Release 9.2.0
Part Number A96674-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle Enterprise Manager Concepts Guide Release 9.2.0 Part Number A96674-01 |
|
Oracle Enterprise Manager combines Oracle's system management Console, common services, and integrated platform graphical tools. It provides an integrated set of standard database administration applications to help automate and simplify the common daily tasks of administrators. These supplemental applications focus on specific areas of database administration, helping administrators with their daily and routine tasks of managing databases and other services and keeping them operational.
This chapter presents an overview of Oracle Enterprise Manager's benefits, architecture, and major components.
The chapter is divided into the following sections:
The primary interface to managing your Oracle environment is the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console, the client interface. The Console is part of the Oracle Enterprise Manager three-tier architecture, which is discussed in more detail later in this chapter.
From the Console, you can perform the following tasks:
Oracle Enterprise Manager architecture consists of a three-tier framework. Unlike a two-tier client-server structure, where a client tier responsible for the presentation of information accesses data from a server, Oracle Enterprise Manager utilizes a three-tier architecture which includes:
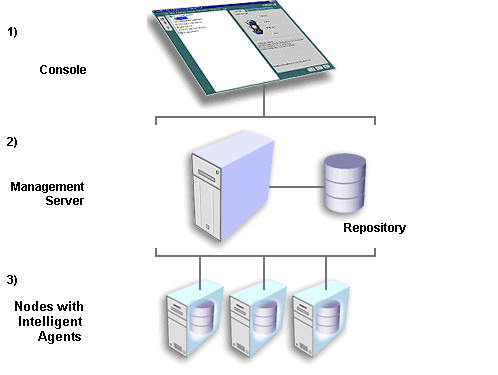
Text description of the illustration architec.gif
With Oracle Enterprise Manager's three-tier framework, data-intensive business logic is moved off the client and is recast as shared services on one or more middle-tier Oracle Management Servers, providing reliability, scalability, and fault tolerance for enterprise environments.
Because not all enterprises need to implement Enterprise Manager as a three tier system, Enterprise Manager is also available in standalone mode, a two-tier framework which connects directly to the databases. The Console launched standalone allows a single person to use one or more applications without requiring an Oracle Management Server or Intelligent Agent.
Use the standalone Console if you want to perform basic administrative tasks that do not require the job, event, or group system.
If you want to use events, jobs, sharing of administrative data, blackouts, groups, enhanced notifications, historical collections, and have the ability to run applications in a web browser, use Enterprise Manager connected to the Management Server. For more information about the standalone Console, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Configuration Guide.
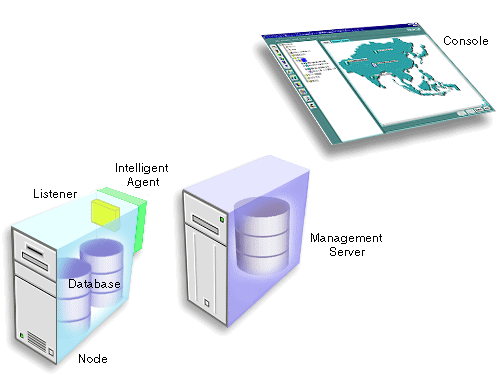
The first tier of Oracle Enterprise Manager is comprised of clients such as consoles and management applications, which present a graphical user interface to administrators for all management tasks. These client components can be installed locally or brought up with a web browser.
The first-tier clients depend on second-tier Oracle Management Servers for the bulk of their application logic.
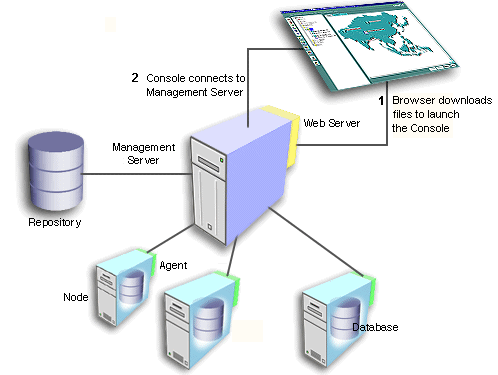
Text description of the illustration first_ti.gif
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Console provides menus, toolbars, and drawers allowing access to Oracle tools.
