2.XMLAttrList.put(XMLAttrList.java:251) at oracle.xml.parser.v2.XMLElement.setAttribute(XMLElement.java:260) at oracle.xml.parser.v2.XMLElement.setAttribute(XMLElement.java:228) at cars.XMLServer.processEXL(XMLServer.java:122)
It's trying to create a new XML attribute and crashes with OutOfMemoryError.
Answer: You should not be using the DOM parser for parsing a 50Mb XML file. You need to use the SAX parser, which parses files of arbitrary size because it does not create an in-memory tree of nodes as it goes.
If you are using DOM, you should seriously consider moving to SAX which processes the XML file sequentially instead of trying to build an in-memory tree that represents the file.
Using SAX we process XML files in excess of 180Mb without any problems and with very low memory requirements.
Rule of thumb for choosing between DOM and SAX:
DOM:
SAX:
Answer: While the memory use is directly dependent on the document size, it should also be realized that the PL/SQL parser uses the Java parser and thus the Oracle JServer is being run. JServer typically requires 40-60 MB depending on its configuration.
Answer: Yes, if you are running the parser in the database, you do need JServer because the PL/SQL parser currently uses the XML Parser for Java under the covers. JServer exists in both the Standard and Enterprise versions. A forthcoming version of XML Parser for PL/SQL using C underneath is being developed for applications that do not have access to a Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Answer: The XML parser accepts any XML document and gives you a tree-based API (DOM) to access or modify the document's elements and attributes. It also supports XSLT which allows transformation from one XML document to another.
Answer: No, you need to include the proper encoding declaration in your document according to the specification. You cannot use setCharset(DOMDocument) to set the encoding for the input of your document. SetCharset(DOMDocument) is used with oracle.xml.parser.v2.XMLDocument to set the correct encoding for the printing.
How do I get the number of elements in a tag using the Parser?
Answer: You can use the getElementByTagName (elem DOMElement, name IN VARCHAR2) method that returns a DOMNodeList of all descent elements with a given tag name. You can then find out the number of elements in that DOMNodeList to determine the number of the elements in the particular tag.
Answer: We do not currently have any method that can directly parse an XML document contained within a string. You can use one of the following as a workaround:
parse (Parser, VARCHAR2) to parse XML data stored in the given URL or the given file,parseBuffer (Parser, VARCHAR2) to parser XML data stored in the given buffer, orparseCLOB (Parser, VARCHAR2) to parse XML data stored in the give CLOB.Answer: If you are using Internet Explorer 5 as your browser, you can display the XML document directly. Otherwise, you can use our XSLT processor in version 2 of the parser to create the HTML document using an XSL Stylesheet. Our Java Transviewer bean also enables you to view your XML document.
Answer: You can specify the character sets for writing to a file or a buffer. Writing to a CLOB will be use the default character set for the database that you are writing to. Here are the methods to use:
procedure writeToFile(doc DOMDocument, fileName VARCHAR2, charset VARCHAR2);procedure writeToBuffer(doc DOMDocument, buffer IN OUT VARCHAR2, charset VARCHAR2);procedure writeToClob(doc DOMDocument, cl IN OUT CLOB, charset VARCHAR2);Answer: You cannot have "raw" ampersands in XML data. You need to use the entity, & instead. This is defined in the XML standard.
Answer: Refer to the following example:
inpPath VARCHAR2; inpFile VARCHAR2; p xmlparser.parser; doc xmldom.DOMDocument; -- initialize a new parser object; p := xmlparser.newParser; -- parse the file xmlparser.parse(p, inpPath || inpFile); -- generate a document object doc := xmlparser.getDocument(p);
Answer: As long as a version 1.1.x or 1.2.x JavaVM for Linux exists in your installation, you can run the Oracle XML Parser for Java there. Otherwise, you can use the C or C++ XML Parser for Linux.
Answer: The current XML Parsers support Namespaces. Schema support will be included in a future release.
