Release 2 (9.2)
Part Number A96657-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle9i Support for JavaServer Pages Reference Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96657-01 |
|
The Oracle JSP container provides standard globalization support (also known as National Language Support, or NLS) according to the Sun Microsystems JavaServer Pages Specification, Version 1.1, and also offers extended support for servlet environments that do not support multibyte parameter encoding.
Standard Java support for localized content depends on the use of Unicode 2.0 for uniform internal representation of text. Unicode is used as the base character set for conversion to alternative character sets.
This chapter describes key aspects of how the Oracle JSP container handles Oracle Globalization Support. The following topics are covered:
You can use the page directive contentType parameter to set the MIME type and to optionally set the character encoding for a JSP page. The MIME type applies to the HTTP response at runtime. The character encoding, if set, applies to both the page text during translation and the HTTP response at runtime.
Use the following syntax for the page directive:
<%@ page ... contentType="TYPE; charset=character_set" ... %>
or, to set the MIME type while using the default character set:
<%@ page ... contentType="TYPE" ... %>
TYPE is an IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) MIME type; character_set is an IANA character set. (When specifying a character set, the space after the semi-colon is optional.)
For example:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" %>
or:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html" %>
The default MIME type is text/html. The IANA maintains a registry of MIME types at the following site:
ftp://www.isi.edu/in-notes/iana/assignments/media-types/media-types
The default character encoding is ISO-8859-1 (also known as Latin-1). The IANA maintains a registry of character encodings at the following site. Use the indicated "preferred MIME name" if one is listed:
http://www.iana.org/assignments/character-sets
(There is no JSP requirement to use an IANA character set as long as you use a character set that Java and the Web browser support, but the IANA site lists the most common character sets. Using the preferred MIME names they document is recommended.)
The parameters of a page directive are static. If a page discovers during execution that a different setting is necessary for the response, it can do one of the following:
For situations where the appropriate content type for the HTTP response is not known until runtime, you can set it dynamically in the JSP page. The standard javax.servlet.ServletResponse interface specifies the following method for this purpose:
public void setContentType(java.lang.String contenttype)
The implicit response object of a JSP page is a javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse instance, where the HttpServletResponse interface extends the ServletResponse interface.
The setContentType() method input, like the contentType setting in a page directive, can include a MIME type only, or both a character set and a MIME type. For example:
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8");
or:
response.setContentType("text/html");
As with a page directive, the default MIME type is text/html and the default character encoding is ISO-8859-1.
This method has no effect on interpreting the text of the JSP page during translation. If a particular character set is required during translation, that must be specified in a page directive, as described in "Content Type Settings in the page Directive".
Be aware of the following important usage notes.
setContentType() method. It is buffered by default; do not set buffer="none" in a page directive.setContentType() call must appear early in the page, before any output to the browser or any jsp:include command (which flushes the JSP buffer to the browser).response object has a setLocale() method that sets a default character set based on the specified locale, overriding any previous character set. For example, the following method call results in a character set of Shift_JIS:
response.setLocale(new Locale("ja", "JP"));
Character encoding of request parameters is not well defined in the HTTP specification. Most servlet containers must interpret them using the servlet default encoding, ISO-8859-1.
For such environments, where the servlet container cannot encode multibyte request parameters and bean property settings, the Oracle JSP container offers extended support in two ways:
or:
Oracle provides a setReqCharacterEncoding() method that is useful in case the default encoding for the servlet container is not appropriate. Use this method to specify the encoding of multibyte request parameters and bean property settings, such as for a getParameter() call in Java code or a jsp:setProperty statement to set a bean property in JSP code. If the default encoding is already appropriate, then it is not necessary to use this method, and in fact using it may create some performance overhead in your application.
The setReqCharacterEncoding() method is a static method in the PublicUtil class of the oracle.jsp.util package.
This method affects parameter names and values, specifically:
getParameter() method outputgetParameterValues() method outputgetParameterNames() method outputjsp:setProperty settings for bean property valuesWhen invoking the method, input a request object and a string that specifies the desired encoding, as follows:
oracle.jsp.util.PublicUtil.setReqCharacterEncoding(myrequest, "EUC-JP");
|
Notes:
|
This section describes how to use the JSP translate_params configuration parameter for encoding of multibyte request parameters and bean property settings, such as for a getParameter() call in Java code or for a jsp:setProperty statement to set a bean property in JSP code.
Note that beginning with Oracle JSP 1.1.2.x releases, it is preferable to use the PublicUtil.setReqCharacterEncoding() method instead. See "The setReqCharacterEncoding() Method" above.
Also note that you should not enable translate_params in any of the following circumstances:
Setting translate_params to true in this situation will cause incorrect results. As of this writing, however, it is known that JServ, JSWDK, and Tomcat all do not properly handle multibyte parameter encoding.
page directive or setContentType() methodtranslate_params accomplishes is already present in the JSP page
See "Code Equivalent to the translate_params Configuration Parameter".