The Console uses a master/detail configuration to provide an integrated, consistent, and efficient way of managing your enterprise environment. When an object in the Navigator (master) is selected, the appropriate interface is displayed on the right-hand side of the Console (the detail pane). Information displayed on the right-hand side of the Console can be a multi-column list, property sheet, or overview page.
In addition, Events, Jobs, Groups, and Report definitions have been integrated into the Navigator as well.
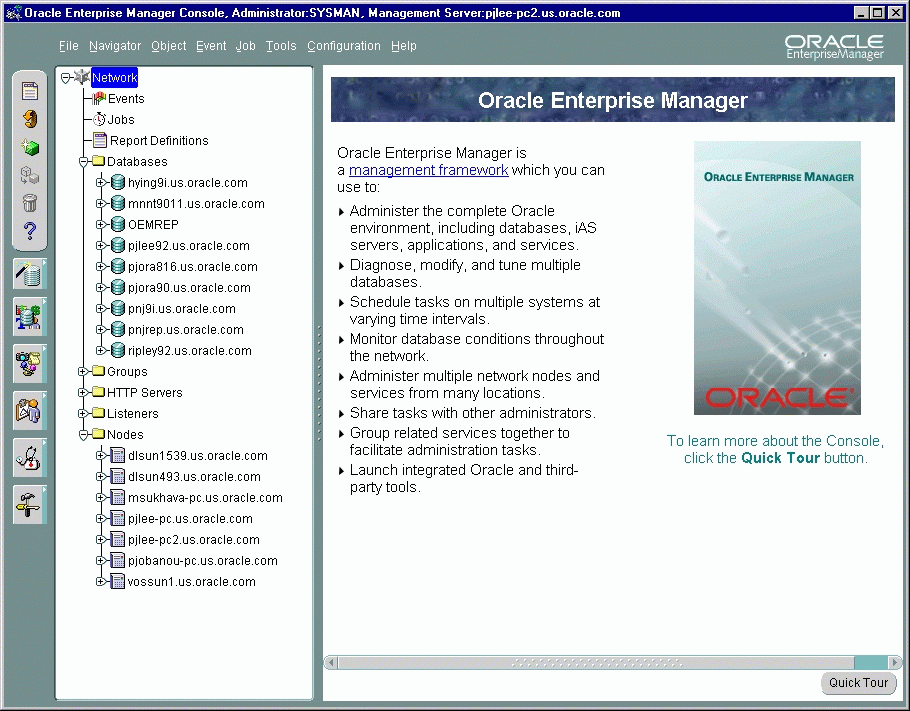
Text description of the illustration console.gif
|
Note: See Chapter 2, "The Console" for descriptions of the basic components of the Console and how they are organized. For information about the Console menus, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide. |
The second tier of the Oracle Enterprise Manager framework is comprised of one or more Oracle Management Servers. The Management Server is the core of the Enterprise Manager framework. It provides administrative user accounts, processes management functions such as jobs and events, and manages the flow of information between the Console (first tier) and the nodes with Intelligent Agents (third tier).
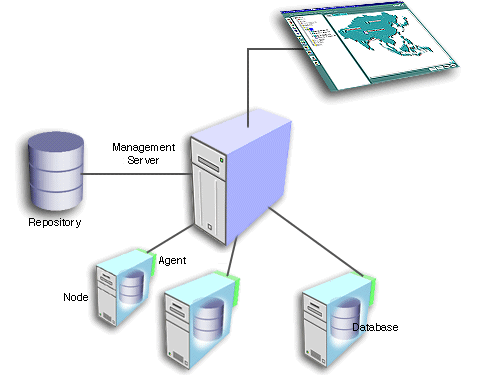
Text description of the illustration oms.gif
The Oracle Management Server uses a repository to store all system data, application data, information about the state of managed nodes, and information about any system management packs. A repository is a set of database tables that must be located in a supported Oracle database accessible to the Oracle Management Server.