Answer: The DTD file defined in the <!DOCTYPE> declaration must be relative to the location of the input XML document. Otherwise, you'll need to use the setBaseDir(Parser, VARCHAR2) functions to set the base URL to resolve the relative address of the DTD.
Answer: You need to include a reference to the applicable DTD in your XML document. Without it there is no way that the parser knows what to validate against. Including the reference is the XML standard way of specifying an external DTD. Otherwise you need to embed the DTD in your XML Document.
Answer: Yes, DTD caching is optional and it is not enabled automatically.
Answer: You need to do some preprocessing to the file, and then put it through the DOM parser again, which will produce a valid, well-formed XML document with the DOCTYPE tag contained within.
Answer: The parser accepts an XML formatted document and constructs in memory a DOM tree based on its structure. It will then check whether the document is well-formed and optionally whether it complies with a DTD. It also provides methods to traverse the tree and return data from it.
Answer: If you check the DOM spec referring to the table discussing the node type, you will find that if you are creating an element node, its nodeValue is to be null and hence cannot be set. However, you can create a text node and append it to the element node. You can store the value in the text node.
Answer: If you're using DOM, the you can use the NamedNodeMap methods to get the elements.
Answer: Use the createTextNode() method to create a new text node. Then convert the DOMElement to a DOMNode using makeNode(). Now, you can use appendChild() to append the text node to the DOMElement.
Answer: You need to check at which level your data resides. For example,
The text is the first child node of the first DOM element in the document. According to the DOM Level 1 spec, the value of an ELEMENT node is null and the getNodeValue() method will always return null for an ELEMENT type node. You have to get the TEXT children of an element and then use the getNodeValue() method to retrieve the actual text from the nodes.
Answer: Yes it can.
Answer: Here are two frequently missing steps in installing the PL/SQL parser:
$ORACLE_HOME/javavm/install/initjvm.sqlI am having problems parsing a DTD file contained in a CLOB. I used the xmlparser.parseDTDClob API, provided by the XML Parser for PL/SQL.
The following error was thrown:
"ORA-29531: no method parseDTD in class oracle/xml/parser/plsql/XMLParserCover"
I managed to work out the following:
The procedure xmlparser.parseDTDClob calls a Java Stored Procedure xmlparsercover.parseDTDClob, which in turn calls another Java Stored Procedure xmlparsercover.parseDTD.
I have confirmed that the class file oracle.xml.parser.plsql.XMLParserCover has been loaded into the database, and that it has been published. So the error message does not make sense.
I am not able to figure out whether I am doing it right or whether this is a bug in the parser API.
The procedure use to call "xmlparser.parseDTDClob" : ---------------------------------------------------- create or replace procedure parse_my_dtd as p xmlparser.parser; l_clob clob; begin p := xmlparser.newParser; select content into l_clob from dca_documents where doc_id = 1; xmlparser.parseDTDClob(p,l_clob,'site_template'); end;
API Documentation for xmlparser.parseDTDClob:
parseDTDClob PURPOSE Parses the DTD stored in the given clob SYNTAX PROCEDURE parseDTDClob(p Parser, dtd CLOB, root VARCHAR2); PARAMETERS p (IN)- parser instance dtd (IN)- dtd clob to parse root (IN)- name of the root element RETURNS Nothing COMMENTS
Any changes to the default parser behavior should be effected before calling this procedure. An application error is raised if parsing failed, for some reason.
