Release 2 (9.2)
Part Number A96596-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle9i Real Application Clusters Administration Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96596-01 |
|
This chapter describes how to use Oracle Enterprise Manager to administer Real Application Clusters databases. This chapter only describes Oracle Enterprise Manager administration for Real Application Clusters. Use this section as a supplement to information in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide and other Oracle Enterprise Manager documentation. The topics in this chapter are:
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Console provides a central point of control for the Oracle environment through a graphical user interface (GUI). You can use the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console to initiate a variety of cluster database management tasks.
Once you have created or modified the configuration of a cluster database, then you should use Oracle Enterprise Manager to discover the nodes on which you configured the cluster database. Once discovery completes, you can administer all of the databases and their instances and listeners that are associated with the nodes discovered by Oracle Enterprise Manager.
This enables you to start, stop, and monitor databases, instances, and their listeners, as well as to schedule jobs or register events. You can perform these tasks simultaneously on multiple cluster databases. You can also use the Console to manage schemas, security, and cluster database storage features.
|
See Also: Oracle9i Real Application Clusters Setup and Configuration for configuration information and the Oracle Enterprise Manager online help system for answers to frequently asked questions |
To use the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console, start the following components:
| See Also:
Oracle9i Real Application Clusters Setup and Configuration for Real Application Clusters-specific information on installing Oracle Enterprise Manager and Oracle Intelligent Agent User's Guide for more information about the Oracle Intelligent Agent |
From the Navigator pane, you can view and manage cluster database instances in the same manner as you view and manage single-instance databases. After Oracle Enterprise Manager discovers a node, the Navigator displays all the cluster databases, their instances and their listeners that are discovered on that node.
The information available for cluster databases is essentially the same as for single-instance databases. Just as in single-instance databases, cluster databases and their related elements can be administered using master and detail views of the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console.
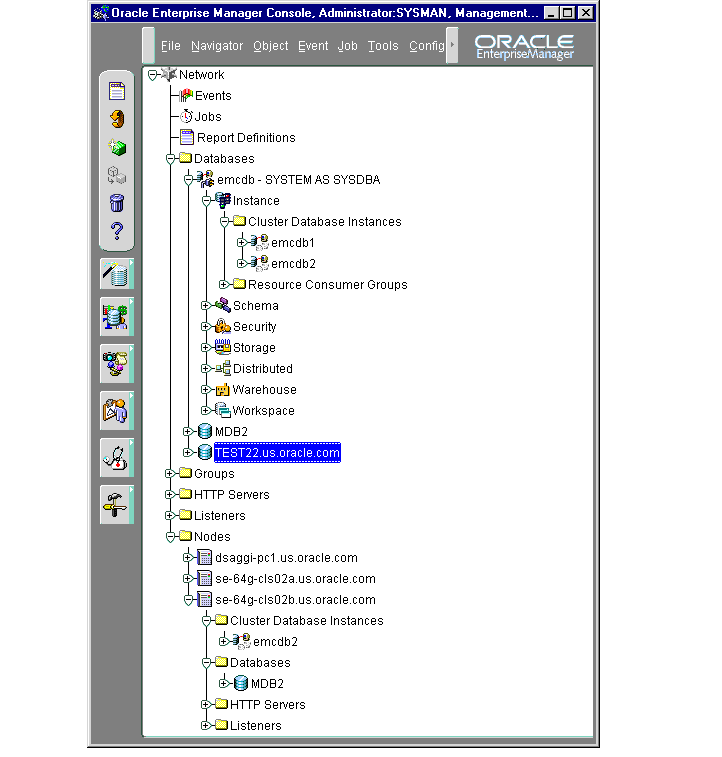
In the Navigator tree, cluster databases are listed under the Databases folder as siblings to single-instance databases. Just as in single-instance databases, each cluster database folder contains the instances and sub-folders for Instance, Schema, Security, Storage, and Distributed as shown in Figure 5-1.
|
Note: If you attempt to expand a cluster database and you have not yet set preferred credentials for the database as described in Oracle9i Real Application Clusters Setup and Configuration, then the Database Connect Information dialog prompts you to enter database connect information. |
By selecting objects within a cluster database subfolder, you can access property sheets to inspect and modify properties of these objects, just as you can for single-instance databases. For example, by expanding the Storage folder and then right-clicking Redo Log Groups subfolder and then choosing Create, you can add a new redo log group. Oracle Enterprise Manager displays all discovered cluster database instances under the Cluster Database Instances folder.