If necessary, a large enterprise can use more than one Oracle Management Server in the middle tier. When multiple Oracle Management Servers are used, they share and balance the workload, ensuring high performance and scalability.
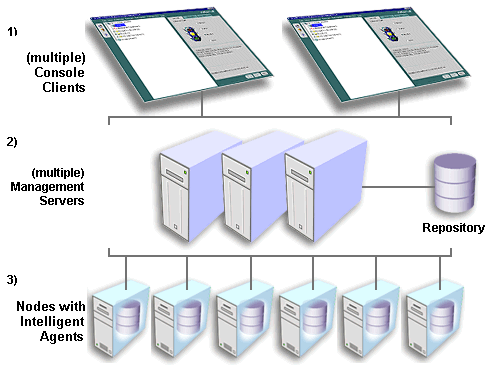
Text description of the illustration second_t.gif
One of the most important responsibilities of the Oracle Management Server is distributing tasks to the Oracle Intelligent Agents, which run on managed nodes in the third tier. The Intelligent Agents are responsible for the localized execution of tasks and the on-going monitoring of databases and other targets on the managed nodes.
Also, the Administrator can reconnect to a Management Server from within the Console should the Management Server to which the Console was originally connected become unavailable whether due to scheduled maintenance on the node or a power outage in the area where the Management Server resides.
The third tier of the Oracle Enterprise Manager framework is comprised of managed nodes which contain databases and other managed targets. Residing on each node is an Oracle Intelligent Agent, which communicates with the Oracle Management Server(s) and performs tasks sent by consoles and client applications.
Text description of the illustration third_ti.gif
The Oracle Intelligent Agent monitors databases and other targets in the node for registered events (potential problem occurrences) and scheduled jobs (activities), both sent by the client via the middle-tier Oracle Management Server(s).
Intelligent Agents function independently of the databases and other targets they support, and also function independently of the Console, management applications, and Oracle Management Servers. By running independently from other components, Intelligent Agents can perform such tasks as starting up and shutting down a database and staying operational if another part of the system is down.
Beginning with Intelligent Agent version 9.0.1, the Intelligent Agent process will be automatically restarted in cases where the Intelligent Agent process exits due to an abnormal condition within the environment in which the Intelligent Agent is running.
Intelligent Agents support Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), enabling third-party applications to communicate with the Intelligent Agent and be managed along with Oracle targets.
The Intelligent Agent handles the collection of system performance data (for example, file I/O or CPU usage data) for Capacity Planner and Performance Manager, which are data-analysis applications in the optional Oracle Diagnostics Pack, Oracle Management Pack for Oracle Applications, and Oracle Management Pack for SAP R/3. You do not have to configure a separate data collection service for this purpose.
|
Note: For more information about the Intelligent Agent, see the Oracle Intelligent Agent User's Guide. |
Oracle Enterprise Manager enables administrators to maintain the highest level of performance and availability while controlling system management costs. This section describes the major benefits of Oracle Enterprise Manager and its scalability, power, and reliability.
| Topic | See Page |
|---|---|
From the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console, you can manage and administer all your distributed systems, databases, tools, and users from a central location. An intuitive graphical user interface that provides powerful and robust system management, the Console gives you a central point of control for the Oracle environment. The easy-to-use interface can simplify tasks for the system administrator.
With Oracle Enterprise Manager, a distributed enterprise can be managed as easily and effectively as a local workgroup, lowering the cost of system ownership. The Oracle Enterprise Manager framework allows the automation and delegation of routine, time-consuming tasks on multiple targets. Jobs can be scheduled on multiple nodes simultaneously and groups of targets can be monitored together.
