| Oracle9i SQL Reference Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96540-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle9i SQL Reference Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96540-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
Use the CREATE OPERATOR statement to create a new operator and define its bindings.
Operators can be referenced by indextypes and by DML and query SQL statements. The operators, in turn, reference functions, packages, types, and other user-defined objects.
| See Also:
Oracle9i Data Cartridge Developer's Guide and Oracle9i Database Concepts for a discussion of these dependencies and of operators in general |
To create an operator in your own schema, you must have CREATE OPERATOR system privilege. To create an operator in another schema, you must have the CREATE ANY OPERATOR system privilege. In either case, you must also have EXECUTE privilege on the functions and operators referenced.
create_operator::=


Specify OR REPLACE to replace the definition of the operator schema object.
You can replace the definition only if the operator has no dependent objects (for example, indextypes supporting the operator).
Specify the schema containing the operator. If you omit schema, Oracle creates the operator in your own schema.
Specify the name of the operator to be created.
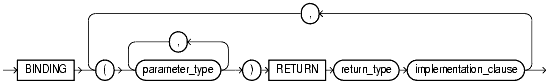
Use the binding_clause to specify one or more parameter datatypes (parameter_type) for binding the operator to a function. The signature of each binding (that is, the sequence of the datatypes of the arguments to the corresponding function) must be unique according to the rules of overloading.
The parameter_type can itself be an object type. If it is, you can optionally qualify it with its schema.
You cannot specify a parameter_type of REF, LONG, or LONG RAW.
| See Also:
PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference for more information about overloading |
Specify the return datatype for the binding.
The return_type can itself be an object type. If so, you can optionally qualify it with its schema.
You cannot specify a return_type of REF, LONG, or LONG RAW.
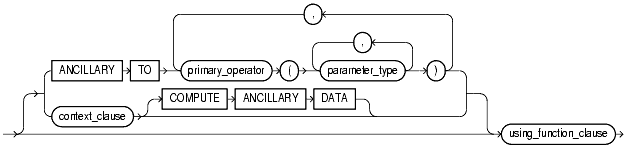
Use the ANCILLARY TO clause to indicate that the operator binding is ancillary to the specified primary operator binding (primary_operator). If you specify this clause, do not specify a previous binding with just one number parameter.
Use the context_clause to specify the name of the implementation type used by the functional implementation of the operator as a scan context.
Specify COMPUTE ANCILLARY DATA to indicate that the operator binding computes ancillary data.
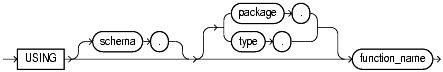
The using_function_clause lets you specify the function that provides the implementation for the binding. function_name can be a standalone function, packaged function, type method, or a synonym for any of these.
This example creates a very simple functional implementation of equality and then creates an operator that uses the function:
CREATE FUNCTION eq_f(a VARCHAR2, b VARCHAR2) RETURN NUMBER AS BEGIN IF a = b THEN RETURN 1; ELSE RETURN 0; END IF; END; / CREATE OPERATOR eq_op BINDING (VARCHAR2, VARCHAR2) RETURN NUMBER USING eq_f;