Setting translate_params to true overrides servlet containers that cannot encode multibyte request parameters and bean property settings. (For information about how to set JSP configuration parameters in a JServ environment, see "Setting JSP Parameters in JServ".)
When this flag is enabled, the Oracle JSP container encodes the request parameters and bean property settings based on the character set of the response object, as indicated by the response.getCharacterEncoding() method.
The translate_params flag affects parameter names and values, specifically:
getParameter() method outputgetParameterValues() method outputgetParameterNames() method outputjsp:setProperty settings for bean property valuesThere may be situations where you do not want to or cannot use the translate_params configuration parameter. It is useful to be aware of equivalent functionality that can be implemented through scriptlet code in the JSP page, for example:
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=EUC-JP" %> ... String paramName="XXYYZZ"; // where XXYYZZ is a multibyte string paramName = new String(paramName.getBytes(response.getCharacterEncoding()), "ISO8859_1"); String paramValue = request.getParameter(paramName); paramValue= new String(paramValue.getBytes("ISO8859_1"), "EUC-JP"); ...
This code accomplishes the following:
XXYYZZ as the parameter name to search for. (Presume XX, YY, and ZZ are three Japanese characters.)ISO-8859-1, the servlet container character set, so that the servlet container can interpret it. (First a byte array is created for the parameter name, using the character encoding of the request object.)ISO-8859-1 encoding.)EUC-JP for further processing or output to the browser.See the next two sections for a globalization sample that depends on translate_params being enabled, and one that contains the equivalent code so that it does not depend on the translate_params setting.
The following sample accepts a user name in Japanese characters and correctly outputs the name back to the browser. In a servlet environment that cannot encode multibyte request parameters, this sample depends on the JSP configuration setting of translate_params=true.
Presume XXYY is the parameter name (something equivalent to "user name" in Japanese) and AABB is the default value (also in Japanese).
(See the next section for a sample that has the code equivalent of the translate_params functionality, so does not depend on the translate_params setting.)
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=EUC-JP" %> <HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE>Hello</TITLE></HEAD> <BODY> <% //charset is as specified in page directive (EUC-JP) String charset = response.getCharacterEncoding(); %> <BR> encoding = <%= charset %> <BR> <% String paramValue = request.getParameter("XXYY"); if (paramValue == null || paramValue.length() == 0) { %> <FORM METHOD="GET"> Please input your name: <INPUT TYPE="TEXT" NAME="XXYY" value="AABB" size=20> <BR> <INPUT TYPE="SUBMIT"> </FORM> <% } else { %> <H1> Hello, <%= paramValue %> </H1> <% } %> </BODY> </HTML>
Following is the sample input:
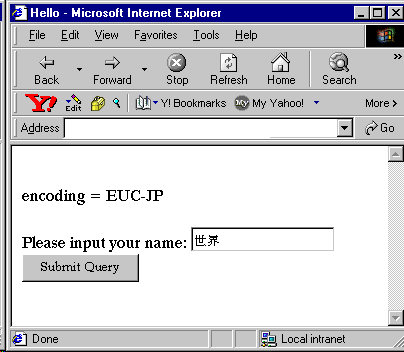
Text description of the illustration nlsin.gif
and the sample output:
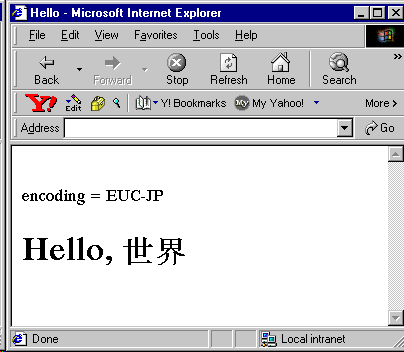
Text description of the illustration nlsout.gif
The following sample, as with the preceding sample, accepts a user name in Japanese characters and correctly outputs the name back to the browser. This sample, however, has the code equivalent of translate_params functionality, so does not depend on the translate_params setting.
|
Important: If you use |
Presume XXYY is the parameter name (something equivalent to "user name" in Japanese) and AABB is the default value (also in Japanese).
For an explanation of the critical code in this sample, see "Code Equivalent to the translate_params Configuration Parameter".
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=EUC-JP" %> <HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE>Hello</TITLE></HEAD> <BODY> <% //charset is as specified in page directive (EUC-JP) String charset = response.getCharacterEncoding(); %> <BR> encoding = <%= charset %> <BR> <% String paramName = "XXYY"; paramName = new String(paramName.getBytes(charset), "ISO8859_1"); String paramValue = request.getParameter(paramName); if (paramValue == null || paramValue.length() == 0) { %> <FORM METHOD="GET"> Please input your name: <INPUT TYPE="TEXT" NAME="XXYY" value="AABB" size=20> <BR> <INPUT TYPE="SUBMIT"> </FORM> <% } else { paramValue= new String(paramValue.getBytes("ISO8859_1"), "EUC-JP"); %> <H1> Hello, <%= paramValue %> </H1> <% } %> </BODY> </HTML>
|
 Copyright © 2000, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|