In many enterprises, teams of database administrators must cooperate to manage numerous systems, often remotely. With Oracle Enterprise Manager, database management tasks can be organized and distributed in multi-administrator enterprises, and system data can be safely shared among administrators.
With Oracle Enterprise Manager, system data, application data, and the state of managed targets is contained in the repository, which stores administrative data. If you are using more than one Oracle Management Server, they can share a repository. Administrative data is stored in a repository.
Administrative data stored in the repository is filtered based on administrator permissions. The Oracle Management Server handles security and distributes notifications and management information to administrators based on the access levels that are set up for them. Each administrator has an account with preferred credentials set which provides access to the Oracle Management Server and the central data stored in the repository. When an administrator connects through the Navigator, the preferred credentials used are those defined explicitly for that administrator. The Oracle Management Server filters information as it flows between different consoles and the targets on the managed nodes.
Typically, all administrators share a single Enterprise Manager repository, which allows administrators to share information. The distribution of information reduces redundancy, which saves time and keeps administrative costs down. Although you can set up multiple repositories, administrators using different repositories will not have access to each other's information; there is no sharing of data between repositories.
With its three-tier architecture, Oracle Enterprise Manager has the ability to maintain performance and automate routine tasks in rapidly growing, distributed environments. As the number of nodes and managed targets in your network increases, or if the current Oracle Management Server is overloaded, you can add more Oracle Management Servers to the middle tier to share and balance the workload. Balancing the workload in the middle tier rather than investing in additional systems management overhead, controls the cost of systems management.
Because multiple Oracle Management Servers can share a repository as their back-end store, they provide fault tolerance for each other. If one Oracle Management Server fails, the clients registered with it can immediately log in again and register with any of the other Oracle Management Servers running with that repository, and work continues seamlessly. Any clients registered with an Oracle Management Server other than the failed one are unaffected.
For failover and scalability of the repository database, Oracle has database solutions such as Oracle9i Real Application Clusters, Oracle Failsafe, Replication Management, and others.
Oracle Enterprise Manager's flexible architecture allows new products and additional modules to be written and added to the suite. Oracle Enterprise Manager's use of open standards (CORBA, IIOP, etc.) makes it possible to integrate third-party tools into the Console.
In a large, distributed database environment, the proportion of managed nodes per administrator increases rapidly, requiring tools that can automate tasks. Oracle Enterprise Manager offers automated, "lights-out" task management and proactive target monitoring for events, which enables control of the enterprise without necessarily needing additional staff to meet increasing system responsibilities.
Using the Job System, you can automate routine tasks such as database backups or running reports on a regular basis. Using the Event System, you can have remote databases and other targets monitored for important occurrences (events) and set up "fixit" jobs that automatically execute in response to events. Monitoring of targets for occurrences and automatic problem correction ensures that problems are dealt with before they noticeably impact end users.
Because jobs are executed locally at the managed nodes, they can be completed even when a crucial part of the network is down. Localized tasks are dependable because all jobs are processed by the Intelligent Agents on the individual managed nodes.
For example, if you schedule a job to run on a node, the job will be executed locally at the node at the specified time, and will run even if a network outage occurs between the node, the Oracle Management Server, and the Console. If a target on the node is down, the Intelligent Agent stores any jobs to be performed on the target until the target is back up. If the Console is down, the Intelligent Agent stores any information about the status of the job until the Console is back in service and can receive information.
Oracle Database Administrators (DBAs) are commonly required to perform tasks such as creating users, performing backups, adding tablespaces or datafiles, managing database objects, and changing instance parameters.
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Console offers database administration functionality that help automate and simplify the daily tasks of a DBA:
|
Note: For an overview of the database administration functionality, see Chapter 4, "Database Administration" or the Oracle Enterprise Manager online help. |
Oracle Enterprise Manager provides a complete user-friendly system management solution that allows administrators to manage distributed environments with a minimum of effort. With the ability to access and manage remote targets, an administrator can more easily make changes and execute commands. The Oracle Enterprise Manager framework is designed to offer high scalability without increasing complexity, allowing an administrator to manage more and more targets, confident that the environment is under control.