When accessing cluster databases, only the Instance folder has subfolder contents that differ from those seen in single-instance databases. Within the Instance folder, the instance database subfolders are split into two parts:
All of the database-specific functionality appears directly under the Instance subfolder for the cluster database. The available database-specific functionality enables you to view, create, and modify resource consumer groups.
All instance-specific functionality appears beneath the individual instance icons within the Cluster Database Instances subfolder. The instance-specific functionality includes:
You can view instance states, view and edit initialization parameters, toggle the archive mode on and off, and view performance statistics of active resource plans. You can also view or modify the current undo tablespace assigned to an instance, as well as the undo tablespace retention period.
You can create, edit, and store multiple startup configurations for instances. This eliminates the need to track initsid.ora parameter files.
You can list the status of connected users, view the latest SQL for sessions, and terminate sessions.
You can view details for currently held User type and System type locks.
You can define and modify the resource plans for the cluster database and also activate a specific resource plan for an individual instance.
You can schedule the activation of a resource plan.
The contents of a typical database folder are shown in Figure 5-1.
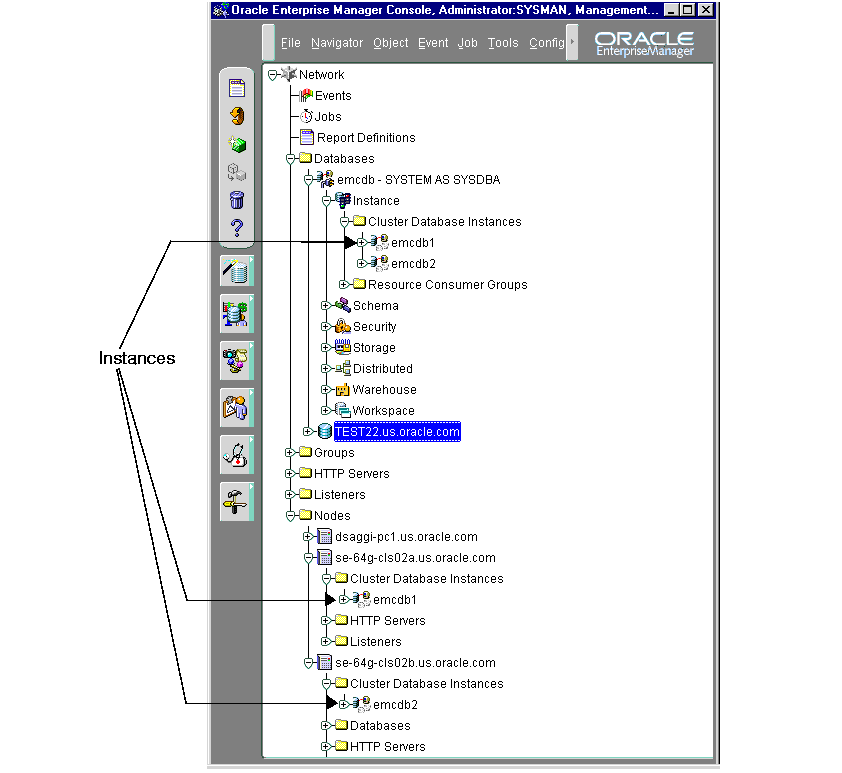
You can expand the Cluster Database Instances folder to display the instances belonging to each discovered database or node, as shown in Figure 5-2.
|
Note: The instances have the same right-mouse menu as the right-mouse menu used in single-instance databases. |
Right-clicking on a cluster database displays the specialized cluster database right-mouse menu. The right-mouse menu contains entries for the functions listed in Table 5-1. All other menus are identical to those appearing in the single-instance version of Oracle Enterprise Manager. When selected, you will see dialogs that differ from single-instance databases.
Table 5-1 Right-Mouse Menu Functions for Real Application Clusters| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
Startup |
See Also: "Starting a Cluster Database" |
|
Shutdown |
See Also: "Shutting Down a Cluster Database" |
|
Results |
|
|
View Edit Details |
Enables inspection of the state of the cluster database, including which instances are active. See Also: "Viewing Cluster Database Status" |
|
Related Tools |
Contains access to other tools which have been enabled for a cluster database. |
The Console enables you to start an entire cluster database or selected instances within a cluster database. To start a cluster database or its instances:
A menu appears with options for the database.
The Cluster Database Startup dialog box appears.
The Select Instances to Start dialog box appears.
The Cluster Database Startup Results dialog box displays the progress of the startup operation, as described in "Viewing the Cluster Database Operation Results". If the instances were started successfully, the Cluster Database Started message box appears with a successful message. Click OK in the Cluster Database Started message to acknowledge the message, then click Close in the Cluster Database Startup Results.
