Release 2 (9.2)
Part Number A96578-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle Label Security Administrator's Guide Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96578-01 |
|
This chapter discusses the fundamental concepts of data labels and user labels, and introduces the terminology that will help you understand Oracle Label Security.
The chapter includes:
Label-based security provides a flexible way of controlling access to sensitive data. Oracle Label Security controls data access based on the identity and label of the user, and the sensitivity or label of the data. This provides an additional level of security to a system.
With an Oracle Label Security policy, access to data is controlled in three dimensions:
Note that the discussion here concerns access to data. The particular type of access (that is, the ability to read or to write the data in question) is covered in Chapter 3, "Understanding Access Controls and Privileges."
When a database table is protected by an Oracle Label Security policy, a column is added to the table. This policy label column contains the label information for each data row. The administrator can choose to display or hide this column.
This section describes the elements which make up a sensitivity label.
A sensitivity label is a single attribute, with multiple components. All data labels must contain a level component; compartment and group components are optional. The administrator must define the label components before he or she can create labels.
Valid characters for all label component specifications include alphanumeric characters and underscores. Additionally, spaces can be used within the string. (Leading or trailing spaces are ignored.)
The following figure illustrates the three dimensions in which data can be logically classified, using levels, compartments, and groups.
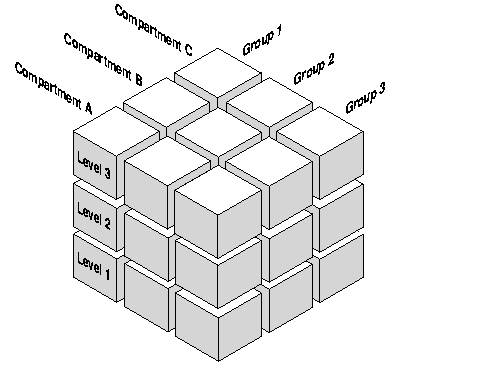
A level is a ranking that denotes the sensitivity of the information it labels. The more sensitive the information, the higher its level. The less sensitive the information, the lower its level.
Oracle Label Security permits up to 10,000 levels in a policy. Every label must include one level. For each level, the Oracle Label Security administrator defines a numeric form and character forms.
For example, you can define a set of levels like the following:
| Numeric Form | Long Form | Short Form |
|---|---|---|
|
40 |
HIGHLY_SENSITIVE |
HS |
|
30 |
SENSITIVE |
S |
|
20 |
CONFIDENTIAL |
C |
|
10 |
PUBLIC |
P |
|
Numeric Form |
The numeric form of the level can range from 0 to 9999. Levels of sensitivity are ranked by this numeric value, so you must assign higher numbers to levels which are more sensitive, and lower numbers to levels which are less sensitive. In Table 2-2, 40 (HIGHLY_SENSITIVE) is a higher level than 30, 20, and 10. Administrators should avoid using sequential numbers for the numeric form of levels. A good strategy is to use even increments (such as 50 or 100) between levels. This enables you to insert additional levels between two pre-existing levels, at a later date. |
|
Long Form |
The long form of the level name can contain up to 80 characters. |
|
Short Form |
The short form can contain up to 30 characters. |
Although the administrator defines both long and short names for the level (and for each of the other label components), only the short form of the name is displayed upon retrieval. When users manipulate the labels, they use only the short form of the component names.
Other sets of labels which users commonly define include TOP_SECRET, SECRET, CONFIDENTIAL, and UNCLASSIFIED; or TRADE_SECRET, PROPRIETARY, COMPANY_CONFIDENTIAL, PUBLIC_DOMAIN.
|
Note: In this guide, all labels (including "TOP_SECRET," "SECRET," "CONFIDENTIAL," and so on) are used as illustrations only. |
Compartments identify areas which describe the sensitivity of the labeled data. They provide a finer level of granularity within a level.
Compartments associate the data with one or more security areas. All of the data related to a particular project can be labeled with the same compartment. For example, you can define a set of compartments like the following:
| Numeric Form | Long Form | Short Form |
|---|---|---|
|
40 |
FINANCIAL |
FINCL |
|
30 |
CHEMICAL |
CHEM |
|
20 |
OPERATIONAL |
OP |
|
Numeric Form |
The numeric form can range from 0 to 9999. The numeric form of the compartment does not indicate greater or less sensitivity. Rather, it controls display order of the short form compartment name in the label character string. For example, assume that a label is created which has all three compartments listed in Table 2-3, and a level of SENSITIVE. If the label containing the level and compartments is displayed in string format, it looks like this: S:OP,CHEM,FINCL This is because 20 comes before 30, and 30 before 40. By contrast, if the numeric form for the FINCL compartment were set to 5, the character string format of the label would look like this: S:FINCL,OP,CHEM |
|
Long Form |
The long form of the compartment name can contain up to 80 characters. |
|
Short Form |
The short form can contain up to 30 characters. |
Compartments are optional; a label can contain zero or more compartments. Oracle Label Security permits up to 10,000 compartments.