In addition, all Oracle Enterprise Manager applications have a similar graphical user interface allowing the administrator to manage the Oracle enterprise using the same familiar front end with each application. This interface can be used by both beginning and advanced users, and also can serve as a training tool when used with the Oracle Enterprise Manager wizards and quick tours.
Oracle Enterprise Manager is made up of common services that help you manage the Oracle environment.
These common services include:
When you launch the Console with a Management Server connection, you can perform service discovery through a Discovery Wizard. This wizard is used to identify nodes in your environment that you want to manage with Enterprise Manager. When you activate the wizard, the Discovery Wizard searches the network for the targets you specify. If that target has an Oracle Intelligent Agent running, it will be added to the Enterprise Manager Console Navigator for management along with any services running on that target. You will be able use these services as targets in jobs, events, and groups.
The Job System enables the automation of standard and repetitive administrative tasks, such as executing a SQL script or executing an operating system command. With the Job system, you can create and manage jobs, share jobs with other administrators, schedule execution of jobs, and view information about the jobs. Jobs can be scheduled on a single node or multiple nodes in the network, provided that the node has an Intelligent Agent running on it.
In-place modification also allows administrators to add and/or remove targets for submitted jobs, regardless of the version of the Intelligent Agent.
Upon job completion or failure, the system can be configured to automatically notify you and/or other administrators through e-mail or page, depending on the access levels and preferred credentials.
Because a job is an administrative entity (object) within the Oracle Enterprise Manager framework, an owner is always specified for the job as well as basic security parameters, which prevent or allow viewing and modifications by other administrators.
|
Note: For more information about the Job System, see Chapter 3, "Job and Event Systems". |
The Event System allows the Oracle environment to be monitored for operational occurrences and borderline conditions such as loss of service, lack of storage, and resource problems such as high CPU usage.
|
Note: Only up/down events are shipped with base Oracle Enterprise Manager; all other more advanced events are bundled with the separately licensable packs. |
These critical occurrences, called "events", are each made up of one or more "tests". When you register an event through the Console, you define the event condition by selecting one or more tests to run on the managed targets (databases, nodes, listeners, or other services), then set the threshold parameters for which you want to be notified.
You can also dynamically change parameters of a registered event by selecting a registered event, adding and/or removing targets, changing some attributes, and then applying the changes to all the targets of that event. For Oracle9i, you can perform a full modification. For pre-9i, you can perform limited modification. For information on Intelligent Agent restrictions, refer to the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide.
In Oracle9i, you can also specify custom operating system scripts as new event tests that will be included as part of the Enterprise Manager events system. User-Defined Events expands the breadth and flexibility of the events system by allowing you to write and incorporate custom scripts that are particular to your environment. Also, you can tie in your existing monitoring scripts into the events system, and thus take advantage of the services provided by the Enterprise Manager framework: paging/e-mail notifications for events that go in alarm, and collaborative administration of targets.
In the Event system, you have the flexibility to schedule the evaluation of an event at specified intervals, on specified day of the week, or on a specified day of the month. It is a useful feature since you can schedule resource intensive jobs during off-peak periods.
When an event occurs and is detected by an Intelligent Agent, specified administrators are notified by Console alert, e-mail, or page, depending on their access levels and preferred credentials. You can also set up a "fixit" job to run automatically in response to an event.
As in the Job System, you can share event information with other administrators connected to the repository. Events are also objects within the Oracle Enterprise Manager framework and are assigned owners and security parameters.
|
Note: For more information about the Event System, see Chapter 3, "Job and Event Systems". |
Administrators can be notified of the status of jobs and events by Console alert, e-mail, or page. When scheduling a job or registering an event, you set up notification procedures and choose which administrators to have notified of job completion or failure or event occurrence. Notification filters allow each administrator to specify when to send an email notification as opposed to a page notification as a result of a job or event status change.