If the startup fails, the Cluster Database Started message box appears with a failure message. Click View Details to see more information in the Cluster Database Startup Results dialog box about the failure, then click Close.
The Console enables you to shut down an entire cluster database or selected instances within a cluster database. Once all instances are shut down, the database is also considered shut down.
|
Note: A cluster database can occasionally be completely down, however, some of its services, such as the database listener, might remain running. |
To shut down a cluster database or its instances:
A menu appears with options for the database.
The Cluster Database Shutdown dialog box appears.
To shut down only selected instances, follow these additional steps:
The Select Instances to Stop dialog box appears.
The Cluster Database Shutdown Progress dialog box displays the progress of the shutdown operation.
If the instances were shut down successfully, the Cluster Database Stopped message box appears with a successful message. Click OK in the Cluster Database Stopped message to acknowledge the message, then click Close in the Cluster Database Shutdown Results window.
If the shutdown fails, the Cluster Database Stopped message box appears with a failure message. Click View Details to see information in the Cluster Database Shutdown Progress dialog box about the shutdown failure, then click Close.
The Cluster Database Startup/Shutdown Results dialog displays information about the progress of the instance startup or shutdown operation you selected: The operation results are presented in two views:
The Cluster Database Startup/Shutdown Results dialog box automatically displays during a startup or shutdown operation. You can also initiate it with the following steps:
A menu appears with options for the database.
While a startup or shutdown operation is running against a cluster, the Status Details tab appears and is updated dynamically as the operation progresses.
A successful startup operation for a two-node cluster looks like the following in the Status Details tab, as shown in Figure 5-3.
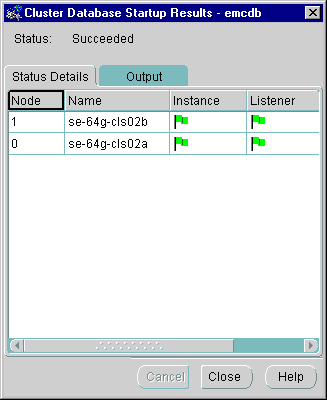
Text description of the illustration startdet.gif
A successful shutdown operation for a two-node cluster looks like the Status Details tab shown in Figure 5-4.
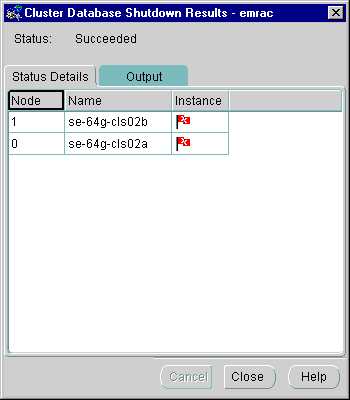
Text description of the illustration sucshuts.gif
Table 5-5 shows the possible states in which each component might appear.
Table 5-4 Possible Component StatesThe Output tab displays the commands executed by the node and any associated error messages in textual format.
A successful shutdown looks like the following in the Output tab as shown in Figure 5-5.
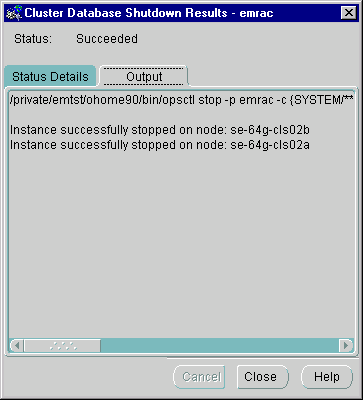
Text description of the illustration succout.gif
Oracle Enterprise Manager displays a Results tab that is similar to the Shutdown tab in Figure 5-5.
The Edit Cluster Database dialog box displays status information about the database, such as instances available in the cluster and the status of cluster components.
|
Note: Because this dialog box requires a connection to a database, this dialog box will not appear if the cluster database is down. |
To view status information about a database:
A menu appears with options for the database.
The Edit Cluster Database dialog box appears.
The operation results are presented in two views:
The General tab displays information about the currently running instances by querying the V$ACTIVE_INSTANCES table as shown in Figure 5-6. Oracle Enterprise Manager makes a connection to the cluster database. Therefore, this tab will not appear if the database is down.