Description of the table dca_documents:
DOC_ID NOT NULL NUMBER DOC_NAME NOT NULL VARCHAR2(350) DOC_TYPE VARCHAR2(30) DESCRIPTION VARCHAR2(4000) MIME_TYPE VARCHAR2(48) CONTENT NOT NULL CLOB CREATED_BY NOT NULL VARCHAR2(30) CREATED_ON NOT NULL DATE UPDATED_BY NOT NULL VARCHAR2(30) UPDATED_ON NOT NULL DATE
The contents of the DTD:
<!ELEMENT site_template (component*)> <!ATTLIST site_template template_id CDATA #REQUIRED> <!ATTLIST site_template template_name CDATA #REQUIRED> <!ELEMENT component (#PCDATA)> <!ATTLIST component component_id ID #REQUIRED> <!ATTLIST component parent_id ID #REQUIRED> <!ATTLIST component component_name ID #REQUIRED>
Answer 1: It appears to be a typo in the xmlparsercover.sql script which is defining the Java Stored Procedures that wrap the XMLParser. It mentions the Java method name parseDTD in the 'is language java name' part when parseDTD should be parseDTDClob (case-sensitive).
If you:
procedure parseDTDClob(id varchar2, dtd CLOB, root varchar2, err in out varchar2) is language java name 'oracle.xml.parser.plsql.XMLParserCover.parseDTD (java.lang.String, oracle.sql.CLOB, java.lang.String, java.lang.String[])';
to say:
procedure parseDTDClob(id varchar2, dtd CLOB, root varchar2, err in out varchar2) is language java name 'oracle.xml.parser.plsql.XMLParserCover.parseDTDClob (java.lang.String, oracle.sql.CLOB, java.lang.String, java.lang.String[])';
That is, change the string:
'oracle.xml.parser.plsql.XMLParserCover.parseDTD
to
'oracle.xml.parser.plsql.XMLParserCover.parseDTDClob
and rerun the xmlparsercover.sql script you should be in business.
I filed a bug 1147031 to get this typo corrected in a future release.
Note: Your DTD had syntactic errors in it, but I was able to run the following without problem after making the change:
declare c clob; v varchar2(400) := '<!ELEMENT site_template (component* )> <!ATTLIST site_template template_name CDATA #IMPLIED tempmlate_id CDATA #IMPLIED > <!ELEMENT component (#PCDATA )> <!ATTLIST component component_id ID #REQUIRED parent_id IDREF #IMPLIED component_name CDATA #IMPLIED >'; begin delete from dca_documents; insert into dca_documents values(1,empty_clob()) returning content into c; dbms_lob.writeappend(c,length(v),v); commit; parse_my_dtd; end;
Answer 2: What do you want to do with the LOB? The LOB can either be a temporary LOB or a persistent LOB. In case of persistent LOBs, you need to insert the value into a table. In case of temp LOB you can instantiate it in your program.
For example:
persistant lob declare clob_var CLOB; begin insert into tab_xxx values(EMPTY_CLOB()) RETURNING clob_col INTO clob_var; dbms_lob.write(,,,,); // send to AQ end; temp lob ----- declare a clob; begin dbms_lob.createtemporary(a,DBMS_LOB.SESSION); dbms_lob.write(...); // send to AQ end; /
Also refer to Oracle9i Application Developer's Guide - Large Objects (LOBs). There are six books (in PDF), one for each language access (C(OCI), Java, PL/SQL, Visual Basic, Pro*C/C++, Pro*Cobol)) and it is quite comprehensive. If this is PL/SQL, I believe you can just do the following:
myClob CLOB = clob();
I have tried the DBMS_LOB.createtemporary() which works.
Answer 3: Here's what you need to do if you are using LOBs with AQ:
create type myAdt (id NUMBER, cdata CLOB);
The queue table must be declared to be of type myAdt
empty_clob() to fill the LOB field
myMessage := myAdt(10, EMPTY_CLOB();
clob_loc clob; enq_msgid RAW(16); DBMS_AQ.enqueue('queue1', enq_opt, msg_prop, myMessage, enq_msgid)
select t.user_data.cdata into clob_loc from qtable t where t.msgid = enq_msgid;
dbms_lob.writeThere is an example of this is in the Oracle9i Application Developer's Guide - Advanced Queuing. If you are using the Java API for AQ, the procedure is slightly more complicated.