All labels need not have all compartments. For example, you can specify HIGHLY_SENSITIVE and CONFIDENTIAL levels with no compartments, and a SENSITIVE level which does contain compartments.
When you analyze your data's sensitivity, you may find that some compartments are only used at specific levels. Figure 2-2 shows how compartments can be used to categorize data.
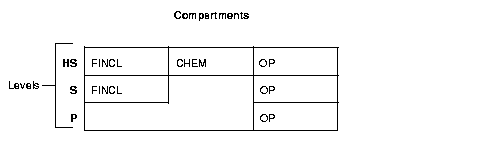
Here, compartments FINCL, CHEM, and OP are used with the level HIGHLY_SENSITIVE (40). The label HIGHLY_SENSITIVE:FINCL, CHEM indicates a level of 40 with the two named compartments. Compartment FINCL is not more sensitive than CHEM, nor is CHEM more sensitive than FINCL. Note also that some data in the protected table may not belong to any compartment.
Groups identify organizations owning or accessing the data, such as EASTERN_REGION, WESTERN_REGION, WR_SALES. All data pertaining to a certain department can have that department's group in the label. Groups are useful for the controlled dissemination of data, and for timely reaction to organizational change. When a company reorganizes, data access can change right along with the reorganization.
Groups are hierarchical: you can label data based upon your organizational infrastructure. A group can thus be associated with a parent group. For example, you can define a set of groups corresponding to the following organizational hierarchy:
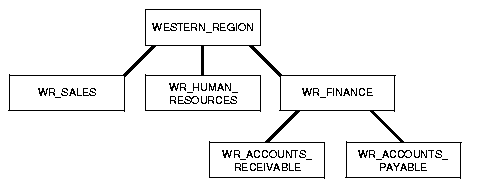
The WESTERN_REGION group includes three subgroups: WR_SALES, WR_HUMAN_RESOURCES, and WR_FINANCE. The WR_FINANCE subgroup is further subdivided into WR_ACCOUNTS_RECEIVABLE and WR_ACCOUNTS_PAYABLE.
Table 2-4 shows how the organizational structure in this example can be expressed in the form of Oracle Label Security groups. Notice that the numeric form assigned to the groups affects display order only. The administrator specifies the hierarchy (that is, the parent-child relationships) separately.
|
Numeric Form |
The numeric form of the group can range from 0 to 9999, and must be unique for each policy. The numeric form does not indicate any kind of ranking. It does not indicate a parent-child relationship, or greater or less sensitivity. It simply controls display order of the short form group name in the label character string. For example, assume that a label is created which has the level SENSITIVE, the compartment CHEMICAL, and the groups WESTERN_REGION and WR_HUMAN_RESOURCES as listed in Table 2-4. When displayed in string format, the label looks like this: S:CHEM:WR,WR_HR WR is displayed before WR_HR because 1000 comes before 1200. |
|
Long Form |
The long form of the group name can contain up to 80 characters. |
|
Short Form |
The short form can contain up to 30 characters. |
Groups are optional; a label can contain zero or more groups. Oracle Label Security permits up to 10,000 groups.
All labels need not have groups. When you analyze your data's sensitivity, you may find that some groups are only used at specific levels. For example, you can specify HIGHLY_SENSITIVE and CONFIDENTIAL labels with no groups, and a SENSITIVE label which does contain groups.
Table 2-5 illustrates the flexibility of Oracle Label Security levels, compartments, and groups, by listing typical ways in which they can be implemented in various industries.
| Industry | Levels | Compartments | Groups |
|---|---|---|---|
|
UNCLASSIFIED |
SIGMA |
||
|
OPERATIONS |
CONSUMER_LOANS |
STAFF |
|
|
PUBLIC |
CRIMINAL |
COURT |
|
|
PATIENT_RELEASE |
INFECTIOUS_DISEASES |
HOSPITAL_STAFF |
|
|
PUBLIC |
PERSONNEL |
ERSATZ_LTD |
After defining the label components, the administrator creates data labels by combining particular sets of level, compartments, and groups. Out of all the possible permutations of label components, the administrator specifies those combinations which will actually be used as valid data labels in the database.
