| Oracle9i Real Application Clusters Setup and Configuration Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96600-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle9i Real Application Clusters Setup and Configuration Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96600-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter describes server parameter file placement and configuration in Oracle Real Application Clusters environments. The topics in this chapter are:
| See Also:
Oracle9i Real Application Clusters Administration for more information about parameters and Oracle9i Real Application Clusters Deployment and Performance for a discussion of parallel execution-related parameters in Real Application Clusters data warehouse environments |
Oracle uses parameter settings in parameter files to determine how to control various database resources. You can use two types of files for parameter administration: the server parameter file or one or more traditional client-side parameter files.
Oracle Corporation recommends that you administer parameters using the server parameter file. If you use client-side parameter files, then Oracle does not preserve parameter changes made for self-tuning after shutdown.
| See Also:
Oracle9i Real Application Clusters Administration for more information about using client-side parameter files |
By default, Oracle creates the server parameter file based on one SPFILE. You can only change parameter settings in the server parameter file using Oracle Enterprise Manager or ALTER SYSTEM SET SQL statements; the server parameter file is a binary file that you should not edit.
|
Note: Oracle Corporation recommends that you avoid modifying the values for self-tuning parameters; overriding these settings can adversely affect performance. |
If you are upgrading from a previous Oracle release, then create and configure the server parameter file for Real Application Clusters using the procedures described in the following section.
The default location of the server parameter file when the database creates it from a PFILE is platform-dependent.
The default location of the server parameter file on UNIX is:
$ORACLE_HOME/dbs/spfile$ORACLE_SID.ora
The default location of the server parameter file on Windows NT and Windows 2000 is:
%ORACLE_HOME%\database\SPFILE%ORACLE_SID%.ORA
The default location of the server parameter file is inappropriate for Real Application Clusters databases because all instances must use the same server parameter file.
Instead, for UNIX platforms Oracle Corporation recommends that you use a PFILE in this directory:
$ORACLE_HOME/dbs/init$ORACLE_SID.ora
For Windows NT and Windows 2000 platforms Oracle Corporation recommends that you use a PFILE in this directory:
%ORACLE_HOME%\database\init%ORACLE_SID%.ora
This path is valid for each instance and it refers to a single, shared initialization parameter file. The file must contain the following entry for UNIX platforms:
SPFILE='/dev/vx/rdsk/oracle_dg/dbspfile'
The file must contain the following entry for Windows NT and Windows 2000 platforms:
SPFILE='dbspfile1'
On UNIX, however, if you use a cluster file system, then use an alternate file location of:
SPFILE='$ORACLE_HOME/dbs/spfile.ora'
On Windows, if you use a cluster file system, then use this syntax:
SPFILE=%ORACLE_HOME%\database\spfile.ora
For Windows use the following location:
SPFILE='C:\oracle\ora92+atabase\spfileMYDB.ora'
You must use the same value of SPFILE so that all instances use the same server parameter file at startup.
To use the DBCA to create your database and to use the server parameter file, on the Initialization Parameters page select the Create server parameter file (spfile) box under the File Locations tab. Then enter either a shared file system filename or the raw device path name in the Server Parameters Filename field as shown in Figure 6-1.
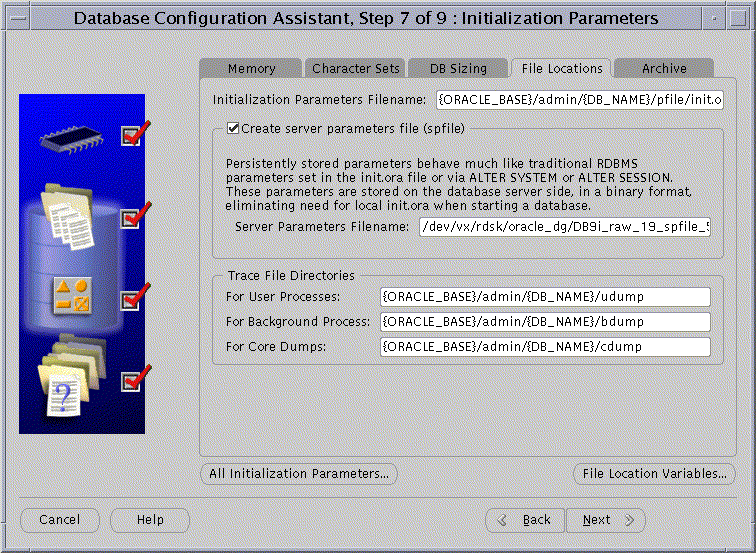
Text description of the illustration fileloc2.gif
Oracle searches for your parameter file in a particular order depending on your platform. On UNIX platforms, Oracle examines directories in the following order:
The search order on Windows NT and Windows 2000 platforms is:
Migrate to the server parameter file by creating and editing the server parameter file using the procedures described in this section.
For single-node cluster-enabled configurations, or if you are using a cluster file system, place the server parameter file on a file system. Otherwise, place the server parameter file on a raw device that is at least 5MB in size.
Migrate to the server parameter file by completing the following procedures:
initdbname.ora file by copying all shared IFILE contents as is. All parameters defined in your IFILE parameter files are global. Therefore, create them as "parameter=value" without sid prefixes.initsid.ora files using the following syntax where sid is the sid of the instance:
sid.parameter=value
CREATE SPFILE statement as in the following example:
CREATE SPFILE='?/dbs/spfile_dbname.ora' FROM PFILE='?/dbs/initdbname.ora'
Otherwise, use syntax as in the following example to create the server parameter file on a raw device:
CREATE SPFILE='/dev/vx/rdsk/oracle_dg/dbspfile' FROM PFILE='?/dbs/initdbname.ora'
These statements read your combined initdbname.ora file that you created by merging your IFILEs. Then it transfers the settings for the parameters from the merged file into your server parameter file.
STARTUP command as in this example:
STARTUP PFILE=$ORACLE_HOME/dbs/initsid.ora
Where the file initsid.ora contains the entry:
SPFILE='/dev/vx/rdsk/oracle_dg/dbspfile'
If you use this STARTUP command syntax, then Oracle uses the server parameter file entry specified in initsid.ora.
Oracle reports errors that occur during server parameter file creation or while reading the file during startup. If an error occurs during a parameter update, then Oracle records the error in your ALERT.LOG file and ignores subsequent parameter updates to the file. If this happens, then do either of the following:
Oracle displays errors for parameter changes that you attempt when you incorrectly use the ALTER SYSTEM SET statement. Oracle does this when an error occurs while reading from or writing to the server parameter file.
Oracle Corporation recommends that you regularly back up the server parameter file for recovery purposes. Do this using the CREATE PFILE statement. For example:
CREATE PFILE='?/dbs/initdbname.ora'
FROM SPFILE='/dev/vx/rdsk/oracle_dg/dbspfile'
You can also recover by starting up an instance using a client-side initialization parameter file. Then re-create the server parameter file using the CREATE SPFILE statement. You can also use RMAN (Recovery Manager) to create backups of the server parameter file.
| See Also:
Oracle9i Recovery Manager User's Guide for more information about RMAN |
| See Also:
Oracle9i SQL Reference for more information about the |