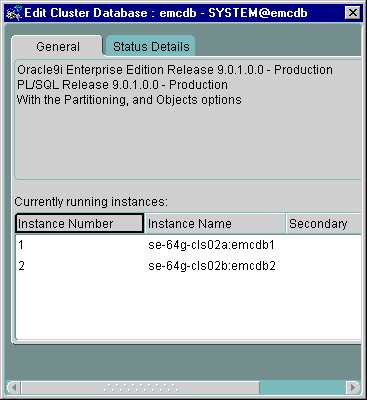
Text description of the illustration viewegen.gif
Table 5-5 describes the Fields in Output Tab Form.
Table 5-5 Fields in Output Tab Form| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Instance Number |
Identifies the instance number |
|
Instance Name |
The name specified for the instance and the node it is running on. This name has the following format: node:instance_name. |
|
Secondary |
A checkmark appears if the node is an secondary instance in a primary/secondary instance configuration |
The Status Details Tab displays an overall view of the state of the cluster and related components as shown in Figure 5-7. This tab displays the status of the various components, such as listeners and instances, for all nodes on which you have configured the cluster database.
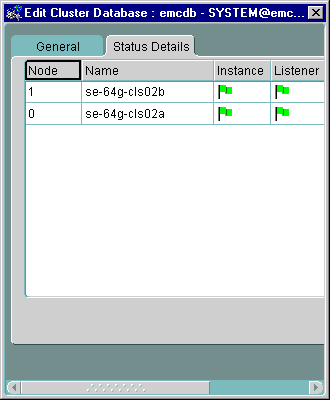
Text description of the illustration viewstat.gif
Table 5-4 shows the possible states in which each component might appear.
The job scheduling system provides a highly reliable and flexible mechanism for you to schedule and automate repetitive jobs on both the cluster database and instances.
The Console contains a full-featured scheduling mechanism that enables you to develop a customized schedule. This provides you with actual "lights out" management capability so that you can focus on other tasks.
You can create a job with a cluster database or instance as the target. To create a new job, follow these steps:
From the Create Job property sheet, you can specify the details of a new job. The Create Job property sheet contains the tabs listed in Table 5-6.
Table 5-6 Tabs Contained in the Create Job Property SheetThe following tabs contain options specific to cluster databases:
| See Also:
Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide for general job scheduling information |
As shown in Figure 5-8, from the General tab you can specify:
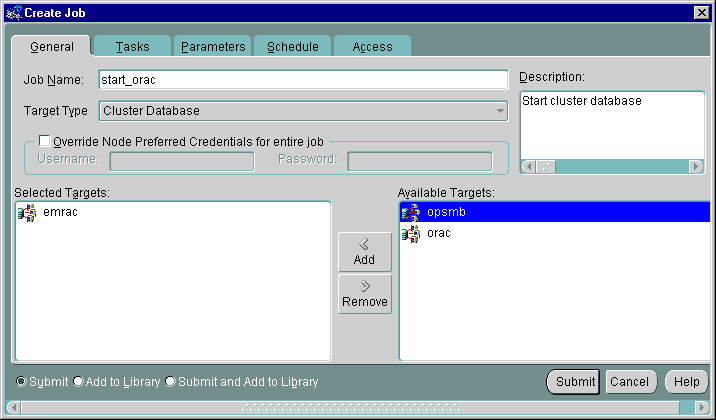
Text description of the illustration creatgen.gif
The General Tab contains the options in Table 5-7.
Table 5-7 General Tab OptionsFrom the Tasks tab, choose the task(s) for the job to perform. The list of tasks that appears is different depending on whether you select a cluster database or cluster database instance as your Target Type from the General tab. Move the tasks between the Available Tasks and Job Tasks lists with the Add and Remove buttons.
If your Target Type is a Cluster Database, then you can select from these tasks that are specific to cluster databases:
| See Also:
Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide for a description of these tasks and the parameters to set |
From the Parameters tab, you can specify parameter settings for the job tasks you selected on the Tasks tab. The parameters that display vary according to the job task. Parameters specific to cluster database startup and shutdown tasks are described in the next subsection.
| See Also:
Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide for a description of parameters to set for instance tasks |
When you select the Startup Cluster Database task on the Tasks tab, the following display appears Figure 5-9.