This can be done using the Oracle Policy Manager graphical user interface, or using a command line procedure. Character string representations of labels use the following syntax:
LEVEL:COMPARTMENT1,...,COMPARTMENTn:GROUP1,...,GROUPn
The text string specifying the label can have a maximum of 4,000 characters, including alphanumeric characters, spaces, and underscores. The labels are case-insensitive; you can enter them in uppercase, lowercase, or mixed case, but the string is stored in the data dictionary and displayed in uppercase. A colon is used as the delimiter between components. It is not necessary to enter trailing delimiters in this syntax.
For example, the administrator might create valid labels such as these:
SENSITIVE:FINANCIAL,CHEMICAL:EASTERN_REGION,WESTERN_REGION CONFIDENTIAL:FINANCIAL:VP_GRP SENSITIVE HIGHLY_SENSITIVE:FINANCIAL
SENSITIVE::WESTERN_REGION
When a valid data label is created, two additional things occur:
| See Also:
Chapter 5, "Creating an Oracle Label Security Policy" for instructions on creating label components and labels |
A user can only access data within the range of his or her own label authorizations. A user has:
For example, if a user is assigned a maximum level of SENSITIVE, then the user potentially has access to SENSITIVE, CONFIDENTIAL, and UNCLASSIFIED data. The user has no access to HIGHLY_SENSITIVE data.
Figure 2-4 shows how data labels and user labels work together, to provide access control in Oracle Label Security. Whereas data labels are discrete, user labels are inclusive. Depending upon authorized compartments and groups, a user can potentially access data corresponding to all levels within his or her range.
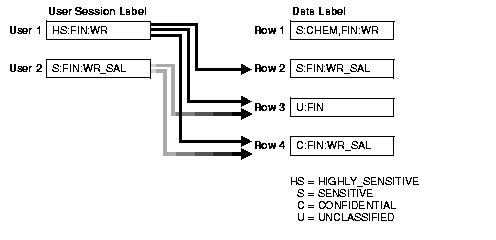
As shown in the figure, User 1 can access rows 2, 3, and 4 because her maximum level is HS; she has access to the FIN compartment; and her access to group WR hierarchically includes group WR_SAL. She cannot access row 1 because she does not have the CHEM compartment. (A user must have authorization for all compartments in a row's data label, to access that row.)
User 2 can access rows 3 and 4. His maximum level is S, which is less than HS in row 2. Although he has access to the FIN compartment, he only has authorization for group WR_SAL. He cannot, therefore, access row 1.
Figure 2-5 shows how data pertaining to an organizational hierarchy fits in to data levels and compartments.
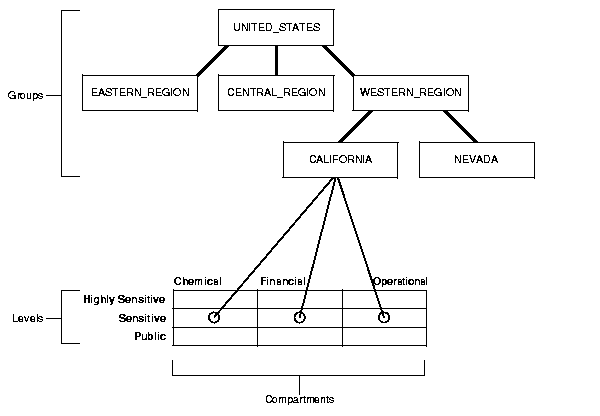
For example, the UNITED_STATES group includes three subgroups: EASTERN_REGION, CENTRAL_REGION, and WESTERN_REGION. The WESTERN_REGION subgroup is further subdivided into CALIFORNIA and NEVADA. For each group and subgroup, there may be data belonging to some of the valid compartments and levels within the database. Thus there may be SENSITIVE data which is FINANCIAL, within the CALIFORNIA subgroup.
Note that data is generally labeled with a single group, whereas users' labels form a hierarchy. If users have a particular group, that group may implicitly include child groups. Thus a user associated with the WESTERN_REGION group has access to all data; but a user associated with CALIFORNIA would only have access to data pertaining to that subgroup.
Oracle Label Security provides administrative interfaces to define and manage the labels used in a database. You define labels in an Oracle database using Oracle Label Security packages, or using the Oracle Policy Manager. Initially, an administrator must define the levels, compartments, and groups that compose the labels, and then she or he can define the set of valid data labels for the contents of the database.
The administrator can apply a policy to individual tables in the database, or to entire application schemas. Finally, the administrator assigns to each database user the label components (and privileges, if needed) appropriate for the person's job function.
| See Also:
Chapter 8, "Applying Policies to Tables and Schemas" for information about the Oracle Label Security interfaces used to manage label components |
|
 Copyright © 2000, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|