Paging/Email Blackout allows an administrator with super administrator privileges to suspend paging and email notifications for specified targets and/or services that have been previously discovered in the Navigator. Paging/email blackouts deactivate enhanced notification (email/paging), thus preventing Enterprise Manager administrators from being flooded with emails and pages if a managed target/service is brought down. For example, if a target is brought down on a regular basis for scheduled maintenance, a super administrator can schedule a paging/email blackout for that target to prevent enhanced notification during the maintenance period.
In addition to paging/email blackouts, the Enterprise Manager administrative framework also allows you to specify target-level blackouts to suspend all management and data collection activity for specific targets in your enterprise.
Security parameters in Oracle Enterprise Manager are defined for targets, objects, and administrators. All administrator accounts are defined by a Super Administrator who creates and defines the access levels of all Enterprise Manager administrators. A Super Administrator can access any object and control its security parameters, including objects owned by other administrators. Security parameters are set up in the Preferences dialog box, shown in Figure 1-7, "Preferences Dialog Box".
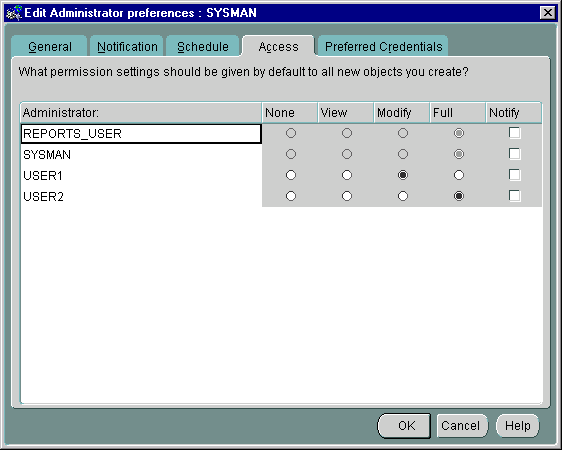
Text description of the illustration preferen.gif
Oracle Enterprise Manager's restricted access to target discovery provides better security of managed systems by allowing only Super Administrators to discover, refresh, and remove targets from the Enterprise Manager Console. This functionality prevents novice or new administrators of a team from adding or deleting targets for which they are not responsible.
The Console improves the security of managed environments by allowing Administrators who are actually responsible for specific targets to view and manipulate only those targets. This feature allows Super Administrators to control and customize the list of managed targets displayed in the Consoles of other, regular Administrators using Enterprise Manager. In addition, restricting certain targets from Administrators' views improves Administrators' ability to manage the targets to which they do have access. For example, rather than viewing all 300 discovered databases in his Console Navigator tree, Administrator Fred's Super Administrator can customize Fred's view such that only the 20 databases he is responsible for appear.
The Enterprise Manager reporting system provides flexible reporting functionality to administrators, permitting quick and easy access to information about the status, configuration, and performance of all monitored systems in their enterprise.
Administrators can create, schedule, and publish a wide variety of enterprise system reports. When published to a website, these reports can be accessed by a wider audience, enabling anyone from administrators to managers to executives to quickly access information regarding their monitored environment. The reporting functionality is fully integrated with the Enterprise Manager Job scheduling system, allowing reports to be generated automatically at specific times or at regular intervals. Reports can also be generated on-demand, such as when an administrator requests to view a specific report by clicking on a link within the reporting website.
A rich set of predefined report definitions are supplied with Enterprise Manager out of the box, allowing you to generate reports without having to create new report definitions. If none of the predefined definitions meets your reporting requirements, you can modify definition parameters from an existing report definition and save it as a new report definition. If your reporting needs go beyond the scope of the predefined report definitions, you can create completely new report definitions.
For more information, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide and the online help.
You can control font size and style of the Console and applications. If the default fonts are too large or small for your display, you can change them from the Console. Any application which is then launched from the Console will display the updated font size.
|
 Copyright © 1996, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|