I downloaded the javaparser, version 2 and the XML parser utility, and I'm using the PL/SQL parser interface. I have an XML file that is a composite of three tags and when parsing it generates the following error:
ORA-20100: Error occurred while parsing: Unterminated string
When I separate the document into individual tags, two are OK, but the third generates this error:
ORA-20100: Error occurred while parsing: Invalid UTF8 encoding
Answer: If you document is the "composite of three tags" then it is not a well-formed document as it has more than one root element. Try putting a start and end tag around the three.
I am working with the XML parser for PL/SQL on NT. According to your Parser API documentation it is possible to parse a given URL, too:> Parses XML stored in the given URL/file and returns> the built DOM DocumentNow, parsing from file works fine, but any form of URL raises ORA-29532:... java.io.FileNotFoundException.
Can you give an example of a call?
Answer: To access external URLs, you need set up your proxy host and port. For example using this type of syntax:
java -Dhttp.proxyHost=myproxy.mydomain.com -Dhttp.proxyPort=3182DOMSample myxml.xml
We need to parse HTML files as follows:
a hrefa href found, extract the file/pathname being linked toa href, passing the file/pathname as a parameter.Does it make sense to use the PL/SQL XML parser to do this? If so, how easy/hard would it be, and how can we find out how to do this?
Answer: Since HTML files aren't necessary well formed XML documents, are you sure you want to use XML parser? Won't Perl be a better choice? I'm not sure whether PL/SQL parser supports the following methods but just for your information:
getElementsByTagName() retrieves all matching nodes.getNodeValue() will return a string.setNodeValue() sets node values.Answer 3: It supports those methods, but not over an ill-formed HTML file.
I'm trying to get the data to a Web browser in the client side while all the processing has to take place on the server (Oracle 7 release 7.3.4), using:
Are these two components sufficient to get the job done?
Answer: Dependencies for XSQL Page Processor states:
You'll also need XSQL Page Processor itself.
Does the XML Parser for Java version 2, work with Oracle 7 release 7.3.4.?
Is XML- SQL Utility part of XML Parser for Java version 2, or does it need to be downloaded separately?
Answer:
I am having problems obtaining the value between XML tags after using xmlparser(). Below is code from the DOMSAMPLE.SQL example:
-- loop through elementsfor i in 0..len-1 loop n := xmlparser.item(nl, i); dbms_output.put(xmlparser.getNodeName(n)
Answer: I encountered the same problem. I found out that getNodeValue() on Element Node returns null. However, getNodeValue() on the text node returns the value.
Is there a way to retrieve all children or grandchildren, and so on, of a particular node in a DOM tree using the DOM API? Or is there a work-around? We are using the XML Parser for PL/SQL.
Answer: Try the following:
DECLARE nodeList xmldom.DOMNodeList; theElement xmldom.DOMElement; BEGIN :nodeList := xmldom.getElementsByTagName( theElement,'*'); :END;
This gets all children nodes rooted as the element in "theElement".
We want to parse XML, apply XSL, and get the transformed result in the form of an XML document. We are using XML Parser for PL/SQL. Our script does not add PI instruction <?xml version="1.0"?> to the transformed result.
XSLProcessor.processXSL method returns documentfragment object.
Create DOMdocument object from that documentfragment object using: finaldoc := xmldom.MakeDocument(docfragnode);
Write to result file using where finaldoc is created of type xmldom.DOMDocument:
xmldom.writeToFile(finaldoc, dir || '/' || resfile);
This method is available for DOMDocument, but we are getting:
ora-29532 "Uncaught java exception:java.lang.ClassCastException"
I am not sure if converting documentfragment to domdocument object adds instruction "<?xml version="1.0"?> ", or must we add this instruction through XSL?
Answer: If you have created a new DOMDocument and then appended the document fragment to it, then you can use xmldom.WriteToBuffer() or similar routine to serialize with the XML declaration in place.
|
 Copyright © 2001, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|