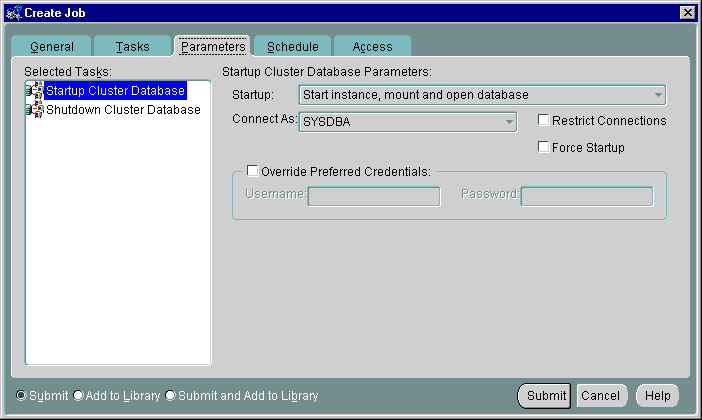
Text description of the illustration job-star.gif
The Parameters tab for Startup contains the options listed in Table 5-8.
Table 5-8 Parameters Tab for Startup| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
|
Startup |
Select the startup modes for the job from the drop-down list box. |
|
Connect As |
Only Normal is allowed for Oracle7. For Oracle8i and subsequent releases, SYSOPER and SYSDBA roles allow you the maximum database administration privileges. You require SYSDBA or SYSOPER privileges to run job tasks such as shutdown or startup on the database. See Also: Oracle9i Database Administrator's Guide for more information about SYSOPER and SYSDBA roles If you attempt to connect as SYSDBA and do not have SYSDBA privileges, an error message states that an invalid user name or password was entered. |
|
Override Preferred Credentials |
You can use the preferred credentials that have been set up for the database, or you can enter another database user name and password. |
When you select Shutdown Cluster Database on the Tasks tab, the display in Figure 5-10 appears.
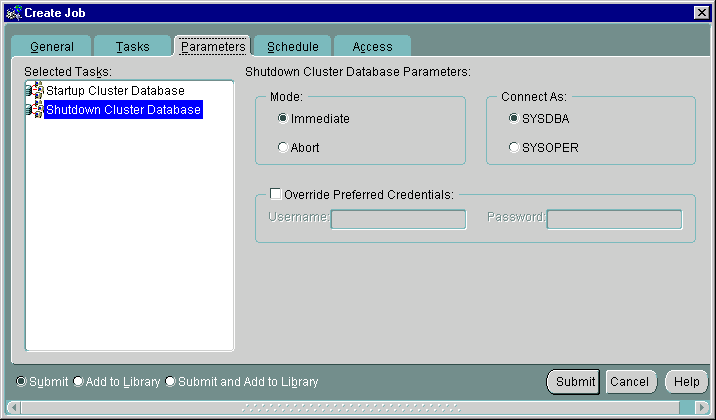
Text description of the illustration shutpara.gif
Complete the parameter entries on the tab and click Submit to run the cluster database shutdown task. The Parameters tab for Shutdown contains the options listed in Table 5-9.
Table 5-9 Parameters Tab for ShutdownOracle Enterprise Manager includes an Event Management feature that enables you to monitor tests on cluster database instances. You can run all tests available for single-instance databases on cluster database instances. In addition to these standard event tests, specialized event tests are available only for cluster database instances. These tests include global cache converts, consistent read requests, and so on. The Intelligent Agents running on the cluster nodes gather the data for the event tests and detect the occurrence of specific event conditions.
To access the Event Management feature, from the Event menu, select Create Event and the Create Event window opens. On the Create Event window you can select targets, set parameters, and set notification preferences, using the following sub-pages:
Figure 5-11 shows the selection list of event tests that are specific to cluster databases.
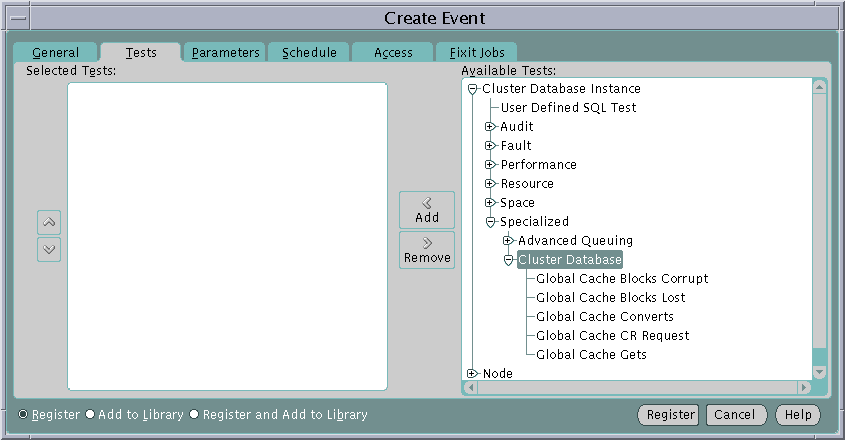
|
 Copyright © 1998, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|